This is an automatically translated article.
Acute thyrotoxicosis occurs as a dangerous complication in patients with hyperthyroidism. Diagnosis of thyrotoxicosis is based on a number of clinical symptoms and laboratory concentrations of substances. Treatment of thyroid hormone toxicity is symptomatic treatment with drugs, treatment of the cause with drugs, radiation therapy or surgery.
1. What is acute thyroid hormone toxicity?
A thyrotoxic crisis, also known as a thyroid storm, is a decompensated state of hyperthyroidism. This is the most severe complication that occurs in hyperthyroid patients, in which Graves' patient has a high rate of thyrotoxicosis and is life-threatening.2. Diagnosis of acute thyrotoxicosis
2.1 Clinical diagnosis of acute thyrotoxicosis C; breathing rate increases from 35-50 times/minute; sweating leads to loss of water in the body; rapid weight loss from 5 to 10 kg; tachycardia > 140 beats/min, arterial hypertension; Congestive heart failure progresses rapidly, causing vascular collapse, acute pulmonary edema; fatigue, insomnia, muscle atrophy, pseudoparalysis, agitation, fatigue, motor and mental disorders; nausea or vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, gastrointestinal disturbances, jaundice. In Graves' patient, there were also signs of severe bulging eyes and enlarged thyroid gland. Acute phase: Manifestations of acute thyrotoxicosis at this stage are the patient's consciousness disturbance, convulsions, severe coma due to cerebral edema or cerebral hemorrhage.

Người bệnh có thể xuất hiện đau bụng và một số triệu khác kèm theo
2.2 Subclinical diagnosis of acute thyrotoxicosis The subclinical diagnosis of acute thyrotoxicosis is based on the following tests:
Blood tests: T3, T4, FT3 and FT4 levels increase; decreased TSH levels; cholesterol, sodium decreased; urea, calcium, and glucose increase. In case of low glucose, liver failure should be monitored, while potassium and sodium decrease as calcium increases, it is necessary to monitor for accompanying adrenal insufficiency. Impaired liver function is demonstrated by bilirubin, elevated liver enzymes and prolonged prothrombin time. A blood count test on a patient with thyrotoxicosis showed an increase in both leukocytes and erythrocytes, with a slight increase in erythrocytes. Electrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram showing T wave inversion, atrial fibrillation, Flutter fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block. Echocardiography: Shows the structure and morphology of the heart, evaluates heart function, thereby serving as a basis for appointing appropriate cardiovascular drugs. In addition, there are other tests such as: urinalysis, chest X-ray, blood culture, ... are indicated to look for favorable factors that have caused acute thyrotoxicosis.
3. Treatment of acute thyroid hormone toxicity
3.1 Symptomatic treatment of acute thyrotoxicosis The aim of treatment for thyrotoxicosis is to relieve symptoms including: fatigue, tremor, palpitations. Treat until thyrotoxicosis is under control. If it is a transient thyrotoxicosis, treatment should be symptomatic until the toxicity resolves.
Drugs to treat symptoms of thyrotoxicosis include:
β-adrenergic receptor blockers: Atenolol 25-100 mg/day, propranolol 40 mg/time, 6-8 hours/time. Calcium channel blockers: Verapamil 40 - 80 mg/time, every 8 hours. Note, the drug is only used in cases of contraindications to β-adrenergic receptor blockers. 3.2 Treatment of causes of acute thyrotoxicosis Basedow: If the cause of acute thyrotoxicosis is Graves' disease, one of the treatment methods can be applied: thionamides, iodine radiation and surgery. Surgery to remove almost the entire thyroid gland. Other causes: Depending on the cause of thyroid hormone toxicity, there will be different treatments. With postpartum thyroiditis or transient thyrotoxicosis, mainly symptomatic treatment with atenolol or propranolol is required. Indications for radiation therapy for toxicosis due to goiter or thyroid tumor. Treatment with thionamides and atenolol for iodine- or amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis.
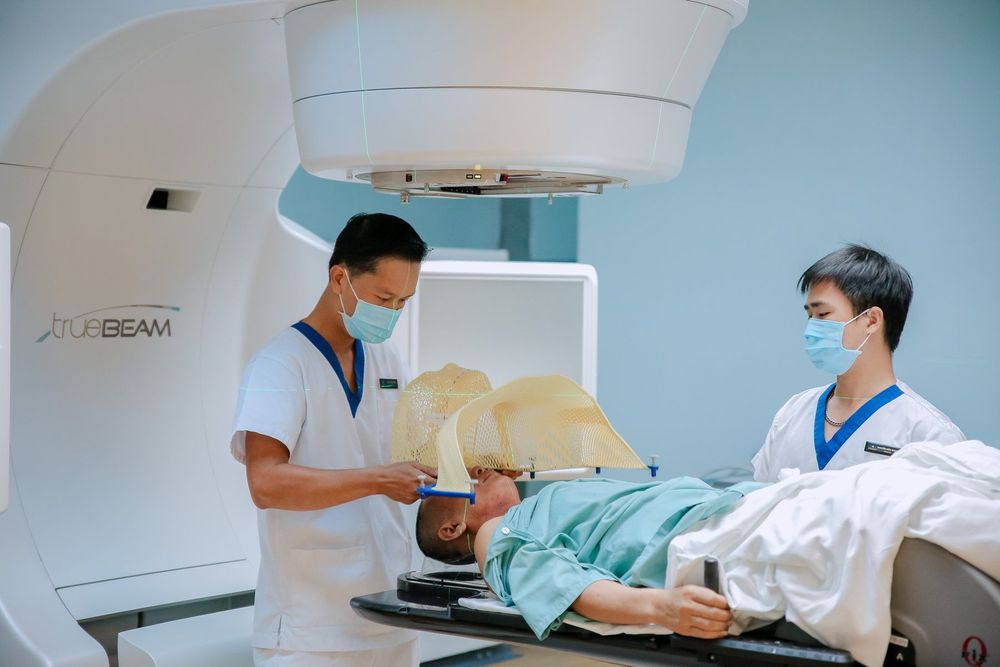
Người bệnh có thể được sử dụng phương pháp xạ trị trong điều trị Basedow
3.2.1 Treatment with Thionamides Treatment of the cause of thyrotoxicosis with Thionamides consists of 3 drugs used: carbimazole (precursor to methimazole), methimazole and PTU. In particular, carbimazole and methimazole are preferred because they help control toxicity quickly and cause less side effects on the liver. PTU is often used in pregnant women in the first 3 months of pregnancy or used to treat thyroid storm.
Effect: inhibiting enzyme peroxidase reduces the synthesis of thyroid hormone.
Dosage: Methimazole 10 - 40 mg/day, 1-2 times (or higher depending on the degree of thyroid hormone toxicity); PTU is initiated at a dose of 600mg/day/3 times. Follow-up: Thyroid status can be restored after a few months of treatment, it is necessary to check and evaluate thyroid function every 4 weeks. Based on that to adjust the dose of thionamides. Response: In mild cases of thyrotoxicosis due to Graves' disease with mild onset, small goiter, treatment with thionamides will decrease, however, may recur in about 6 months after stopping the drug. . Side effects: Some unwanted side effects may occur during treatment from mild, such as fever, rash, urticaria, joint pain, leukopenia transient to severe and can be life-threatening. such as vasculitis, hepatitis, lupus erythematosus, leukopenia. When the drug is stopped, these side effects disappear.
3.3.2. Iodine radiotherapy is contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women. Thionamides should be stopped 3-7 days before radiation therapy because they inhibit the absorption of iodine into the thyroid gland.
Therapeutic dose: Most patients with thyrotoxicosis receive radiation therapy with single dose I-131 that can control the long-term toxic attack, the next dose of radiation therapy will be indicated if the toxic attack is not controlled. Depending on the cause of toxicity, the appropriate dose of treatment will be prescribed based on the concentration of radiation. Follow-up: After a bout of acute thyrotoxicosis, the euthyroid state can be restored after a few months of treatment. It is necessary to check and evaluate thyroid function every 4-6 weeks. If thyroid function is stable and within the normal range, follow-up time is gradually reduced, about once a year. If there are signs of hypothyroidism, treatment with levothyroxine is indicated. If symptoms are mild and transient, follow-up for 4-6 weeks is required for further evaluation. In case, acute thyrotoxicosis continues after 6 months of treatment, the second radiation therapy is indicated. Side effects: Hypothyroidism may occur in the first year after radiation therapy in some patients. In addition, more progressive thyrotoxicosis may also be present. To limit and prevent severe attacks of thyrotoxicosis, treatment with thionamides is required until euthyroid state before radiation therapy.
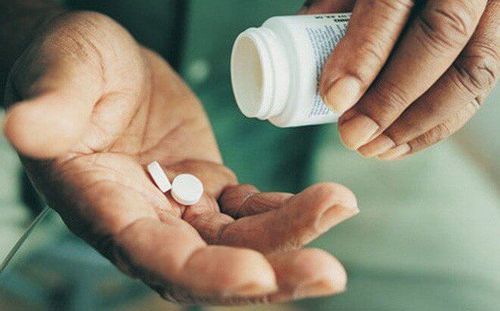
Trước khi xạ trị người bệnh cần ngưng dùng thuốc Thionamides
3.2.3. Proximal thyroidectomy For the long-term management of acute thyrotoxicosis, proximal thyroidectomy may be used. After surgery, thyroid storm can be triggered. Therefore, it is necessary to treat with Thionamides prepared before surgery from 1 to 2 weeks until near euthyroidism and stop using it after surgery. For Atenolol 50 - 100 mg, the therapeutic dose can be increased to help maintain the heart rate, which is still used 5-7 days after surgery.
Follow-up: After surgery to treat thyrotoxicosis, it is necessary to re-evaluate thyroid function 4-6 weeks after surgery. If thyroid function is normal, check again every 3-6 months and gradually decrease every 1 year. If there are signs of hypothyroidism, treatment with levothyroxine is indicated. If hypothyroidism is mild and transient, follow-up should be continued for another 4-6 weeks for evaluation. A small number of cases of thyrotoxicosis persist or recur after treatment. Complications: Hypothyroidism and hypoparathyroidism may occur. However, permanent vocal cord paralysis is very rare. Following treatment of thyrotoxicosis with drugs, radiation, or surgery, thyroid function should be re-evaluated, clinical symptoms and laboratory findings should be checked. Based on that, there is the next treatment.
Acute thyroid hormone toxicity is the most serious complication occurring in patients with hyperthyroidism. Therefore, patients need to be diagnosed early in order to have timely treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used modern facilities and equipment along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of experts. Good doctors, well-trained both at home and abroad.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline for support.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.