This is an automatically translated article.
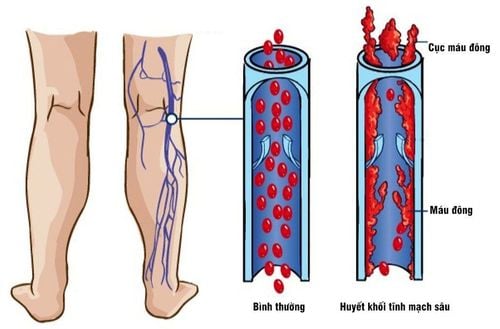
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Cao Thanh Tam - Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities is a condition in which a blood clot forms inside a vein. This phenomenon impedes blood flow to the heart, causing complete or partial blockage of blood flow in the venous lumen leading to serious consequences.
1. Pathological causes
There are many causes leading to deep vein thrombosis in the lower extremities. There are 3 main causes, which are: circulatory stagnation, increased blood coagulation and venous endothelium damage. Any cause that leads to the above 3 factors can cause deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities.2. Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis of lower extremities
Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities is based on the clinical symptoms of the patient. The doctor will exploit the predisposing risk factor. Then evaluate the clinical risk of deep vein thrombosis in the lower extremities to select the appropriate testing methods and diagnosis:Patients with low probability of disease: test D - dimer . Patients with moderate or high clinical probability: intravenous Doppler ultrasound is indicated. Some clinical symptoms of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities:
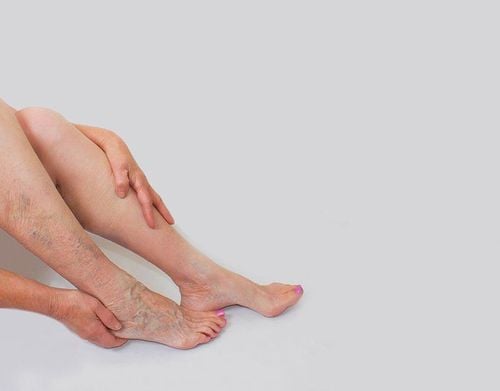
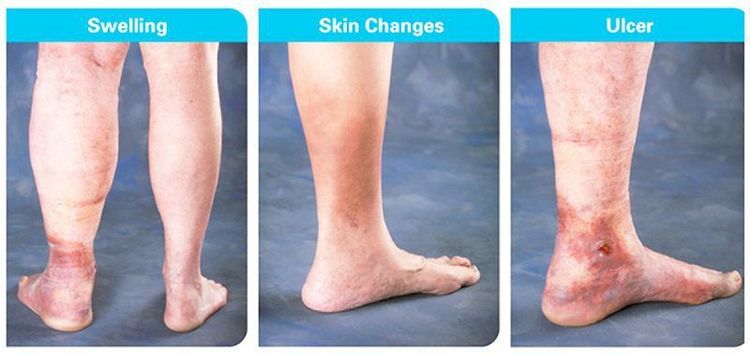
Skin of the legs is hot, there is pain when touching or when flexing the instep of the foot to the lower leg; Erythema; Increased tone; Superficial varicose veins; Increase the circumference of calves, thighs; Ankle edema. Differential diagnosis Need to differentiate leg edema in posterior deep vein thrombosis from leg edema in other conditions such as: heart failure, lymphedema, renal edema (bilateral leg edema), popliteal cyst rupture or hematoma in the muscle. In doubtful cases, the doctor will conduct Doppler ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the cause The cause may be congenital hypercoagulability; or acquired hypercoagulability due to coagulopathy. The tests to be done are as shown in the following table:
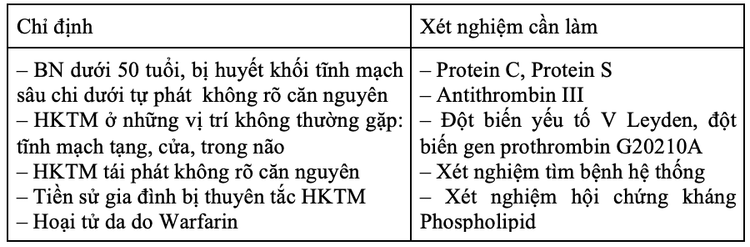
Cancer pathology: Cancer is a risk factor, especially in patients with thromboembolism and the elderly. Depending on clinical symptoms such as weight loss, lymphadenopathy, hemoptysis, bloody stools, hematuria... the doctor will assign appropriate diagnostic tests: Routine subclinical exploration: X - Cardiopulmonary, abdominal ultrasound, appendages, vaginal smear, urinalysis, liver and kidney function, blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate... Expanded paraclinical exploration: Computed tomography chest, abdomen, gastroscopy, colonoscopy, cancer marker testing (cancer markers are not indicated for the purpose of cancer screening). Depending on the stage of the disease, doctors will have different methods and treatment times.
3. Methods of treatment of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities
Some non-specific measuresPatients are encouraged to mobilize early from the first day after being wrapped in elastic bandages, medical pressure socks. The patient's foot is slightly elevated. Bandage the patient's feet with an elastic band Anticoagulant
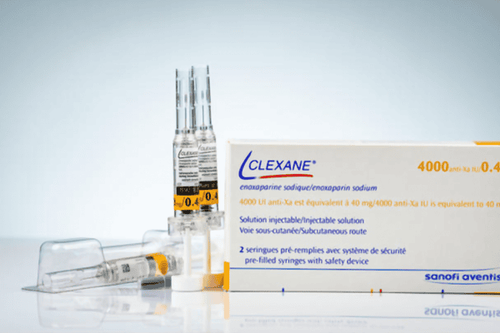
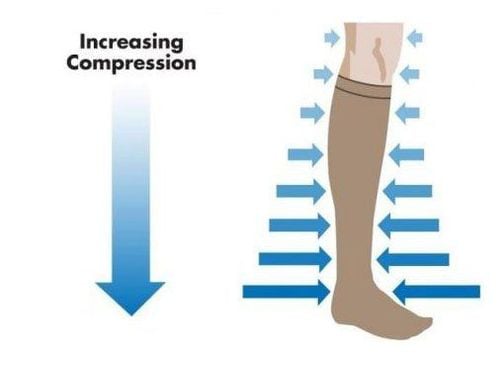
Heparin unfractionated: Infuse an electric syringe at a dose of 50 units/kg (intravenously) then maintain 500 units/kg/day. Follow up Howell time 2-3 times more than control is okay. Low molecular weight heparin: the advantage is that the drug has high safety, good absorption and stability. Usage and dosage: Injected under the skin of the abdomen 70-100UI/Kg/12h, Monitoring: Platelets, it is necessary to adjust the dose in patients with renal failure. In people with glomerular filtration rate <70ml/min, obesity and people >80 years old, anti-Xa should be measured 3 hours after the first injection to prevent bleeding. If the glomerular filtration rate is < 30 ml/min, low molecular weight heparin is contraindicated. Vitamin K antagonists: Start on day one to minimize the length of time you take Heparin. Test INR after 48 hours, then repeat until an INR of 2 to 3 is achieved. Extend treatment with this drug for 3 months, sometimes longer in case of chronic thrombophlebitis; Sometimes lifelong treatment is required if there is a blood clotting abnormality. Patients are explained, educated on how to use, how to monitor when using this drug, and distribute anticoagulant monitoring books to patients. Bandages or compression stockings will be of great help in treatment. Helps to quickly relieve symptoms, reduce the risk of post-thrombotic disease. You can use elastic bandages or pressure socks of degree 2-3. You should wear compression stockings or an elastic band for the first few days. Then need to wear socks during the day may not wear pressure socks at night.
No more benefit than conventional treatment. Can be applied to the case of blue vein thrombosis. Thrombectomy surgery:
May be indicated when thrombosis proximal, spreading with blood clot. The patient was admitted to the hospital in the first hour. Thrombophlebectomy: Very rarely used.
Prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities To prevent deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, there are a few things to keep in mind:
Do not get up early after surgery or after giving birth. Bedridden with the elderly and people with heart failure should be avoided. Prophylactic anticoagulation should be used in high-risk subjects: + High-risk surgery: Lovenox 4000 units/day.
+ Low-risk surgery: Lovenox 2000 units/day
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: vnha.org.vn, msdmanuals.com