This is an automatically translated article.
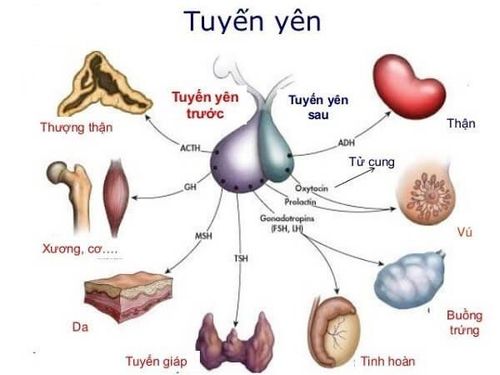
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Thi Duyen - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.TSH stands for thyroid-stimulating hormone, which is produced by the pituitary gland in the brain. This gland tells your thyroid gland to make and release thyroid hormones into the bloodstream.
1. What is TSH hormone?
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 28,000 daltons secreted by the anterior pituitary gland under the control of a hypothalamic hormone (TRH). When thyroid hormone levels in the circulation drop or when the body is faced with physical or mental stress, the hypothalamus is stimulated to release hormones that cause the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TRH). TRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Then, TSH stimulates the production and release of Triiodothyroxine (T3) and Thyroxin (T4). TSH is a very valuable test in the diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid disease, especially in Basedow's disease.2. What is a TSH test?
The main purpose of the TSH test is to see if the thyroid gland is functioning as it should. At the same time, it is very important to diagnose early thyroid dysfunction diseases (hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism) and the causes as well as the origin of such disorders to have timely and early treatment advice and treatment. provide a better quality of life. Example: Hypothyroidism due to the thyroid gland (primary hypothyroidism) or outside the thyroid gland (secondary) when the concentration of free T4 is measured simultaneously.Help monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment in patients with thyroid dysfunction (basedow's disease, hypothyroidism). TSH is also a means of predicting whether the disease will stabilize or recur after treatment. If the TSH level remains low for a long time, it means that the disease has not responded well and will easily relapse if the drug is stopped.

3. TSH . hormone testing process
A TSH test is simply taking some blood from the body in the morning. The blood will then be analyzed in a laboratory. It's best to do this in the morning because your TSH levels can fluctuate throughout the day. There is no need to do a lot of preparation before the test (such as fasting overnight). However, if you are taking certain medications, such as dopamine and lithium, you need to stop using them first. You will not feel too much pain after the blood draw, however, there will be a bruise on your hand. When treating thyroid diseases such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism with the aim of bringing TSH levels back to normal. To make sure you're taking the right dose, your doctor will periodically check your TSH test every 1 month for the first 6 months, and every 3 months after that.
4. Clinical significance of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test index
The TSH test is very valuable for diagnosing thyroid dysfunction and its causes. This is also a means to help predict whether the disease will stabilize or recur after treatment. If the TSH level remains low for a long time, it means that the disease has not responded well and will easily relapse if the drug is stopped. When thyroid dysfunction is clinically suspected, a quantitative TSH test is the first indication:Normal TSH:
Normal TSH value is 0.4 to 5 mIU/L (milli). - international units per liter). Severe increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels:
Hypothyroidism of glandular origin: Latent hypothyroidism: If T3 and T4 levels are normal. Overt hypothyroidism: If T3 and T4 levels are lower than normal. Due to the use of drugs that cause complications of hypothyroidism (hypothyroidism after treatment): Antithyroid drugs such as PTU, Amiodaron, Lithlum. Anti-TSH antibodies are present. Removal of part or all of the thyroid gland. Hyperthyroidism of pituitary origin. TSH production is out of place. Primary adrenal insufficiency. Decreased levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) are important:
Hyperthyroidism originates in the thyroid gland. Hypothyroidism of pituitary or hypothalamic origin (secondary hypothyroidism). Multinodular thyroid gland. Due to drug use: Thyroid essence, Amlodarone, Preparations containing iodine. Decreased pituitary function. In addition, the TSH test is also valuable to help monitor the progression of thyroid disease and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
For pregnant mothers: Mothers with hypothyroidism during pregnancy may be at high risk for anemia, pre-eclampsia, premature birth, placental abruption, intrauterine growth retardation, malnutrition fetus.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.