This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted professionally with MSc. Doctor Vu Thi Duyen - Doctor of Nephrology - Endocrinology, Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Controlling blood sugar in patients with diabetes with insulin injections is one of the routine treatments. However, if the insulin injection technique is not correct, it will be dangerous for the patient. Therefore, when administering insulin injections, it is important to understand and follow your doctor's instructions on how to inject and where to inject insulin.
1. Injecting insulin in diabetic patients
In order to control blood sugar well in diabetes, it is necessary to combine many methods such as adjusting diet and lifestyle, and oral drugs, insulin injections, etc. In which insulin injection is an effective method if people The disease is injected correctly and according to the indications.Insulin is essentially a hormone that helps control blood sugar when injected into the body. Currently, there are many different types of insulin and there are many different injection regimens depending on the individual patient. The main effect of insulin is to promote the transport of glucose across cell membranes. Insulin is a hormone secreted continuously 24 hours by pancreatic beta cells and is most abundantly secreted after a meal.
However, insulin cannot be taken in pill or oral form, it is only available in injection form. It is also a protein affected by the stomach's digestive enzymes that break down insulin before it enters the bloodstream.
2. Insulin injection sites
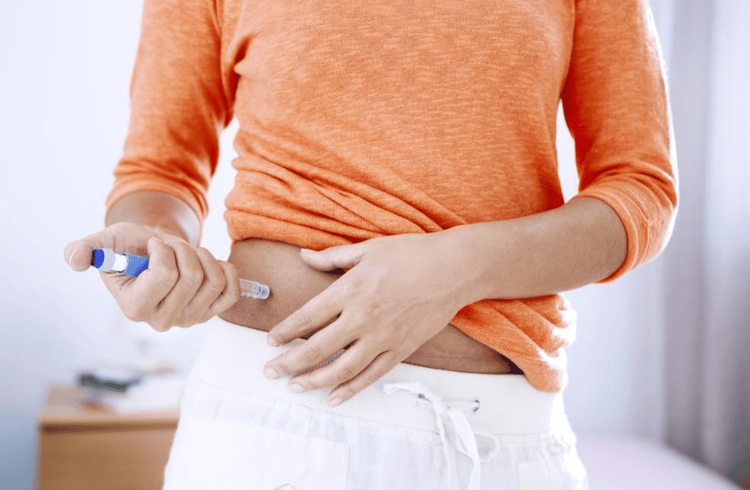

Bụng là vị trí được nhiều bệnh nhân cũng như bác sĩ lựa chọn tiêm insulin nhất
First: Need to disinfect the insulin injection site because this is the best condition for insulin to be absorbed. The skin at the injection site must be kept clean, and the muscle and subcutaneous fat in this area should be completely normal. Insulin is injected into the layer of fat just under the skin called the subcutaneous tissue. In addition, to prevent infection at the injection site. Prophylaxis of sepsis (if not sterile, it may be an entrance to infection because diabetic patients have a weak immune system).
Second: Currently, there are many types of insulin used, so depending on each type, there is a different injection time prescribed by an endocrinologist for the patient. Rapid-acting insulin: It takes effect 15-30 minutes before eating. Moderately effective type of insulin: 15 minutes - 2 hours after injection, usually 1 hour on average, before eating. The drug is injected with a fine needle or a pen-like device such as the now commonly used Novomix 30 plexpen (300 units/300 units/ml).
Some of the best insulin injection sites should be injected:
Abdominal skin location: The abdomen is the location that many patients as well as doctors choose to inject insulin the most, which is the area around the navel. To inject into the abdomen, pinch the fatty tissue from the side between the waist and hip bones. This should be about 5cm away from the navel. Inject clockwise and change injection sites continuously to avoid injection side effects such as dystrophy at the injection site. Arm skin position: This position is also a good choice if the abdomen is contraindicated because the insulin absorption rate is moderate but not as rapid as the abdomen. To inject into the arm the needle must be placed on the back of the arm (the triceps area, or biceps) approximately between the shoulder and the elbow. Arms often make it difficult to inject themselves and need help. Thigh skin position: This is the slowest insulin absorption site but a convenient location for patients to self-inject. When injecting the thigh, it is necessary to insert the needle into the front of the thigh, between the knee and the groin, slightly to the outside of the leg, note, inject the drug into the skin pinch at least 2.5 - 5cm. Back or hip skin: The rate of drug absorption is quite slow and this is also the location for the patient to self-inject. When injecting at the waist or hip, draw an imaginary line through the top of the buttock connecting the two sides. The needle must be placed above this line but below the line, approximately midway between the spine and the midaxillary line.
3. All insulin injection sites must be rotated and changed continuously to limit side effects
In patients with diabetes, insulin injections are indicated to control blood sugar to limit complications as well as to irritate the skin and subcutaneous adipose tissue, which can increase discomfort, requiring rotation of injection sites. Especially for cases where 2 or more injections are used in a day, they must be injected at different locations and in different areas. Patients absolutely avoid injecting into the same site over and over again. This can lead to hard lumps or fatty deposits developing under the skin and affecting absorption of the drug.When alternating injection sites, injections at a certain hour of the day should be administered at the same site. However, it is important to move around the site to ensure that the injection is not in one spot.
For example, when injecting a long-acting insulin dose at night, the patient always injects it into the thigh. However they will alternate between the right and left thighs every night.
If a person always injects a morning dose of rapid-acting insulin into the abdomen, it should be rotated around different areas of the abdomen, so that the injection is not in the same place.

Hạ đường huyết là biến chứng phổ biến mà người bệnh đái tháo đường khi tiêm insulin thường gặp phải, do tiêm thuốc quá liều
4. Complications when injecting insulin
Hypoglycemia: This is a common complication that diabetics when injecting insulin often experience due to insulin overdose. If the patient has mild hypoglycemia, they can drink a glass of sugar water and eat sweets. In severe cases, it is necessary to go to a medical facility for intravenous infusion of 20-40ml of a 20% glucose solution or 1-2mg of glucagon and take it to the emergency room. Therefore, after insulin injection, patients need to carefully monitor blood sugar and report to the endocrinologist to advise on adjusting the most appropriate injection dose. It is best for patients to keep a record of their blood sugar in a notebook so that they can share it with their doctor. Abnormal parameters should be reported to the doctor immediately so that the insulin dose can be adjusted if necessary.Infection at the injection site: D in the first place if the patient does not take adequate steps to clean the injection site. In this case, the patient can consult a doctor for advice on the use of antibiotics. Local insulin response: The subcutaneous fat layer is atrophied due to the use of human insulin. In contrast, there is often hyperplasia of subcutaneous fat at the injection site, because insulin stimulates the growth of fat cells. In case of injury, the injection site must be changed. The principles to remember when injecting insulin have been discussed above. Vials of insulin in use should not be refrigerated.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.