This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Resident Doctor Trinh Ngoc Anh - Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International HospitalWhen toxic multinodular goiter is suspected, doctors will order tests and imaging to confirm the disease. After the results are available, a specific treatment regimen will be developed on a case-by-case basis.
1. What is toxic multinodular goiter?
Toxic multinodular goiter is a condition in which the thyroid gland has many self-functioning nodules in addition to healthy thyroid tissue, leading to an increased secretion of thyroid hormone.Hyperthyroidism in toxic multinodular goiter usually begins after iodine administration (also called Basedowization or iodine-induced hyperthyroidism). Some thyroid nodules are not subject to the Wolff Chaikoff effect (a decrease in thyroid hormone levels thought to be caused by consuming large amounts of iodine) and cannot accept iodine, thus increasing thyroid hormone synthesis even in the presence of high iodine concentrations. . This mechanism explains why people are more susceptible to hyperthyroidism after taking drugs or foods high in iodine (cordarone, intravenous contrast agents, eating a lot of seafood).
2. How is toxic multinodular goiter diagnosed?
When toxic multinodular goiter is suspected, doctors will order tests and imaging to confirm the disease. The techniques used include:Quantification of thyroid hormone: The results show that the free or total T3 and T4 in the blood are increased, sometimes the T3 is mainly elevated; Blood TSH decreased. Immunological investigations: Anti-TSH receptor antibodies and thyroid autoantibodies are mostly negative. Diagnostic imaging: The scintigraphy with Tc 99m or 131I and 123I shows radioactive substances that are not homogenously concentrated in many areas with unequal sizes, alternating areas of increased acquisition with areas of decreased radiation, there may be areas of radioactivity. isoradiance. Thyroid ultrasound: Thyroid gland is often enlarged, can sink into the thorax, parenchyma is heterogeneous, there are many nuclei, these nuclei can increase angiogenesis, calcification in the organization. X-ray, CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): The neck or chest area shows a sunken thyroid, tracheal compression, and calcification.
3. How is toxic multinodular goiter treated?
The process of monitoring toxic multinodular goiter in patients is often difficult. Doctors can control thyrotoxicosis with antithyroid drugs and then subtotal thyroidectomy.In fact, most patients with toxic multinodular goiter are older and have some other medical conditions, so surgery may be difficult. In this case, toxic multinodular goiter can be treated with radioactive iodine with 1 or more courses.
Mild cases of thyrotoxicosis can be controlled with antithyroid drugs. However, this is only a solution to treat the symptoms of toxic multinodular goiter, but cannot cure it completely. To get effective treatment and cure the disease, it is necessary to choose surgery or use radioactive iodine.
3.1. Surgery Surgery is the basic treatment measure, both to cure toxic multinodular goiter and at the same time to remove the cold nodules that have not ruled out cancer. After preparing well with antithyroid drugs, the surgeons will take a fairly large tissue to avoid recurrence, from removing the nucleus to removing the entire thyroid gland. After surgery, some complications may occur such as: hypothyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, recurrent nerve palsy...and need long-term treatment.
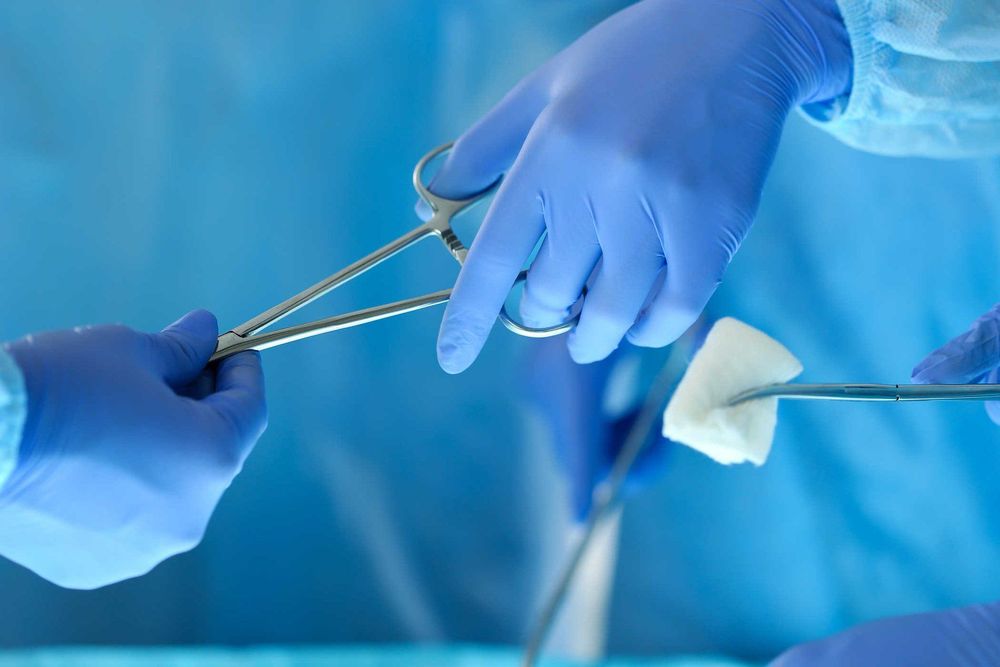
Có thể điều trị bướu giáp đa nhân bằng phương pháp phẫu thuật
Most patients with toxic multinodular goiter should be treated with antithyroid drugs before to avoid complications during radiation therapy (acute hyperthyroidism).
Compared with surgery, the treatment of toxic multinodular goiter with radioactive iodine will often have slow results, return to normal after 4-6 months, sometimes requiring additional treatment with multiple courses. In addition, the risk of cancer and hypothyroidism can still occur, so regular monitoring is required.
To ensure safety and improve treatment efficiency, patients need to go to a reputable hospital to conduct examination and treatment as soon as there are signs of toxic multinodular goiter. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the top quality hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment: 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 light machine, 1 general machine and 1 mammography machine) , 2 DR mobile X-ray machines, 2 multi-row computer tomography rooms with receivers (1 128 series and 1 16 series), 2 Magnetic Resonance imaging rooms (1 3 Tesla machine and 1 1.5 Tesla machine). ... Vinmec is also a place to gather a team of experienced doctors and doctors who will greatly assist in the diagnosis and early detection of abnormal signs of the patient's body. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.