This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Gastritis is a term used to describe a group of problems with one thing in common: inflammation of the stomach lining. The inflammation of gastritis is usually the result of an infection with the same bacteria that cause stomach ulcers. However, other factors such as trauma, frequent use of certain pain relievers or drinking too much alcohol can also contribute to gastritis.
Gastritis can happen suddenly (acute gastritis) or it can happen slowly over time (chronic gastritis). In some cases, gastritis can lead to ulcers and an increased risk of stomach cancer.
However, for most people, gastritis is not serious and improves quickly with treatment. Among the forms of gastritis, there is one form of gastritis that has received little attention, which is autoimmune gastritis (VDD).
I. Outline of Autoimmune Gastritis
Autoimmune gastritis (VDDTM) is an atrophic gastritis of the gastric mucosa, concentrated mainly in the body and gastric aneurysm, due to the appearance of antibodies against the parietal cells of the stomach and intrinsic factors, which can lead to destroys the stomach lining, resulting in anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency, even leading to stomach cancer.
In 1849, Thomas Addison was the first author to describe megaloblastic anemia (Addison's anemia) then gradually appeared studies that recognized the association between atrophic gastritis of the stomach lining with anemia. this blood.
By 1921, the authors Samuel and William reported in a case series of 107 cases of megaloblastic anemia, 104 patients with no detectable hydrochloric acid in gastric juice. This can be considered as one of the first descriptions of autoimmune gastritis. Up to now, autoimmune gastritis (VDDTM) is defined as atrophic inflammation of the gastric mucosa concentrated mainly in the body and gastric bulge due to the presence of antibodies against the parietal cells of the stomach. . Regarding clinical symptoms, patients often come to the doctor because of abnormalities related to the hematological system or due to vitamin B12 deficiency, chronic iron deficiency. The prevalence of VTE with symptoms of megaloblastic anemia accounts for about 0.1% of the population but increases to approximately 2% in people over 60 years of age. Some studies have shown that being female may be a risk factor, while ethnicity does not appear to be much different, although early reports of the disease noted that it is more common in the region. Northern Europe.
The second limitation is that there is no consensus on histopathological diagnostic criteria, often the results returned in many cases are only chronic gastritis, so it can be missed.
II. Clinical symptoms
Symptoms related to chronic atrophic gastritis progress slowly over a long time, so the diagnosis is often late and difficult. Patients with clinical symptoms are often symptomatic of megaloblastic anemia or neurologic symptoms of varying degrees due to chronic vitamin B12 deficiency.
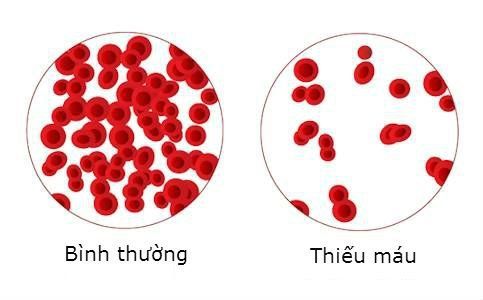
Symptoms of anemia: the early stage of autoimmune gastritis is iron-deficiency anemia due to a decrease in Hcl acid in the stomach, the later stage of the disease shows megaloblastic anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency.
1. Symptoms related to the hematologic system
In the early stages of VTE, patients may have iron deficiency anemia due to a decrease in hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Several studies have documented persistent iron-deficiency anemia, unresponsive to treatment, in both adult and pediatric patients with VSD.
In the later stages of the disease, anemia manifests as megaloblastic anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency leading to disturbances in DNA synthesis. Patients may have symptoms of anemia such as fatigue, headache, palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath.
Vitamin B12 deficiency also causes increased homocysteine in the blood leading to increased platelet aggregation and the risk of thrombosis. There have been a few cases of young patients with myocardial infarction and pulmonary infarction due to hyperhomocysteinemia secondary to macrocytic anemia.
2. Neurological symptoms
The neurological symptoms of chronic vitamin B12 deficiency are caused by a long period of demyelination resulting in axonal damage. The patient's initial symptoms are usually sensory disturbances including loss of sensation to vibration and posture. In the late stage, the patient may have Lichtheim disease - Degenerative syndrome of the posterior and lateral spinal columns. In many cases, these nerve damage is irreversible, but vitamin B12 treatment will help prevent progression of symptoms. Some patients have peripheral neurologic disturbances including paresthesias and numbness mainly in the legs. It is sometimes difficult to distinguish clinically whether a patient's symptoms are due to peripheral neuropathy or Lichtheim's disease.
3. Symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract

VDD rarely causes serious gastrointestinal symptoms. The decrease in gastric acid secretion can lead to uncomfortable symptoms such as bloating, rapid satiety, epigastric tenderness, or increase the risk of gastrointestinal infections such as bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine, inflammation. Colitis caused by Clostridium difficile , glossitis. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause a burning sensation in the tongue.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
ReferencesDao Viet Hang - Dao Van Long (2018), “Autoimmune gastritis”, Autoimmune diseases – gastrointestinal allergies, Medical Publishing House. Carmel R (2996) Prevalence of undiagnosed pernicious anemia in the elderty Arch InternMed,156, 1097-200. Kulnigg-Dabsch S.(2016), “Autoimmune gastritis”, Wien Med Wochenschr 166(13-14):424-430