This is an automatically translated article.
Anemia is a condition that can occur in any age and gender due to causes such as blood loss, hemolytic disease or disorders of the blood formation in the body. Anemia classification has 3 levels: mild anemia, moderate anemia and severe anemia based on the patient's hemoglobin level.
1. What is anemia?
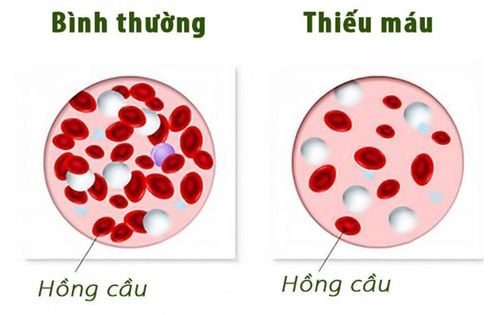
Anemia according to WHO (World Health Organization) is a condition in which a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells in the external blood leads to a lack of oxygen supply to tissues in the body. Depending on sex and age, anemia is determined based on the following levels:
For men: Hb < 13 g/dl (130 g/l) For women: Hb < 12 g/ dl (120 g/l) For the elderly: Hb < 11 g/dl (110 g/l)

Pale skin, pale mucous membranes, tinnitus, dizziness, dizziness, fainting Anorexia, digestive disorders Or nervousness, fast heartbeat, easy fatigue. Endocrine system disorder, women may not menstruate
Trắc nghiệm: Bận rộn có ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe của bạn không?
Cuộc sống hiện đại khiến chúng ta vì quá bận rộn mà quên chăm sóc sức khỏe cho chính mình. Ai cũng biết rằng lịch trình làm việc cả ngày có thể khiến bạn kiệt sức, nhưng cụ thể bận rộn ảnh hưởng thế nào tới sức khỏe? Hãy cùng làm thử bài trắc nghiệm dưới đây.
2. How is anemia classified?
There are 4 ways to classify anemia depending on the degree, course, cause of anemia and red blood cell characteristics as follows
2.1 Degree of anemia For acute blood loss, the anemia classification will be based on the rate of anemia. blood loss and hemodynamic changes. Specifically, a loss of more than 15% of the blood volume (500ml) is considered severe anemia.
For chronic anemia, the grading is based on the amount of hemoglobin measured in the blood as follows:
Grade 1: 10 g/dl ≤ Hb < 12 g/dl Grade 2: 8 g/dl ≤ Hb < 10 g/dl Level 1: 6 g/dl ≤ Hb < 8 g/dl Level 1: Hb < 6 g/dl Besides, the degree of anemia is also divided according to each subject based on the assessment table of the degree of deficiency the following blood:
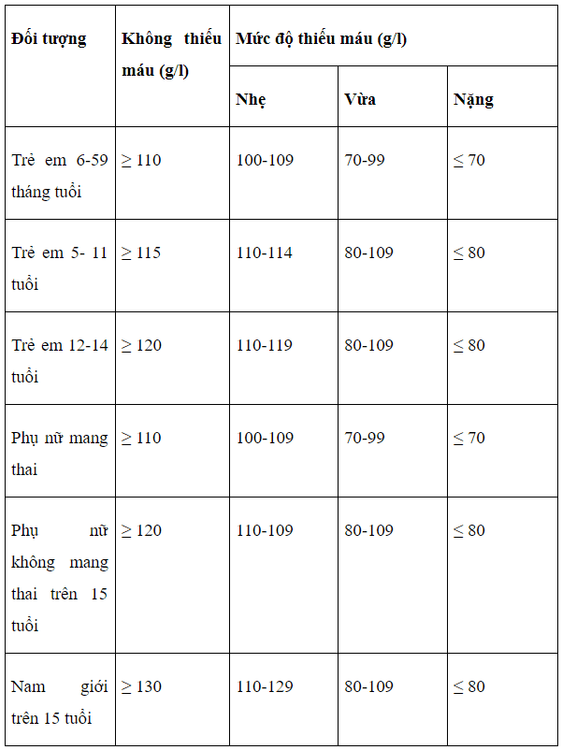
2.2 Anemia progression Acute anemia: anemia that comes on quickly, for a short time internal and external factors that cause damage such as trauma, menorrhagia or stomach bleeding. Hemolytic anemia: is a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed faster than they are created due to causes such as Thalassemia, blood cancer, taking anti-malarial drugs,... Anemia due to blood disorders Hematopoietic process: Bone marrow diseases are the cause of anemia such as: bone marrow failure, bone marrow disorders or blood cancer. 2.4 Characteristics of red blood cells Based on MCV: classified as small or macrocytic anemia Based on MCH (mean red blood cell hemoglobin): classify hypochromic or hypochromic anemia
3. Anemia treatment
Depending on the cause of the anemia, there are different treatments. However, the general principles for the treatment of anemia are as follows:Identify and treat according to the cause, combine treatment of the cause and compensate for red blood cells;

Based on the hemoglobin tests and the patient's clinical condition, the treating doctor will prescribe the number of red blood cells to compensate; Maintain a minimum hemoglobin level of 80 g/l (in case of chronic heart and lung disease, it should be maintained from 90 g/l). Anemia if not detected and treated promptly will cause many dangerous complications. You should have regular health check-ups to detect diseases early.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has General Health Checkup Packages for many different subjects. You can choose a package that suits your needs such as:
Children's General Health Checkup Standard General Health Checkup Comprehensive General Health Checkup Special General Health Checkup VIP General Health Checkup General health Diamond To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.
MORE:
Iron deficiency anemia: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Recognizing and preventing nutritional anemia Hemolytic anemia: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment