This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Van Sang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.1. What is dermatomyositis?
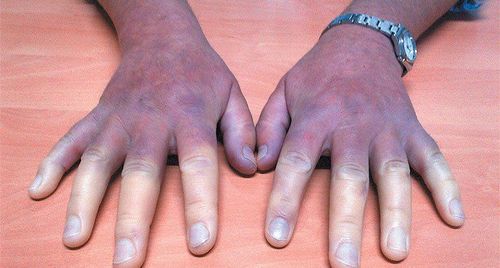
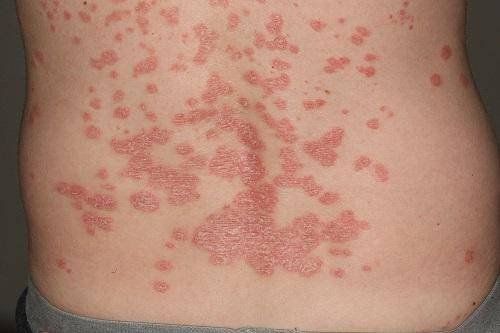
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune connective tissue disease, common in two age groups: children and adults.Clinical manifestations of dermatomyositis are inflammation of the muscles of the extremities, skin lesions, red-purple skin, distributed in places exposed to light such as scalp, face (usually appearing around eyes), lateral surfaces of hands and feet, and accompanied by vasodilatation at the nail bases.
Patients with dermatomyositis will be affected mainly by inflammation of the skin and muscles.
2. Symptoms of dermatomyositis
Subclinical signs of dermatomyositis are increased muscle enzymes, histopathology shows mucin deposition in the inflamed skin, infiltration of lymphocytes in the inflamed muscle.
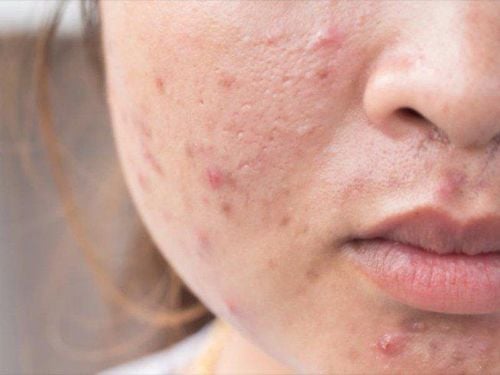
2.1 Skin lesions Initially the skin is burning, red, after a while scabs, the skin color fades. After a while appears skin atrophy, pigmentation decreases. Papules on the skin on the joints of the fingers, hands, elbows, knees, or legs. Fingernails and toenails are red. Caused by vasodilation. Fingers are dry, cracked, and thickened. Patchy skin color: due to the severity of skin damage, it leads to decreased pigmentation. The back, chest, and neck area are the most likely places for this phenomenon to occur. Subcutaneous calcium deposition: Young people are most likely to have this sign when having dermatomyositis 2.2 Muscle damage 2.2.1 Muscle weakness This is the first clinical manifestation of people with dermatomyositis. People with the disease find it difficult to need to, hold heavy objects, have difficulty walking, difficult to climb stairs, walk or squat, can't raise their arms high,...
2.2.2 Muscle pain When moving muscle pain. The larynx and esophagus also feel pain, making it difficult for the patient to swallow and breathe.
2.2.3 Muscle atrophy If left untreated for a long time, the patient will have muscle atrophy, unable to walk.

3. Causes of dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is considered a rare disease, the exact cause of which has not been found. According to research, women suffer from the disease more than men, the rate of dermatomyositis is only 1 in 100,000.The cause of dermatomyositis is currently unknown, but research shows that there are 3 factors present in people with dermatomyositis:
Genetics Infection: Coxsackie B, Echovirus, Streptococcus pyogenes, bacterial infection respiratory and gastrointestinal tract and/or antibiotic use. Malignancy: Dermatomyositis of onset in the elderly, usually as a hard tumor or a hematologic malignancy.

4. Treatment of dermatomyositis
The purpose of the treatment of dermatomyositis is to improve muscle strength, prevent muscle atrophy and stiffness, prevent and reduce extramuscular complications, and reduce skin damage.Need to do related tests: Need to test CPK enzyme (Creatine phosphokinase) elevated, electromyography abnormal. An ultrasound or X-ray is needed to check for internal tumors. If the diagnosis is difficult, a skin and muscle biopsy should be performed.
Currently there are types of medicinal products commonly used by patients to treat:
Topical: Corticosteroid ointments for skin lesions. Corticosteroids: Prednisolone 0.5-1.0 mg/kg/day (Intravenous Solumedrol), depending on individual patient response. Especially, it is necessary to maintain a low dose (5-10mg/day) for a long time to avoid recurrence of the disease. Colchicine: Helps reduce calcium deposition. Currently, some other immunosuppressive drugs are also used such as: Azathioprin, Cyclophosphamide, Rituximab... Note: In the acute phase, patients must rest. Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.