This is an automatically translated article.
Anemia can make the body tired, lethargic or exhausted not having enough energy to perform daily tasks. Because the blood is responsible for providing nutrients and oxygen to maintain all the normal functioning of the organs in the body. The extent to which anemia can deplete the body will be discussed in this article.
1. What is anemia?
Anemia is a condition in which there are not enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout the body. Anemia can be acute or chronic. In many cases, the condition is mild, but anemia can also be serious and life-threatening.
Anemia can happen because:
The body does not make enough red blood cells as it needs. Bleeding causes you to lose red blood cells faster than those that can be replaced. Your body destroys red blood cells.
2. Why you can die of anemia
Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body. When you don't have enough red blood cells, your organs don't get enough oxygen and can't function properly, which can have serious consequences. Types of anemia that can be life-threatening include:
2.1. Non-regenerative anemia
Aplastic anemia occurs when your bone marrow is damaged, and so your body stops producing new blood cells. It can be sudden or get worse over time and be depleted by anemia.
Common causes of aplastic anemia can be:
Cancer treatment Exposure to toxic chemicals Pregnancy Autoimmune disorders Viral infections Anemia can also have no known cause, known as anemia groundless real estate.

Thiếu máu bất sản xảy ra khi tủy xương của bạn bị tổn thương
2.2 Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is a rare, life-threatening disease. This condition causes blood clots, destroys blood cells, and impairs bone marrow function. It is an inherited condition, usually diagnosed in people in their 30s or 40s.
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is associated with aplastic anemia. It usually begins as aplastic anemia or arises after treatment of this condition.
2.3. glial syndrome
Myeloma is a group of conditions that cause the blood-forming cells in your bone marrow to become abnormal. When it does, your bone marrow doesn't make enough cells, and the cells it does make are often faulty. These cells die earlier and are more likely to be destroyed by your immune system.
Myelodysplastic syndrome is considered a type of cancer. They can turn into acute myeloid leukemia, a type of blood cancer.
2.4. Hemolytic anemia, anemia
Hemolytic anemia is when your red blood cells are destroyed faster than your body can make them, which can be temporary or chronic.
Hemolytic anemia can also be hereditary, which means it is inherited through your genes or acquired.
Potential causes of acquired hemolytic anemia include:
Infection Certain medications, such as penicillin Blood cancers Autoimmune disorders An overactive spleen Some tumors severe reaction to blood transfusion
2.5. Sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease is an inherited type of anemia. This disease causes your red blood cells to become deformed - they become sickle-shaped, hard, and sticky. This causes them to get stuck in small blood vessels, blocking the flow of blood throughout the body, depriving tissues of oxygen. This disease is more common in people of African descent.
Sickle cell disease causes very painful episodes, swelling and frequent infections. Malaria Anemia: Malaria anemia is a major symptom of severe malaria. Many factors contribute to its development, including: Malnutrition; bone marrow problems; malaria parasites invade red blood cells Fanconi anemia: Fanconi anemia (FA) is an inherited condition that degrades bone marrow and leaves you with lower than normal counts of all types of blood cells. . Fanconi anemia also often causes physical abnormalities, such as: Deficiency anemia, malformed thumb or forearm, bone abnormalities, malformed or missing kidneys, and sugar abnormalities digestion, infertility, and vision and hearing problems. Fanconi anemia can also cause an increased risk of leukemia, as well as cancers of the head, neck, skin, reproductive and gastrointestinal tract.
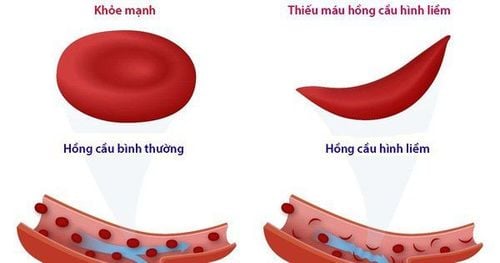
Bệnh hồng cầu hình liềm là một loại bệnh thiếu máu di truyền
3. Symptoms of anemia
Common symptoms of anemia include: Fatigue; cold hands and feet; dizzy; headache; lightheadedness; irregular heartbeat; chest tightness; pale or yellowish skin; short of breath; weak; humming or pounding in your ears
4. What causes life-threatening anemia?
Anemia occurs when your body doesn't make enough blood cells, it destroys your red blood cells, or the red blood cells it makes are malformed.
Various causes of these conditions include:
Genetics: These conditions cause anemia and are hereditary, which means they are inherited through one or both parents through the parent's genes. friend. Sickle cell thalassemia Certain hemolytic anemias Fanconi anemia Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Bleeding Heavy bleeding can cause sudden, short-term anemia. For example, this can happen after an injury that causes you to lose a lot of blood. Cancer Cancer of the blood, lymphatic system, and bone marrow can cause anemia. Examples include: Non-regenerative anemia; some hemolytic anemias glial syndrome Disease Acquired diseases, including malaria, can cause anemia. Other infections can cause aplastic anemia or hemolytic anemia. Autoimmune diseases are also a potential cause of anemia, as they can cause your body to attack red blood cells.
5. Diagnosis of anemia
Your doctor will take your medical history along with a physical exam to look for symptoms of anemia. Finally, your doctor will draw blood to do some tests: complete a complete blood count to count your red blood cells and hemoglobin levels in your blood; tests to see the size and shape of your red blood cells. After you're diagnosed with anemia, your doctor may do more tests to see if they can find the underlying cause of your anemia. For example, your doctor may do a bone marrow test to see how well your body makes red blood cells, look for internal bleeding, or scan for tumors.

Nói chuyện với bác sĩ để tìm ra các triệu chứng thiếu máu
6. Treatment of severe anemia
Treating severe anemia is more than just making dietary and lifestyle changes, although eating a healthy diet with plenty of iron can help keep you healthy. Sometimes, treating anemia requires treating the underlying cause. Examples include: Chemotherapy for myelodysplastic syndromes; eculizumab (Soliris) treats paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, which keeps your body from destroying red blood cells; immunosuppressants for certain types of aplastic anemia and hemolytic anemia
In all forms of anemia, a blood transfusion can help replace lost or faulty red blood cells and reduce symptom. However, it often does not address the underlying cause.
A bone marrow transplant, also known as a stem cell transplant, is an option if you cannot make healthy red blood cells. In this procedure, your bone marrow is replaced with donor marrow that can make healthy cells. This is the only cure for some types of anemia, such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
Anemia if not detected and treated promptly will cause many dangerous complications. You should have regular health check-ups to detect diseases early.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package general health Vip Special general health checkup package Standard general health checkup package Patient's examination results will be returned to your home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com