This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Anh Viet - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. The doctor has 07 years of experience working in the field of diagnostic imaging.Meningeal hernia is a protrusion of the meninges without accompanying spinal cord or nerve tissue. The location of the lesion usually occurs along the spine and can vary in size. This is a type of spinal structural disorder caused by neural tube defects and meningeal hernia can be diagnosed by conventional imaging means such as spine X-ray for early surgical intervention for children.
1. What is meningeal hernia?
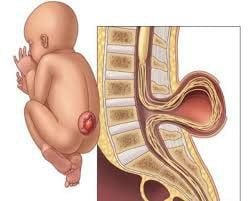
Meningeal herniation can be considered a simple meningioma, consisting of meninges and cerebrospinal fluid protruding subcutaneous tissue due to spinal defects. The cortex covering the meninges is usually intact. Complicated meningeal hernias have been associated with other spinal malformations. However, a common meningeal herniation is a spinal anomaly that is often asymptomatic and unrelated to acute neurological conditions, which belongs to the group of neural tube defects, which is the second most common type of congenital malformation. two after congenital heart defects in infants.
Meningeal hernia has 2 types, divided based on hernia sac open or closed. The meningeal hernia sac structure originates from a defective nerve arc, from which the meninges or its internal components, the medulla and cerebrospinal fluid, herniate out, leading to different clinical manifestations. .
The definite etiology of meningeal herniation is still not well understood. Most cases of neural tube defects are attributed to folate deficiency, likely in combination with genetic and environmental risk factors. Folate deficiency may be related to inadequate intake during pregnancy or the use of folate antagonists, or to genetic predisposition to abnormal folate metabolism. They may also be associated with chromosomal anomalies or single-gene disorders.
Hereditary syndromes associated with meningeal hernias include hydrocephalus, retinal dysplasia, Meckel-Gruber syndrome, trisomy 13 or 18. Maternal factors associated with risk High prevalence of neural tube defects including advanced maternal age, low socioeconomic status, maternal alcohol use during pregnancy, smoking, caffeine use, obesity, high glycemic index or gestational diabetes . Maternal use of anticonvulsants such as valproic acid and carbamazepine can also cause neural tube defects in the fetus. In addition, factors that increase maternal body temperature during the first trimester, such as fever, may be associated with meningeal hernias. Finally, environmental factors such as exposure to agrochemicals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons can also cause neural tube defects in general.
2. Manifestations of meningeal hernia like?
Meningeal hernias can be detected early through prenatal screening for neurological abnormalities, including measurement of maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein and third-trimester ultrasound. Meningeal hernia sac presents as a bump on the back covered with skin, present at birth. The location of the defect can appear in the spine in the lumbar, abdominal and thoracic regions or even in the sacrum, coccyx. On clinical examination, the meningeal hernia is a sac in the midline of the back that is relatively oscillating and penetrating.
At this point, an initial assessment of the infant is essential at birth. A detailed examination of the head and neck, including head circumference, skull bones, and the size and shape of the anterior fontanel should be performed. Next, the child will have a complete neurological exam to rule out any abnormalities in neurological function. The clinical presentation of meningeal hernia is approximately related to the size and proximity of the hernia sac to surrounding structures. Specifically, the child may present with back pain, dyspnea, cough, and palpitations if the herniated mass compresses the pulmonary and mediastinal structures.
3. Meningeal hernia is diagnosed by what medical technique?
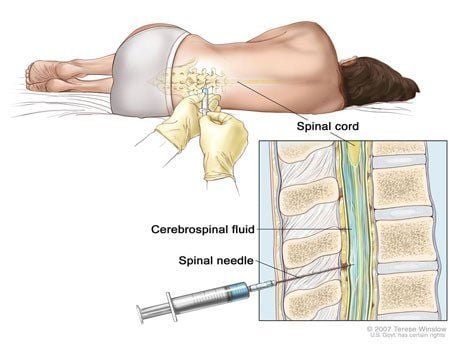
All patients with meningeal hernia should be evaluated with at least one radiograph of the spine after birth, depending on the clinical situation. X-rays alone show any associated spinal and skull defects, skeletal abnormalities, and spinal deformities.
Simultaneously, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine will be the next step to investigate the nature of meningeal hernia. It is the best diagnostic test to study abnormalities of nerve tissue and to evaluate for any other associated malformations such as hydrocephalus.
In addition, ultrasonography to rapidly assess the nature or status of meningeal hernia and hydrocephalus may also be helpful. From there, the results of these imaging tools can decide the indications for surgical intervention that should be performed, especially when it is necessary to evaluate the urgent need to repair neural structures, to avoid dangerous complications.
4. Treatment methods for meningeal hernia
Management of children with meningeal hernia is primarily a multidisciplinary approach. It is important to counsel the family about the immediate and long-term effects of treatment.
In which, surgical intervention is preferred as soon as possible on large meningeal hernia sacs. However, in cases of suspected CNS infection or meningitis, treatment will be initiated with prophylactic antibiotics and anticonvulsants immediately. During this time, the patient should be monitored in the neonatal intensive care unit with regular electrolyte and blood count assessment.
The relationship of meningeal hernia with ligament syndrome is relatively close. In these cases, an MRI of the spine is essential to accurately diagnose the nature of the meningioma.
In general, regardless of the specific structure of the meningeal hernia sac, aggressive surgical treatment will be recommended as soon as a definitive diagnosis is established. During surgery for meningeal herniation, the surgeon will probe the spinal canal and release the hernia sac neck, repair the protruding meninges, and reconstruct the spinal canal.
5. Differential diagnosis of meningeal hernia
Meningeal herniation belongs to the group of spinal structural abnormalities, described by herniation of nerve tissue through a defect in the spinal canal - skull.
If the hernia is in the nasal cavity, the child has difficulty breathing, headache, then initially suspect the possibility of encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Clinicians usually diagnose polyps or brain tumors. However, inappropriate treatment of an undiagnosed hernia can lead to secondary meningitis or CSF leakage from the incision or perforation of the meningeal hernia.
Therefore, MRI is a safe, non-invasive and always-on imaging method of diagnosing meningeal herniation to allow definitive diagnosis in brain tumors and meningiomas; so that the correct intervention can be made.
In summary, the diagnosis of meningeal hernia has generally become relatively favorable with the role of spine radiographs and spinal MRI. These imaging tools help to accurately assess the structure of the meningeal hernia sac, allowing for accurate interventional planning as well as post-operative follow-up. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment: 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 light machine, 1 general machine and 1 mammography machine) , 2 mobile DR X-ray machines, 2 multi-row CT scanner rooms (1 256 series and 1 512 series), 2 Magnetic resonance imaging rooms (2 3 Tesla machines), 1 angiography room 2-level intervention and 1 room to measure bone mineral density.... Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of experienced doctors and doctors who will greatly assist in the diagnosis and early detection of abnormal signs. usually in the patient's body. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.