This is an automatically translated article.
Because the clinical symptoms of C1 C2 cervical spine injury are very poor, the doctor will ask the patient to perform diagnostic imaging methods such as: X-ray of the spine, tomography, tomography. Magnetic Resonance.
1. Classification of injuries of cervical spine injury C1 C2
Injuries to the cervical spine C1 C2 are classified based on the location of the injury. Specifically as follows:
Dislocation of the neck - occipital: This is a rare injury and has a high mortality rate; Team burn (C1): The main cause of this injury is a traffic accident. Most cases of C1 rupture alone, some combined with C2 cervical spine rupture; Dislocation C1 - C2: The main cause of injury is usually the force of bending - rotation. Can be dislocated on one side or sometimes bilaterally, more seriously, fracture of the combined apex; Cross-waist C2: This is the most common injury in cervical spine trauma. It is usually caused by excessive stretching and flexing forces.
2. Symptoms of cervical spine injury C1 C2
The clinical symptoms of spinal cord injury C1 C2 are usually very few. Therefore, besides the mandatory information for the patient, learning about the mechanism of injury is important in the diagnosis of cervical spine injury. Some common symptoms of cervical spine injury C1 C2 include:
The patient has neck pain, pain spreading to the occipital due to damage to the C1, C2 nerve roots; Stiff neck as well as limited range of motion; Some patients have a feeling of swallowing difficulty if they dislocate much or experience numbness and paresthesia in one or two upper extremities.
3. Diagnosis of cervical spine injury C1 C2 need to do any medical techniques?
Because the clinical symptoms of C1 C2 cervical spine injury are very poor, when in doubt, the doctor will ask the patient to perform the following diagnostic methods:
X-ray: This is a diagnostic method. Imaging is mandatory for the patient when the doctor suspects a cervical spine injury. This method captures upright, leaning, and open-mouthed poses. The purpose of X-ray of the cervical spine is to selectively reveal the entire cervical vertebrae of C1 C2, while erasing the mandibular and maxillary arches. Computed tomography: This diagnostic technique will allow accurate identification of suspected lesions on X-ray films of the cervical spine, bone lesions not visible on imaging as well as bone fragments in the canal. In particular, the tomography technique will allow to see the apical lesions clearly and detect the associated lesions. Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine: This is an imaging technique that helps detect spinal cord injuries. Therefore, it is only applicable in cases of spinal cord injury, in very severe prognosis patients, or used to detect nerve damage secondary to high cervical vertebrae injury.
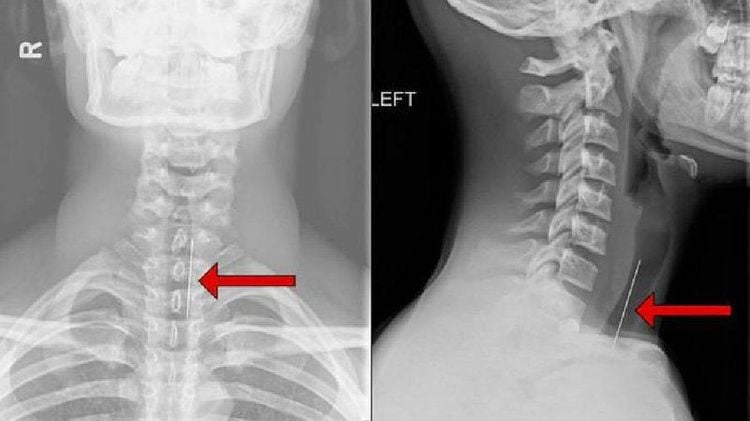
Mục đích của chụp X quang cột sống cổ là nhằm bộc lộ toàn bộ chọn lọc các đốt sống cổ của C1 C2
4. Treatment of cervical spine injury C1 C2
4.1 Initial management after trauma The initial management of cervical spine injuries is important to minimize the consequences of primary and secondary spinal cord injuries. Initial treatment measures include:
Immobilize the patient's cervical spine when a cervical spine injury is suspected, especially for patients who are comatose due to traumatic brain injury. Once the lesion has been ruled out by X-ray of the cervical spine, it is removed. It is best to be immobilized with a neck brace with the neck supine, slightly arched. In the absence of a brace, the neck can be immobilized with two sandbags on either side of the neck to prevent rotation while moving the patient. Next, if there are signs of nerve damage such as paralysis or respiratory and hemodynamic disorders, it is necessary to resuscitate the patient. Give fluids and maintain blood pressure of 110-140mmHg, give the patient oxygen, need to provide respiratory support and put a nasogastric tube to avoid reflux. In the first 8 hours, a high dose of Methylprednisolone can be given intravenously, repeated after 45 minutes and a maintenance dose of 5mmg/kg/hour to limit edema. However, in the case of spinal cord injury or trauma to the ponytail, stomach bleeding, high blood sugar, etc., this drug should not be used in patients. 4.2 Treatment There are many different treatment methods for C1 C2 cervical spine injuries, the treatment method will depend on the injury and different schools. Conservative treatment method:
Neck brace: This conservative treatment method will usually be applied to stable or unstable injuries while waiting for surgery or after surgery such as: Grade 1 and 3 fractures; C2 waist rupture degree 1. Continuous traction: This method is often applied to pre-operative traction for old lesions, difficult to straighten during surgery or inoperable lesions. However, this method makes the patient lie motionless for a long time, which can easily cause complications. Treatment by surgical method:
Tie the arc after C1 and C2: This method will be applied in case of fracture of the apex, dislocation of C1, C2. However, this surgical method has poor stabilization ability and high rate of prosthetic joints. Screw through the joint C1-C2 through the posterior neck line: The doctor will appoint the patient to apply this method in case of fracture of the apex and dislocation of C1-C2. The technique is simple and safe, the stability is high. Direct screw method through the apex according to the anterior cervical line: This surgical method is usually indicated for people with fractures of the apex without a combined C1-C2 dislocation. Direct screw through the apex along the anterior cervical line can stabilize well while still ensuring the function of joint C1-C2, provided that C1-C2 is not dislocated. Screw splint through C1 joint block and C2 pedicle along the following neck line: This method is indicated for patients with C1-C2 dislocation with spinal cord compression, requiring resection of the C1 joint posterior arc, or those with a lot of displacement. C1-C2 transarticular screw surgery is not possible. C2-C3 screw splint through the anterior neck line: This technique is applied in case of C2 waist rupture of 2nd degree and 3rd degree. In short, the patient needs to go to the hospital to conduct examination and treatment as soon as there are signs of stroke. cervical spine injury. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment: 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 light machine, 1 general machine and 1 mammography machine) , 2 DR portable X-ray machines, 2 multi-row CT scanner rooms (1 128 rows and 1 16 arrays), 2 Magnetic resonance imaging rooms (1 3 Tesla and 1 1.5 Tesla), 1 room for 2 levels of interventional angiography and 1 room to measure bone mineral density.... Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of experienced doctors and nurses who will greatly assist in diagnosis and detection. early signs of abnormality in the patient's body. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.