The article was professionally consulted by First Degree Specialist Doctor Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International Hospital.
The formation of a fetal heart and normal development is a good indicator of the fetus's health. However, in many cases, ultrasound results show no fetal heart. What is the reason for this condition, and what should be done in this case?
1. When does the fetus's heart form?
According to normal fetal development, about 22 days after conception, the fetal heart begins to form quite distinctly and starts beating. Thus, in most cases, the fetal heart forms before the mother realizes she is pregnant. With modern ultrasound technology, the fetal heart can appear and be observed as early as the 6th-7th week of pregnancy.
However, in some cases, the heartbeat might only be detected around the 8th to 10th week of pregnancy due to errors in calculating the gestational age.
The formation and development of the fetal heart are closely linked to the development of the fetus, making it a crucial sign of fetal health. Typically, after fertilization, the zygote moves to the uterus and rapidly divides into cells.
Five days after fertilization, the zygote develops into a small mass called a blastocyst, which then reaches the uterus about two days later. At this stage, the blastocyst begins the implantation process by attaching firmly to the uterine lining. It is during this phase that the blastocyst starts secreting HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in urine, which can be detected using a pregnancy test kit. However, at this time, the embryo cannot yet be clearly seen on ultrasound.
During the fetus's development, the heart is one of the first organs to form early. The primitive heart tube, derived from mesodermal tissue, starts beating about 3 weeks after fertilization. This tube continues to develop and bend, forming septa that divide the heart into four chambers. The heart is fully developed when two separate outflow tracts are formed.
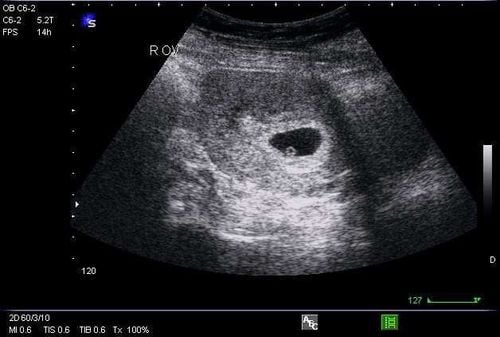
Using real-time two-dimensional imaging of the mother's uterus, ultrasound detects the fetal heartbeat based on heart activity. Calculating gestational age from the last menstrual period places this detection at approximately 5 to 6 weeks of fetal age.
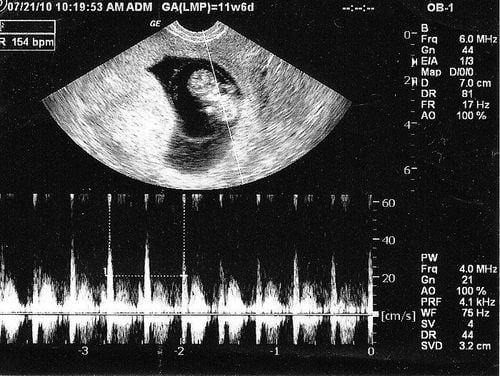
Doppler signals can detect the blood flow from the fetal heart and large blood vessels after 6 weeks of pregnancy. From 20 weeks onward, the fetal heartbeat can be heard with a standard stethoscope. A progressively stronger heartbeat indicates a healthy and well-developing fetus.
From week 6 onward, the fetal heartbeat can be detected by ultrasound, based on the timing and development process. In some cases, detection may be delayed until week 8 due to miscalculations of the menstrual period or gestational age.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có hiểu đúng về dấu hiệu mang thai sớm?
Các dấu hiệu mang thai sớm không phải chỉ mỗi trễ kinh mà còn có rất nhiều dấu hiệu khác như xuất huyết âm đạo, ngực căng tức,… Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu dấu hiệu mang thai sớm thông qua bài trắc nghiệm này nhé!
2. Why is there no fetal heartbeat on ultrasound?
At 6 weeks of pregnancy, if the embryo is fully formed and the heartbeat begins to appear, this is a good sign of the baby's healthy development.
However, mothers should not worry too much if the heartbeat is not yet detected or heard, as doctors will determine and explain the cause. At the next checkup, if the fetus develops normally, the baby's heartbeat will be clear. On the other hand, if the fetus is already at an advanced stage but the ultrasound shows no heartbeat, potential reasons include:
2.1 Miscarriage
Most cases of no fetal heartbeat on ultrasound are due to miscarriage unless there is an error in gestational age calculation. Reasons for miscarriage may include:
- Natural Miscarriage: The cause of the fetal heartbeat stopping suddenly remains unclear, even if the mother’s health appears normal, although the baby is no longer viable.
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: Blighted ovum, poor sperm quality, or abnormal cell division account for 50% of natural miscarriages.
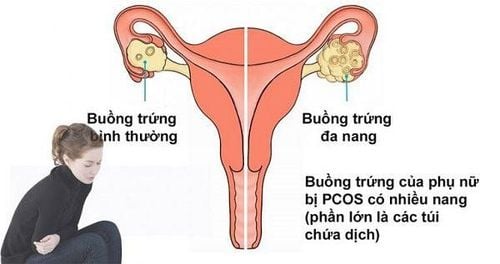
- Maternal Health Issues: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome, diabetes, clotting disorders, thyroid issues, immune disorders, uterine abnormalities, or incompetent cervix increase miscarriage risk.
- External impact: The cause of fetal cardiac arrest and miscarriage may also result from undesirable external environmental impacts, including:
- Impact, abdominal trauma
- Mother is sick, contracting infectious diseases such as rubella, and toxoplasmosis...
- Mother smoking, drinking alcohol, using stimulants, using drugs, being infected with HIV/AIDS...
- Mother has depression, long-term stress
- Mother being exposed to toxic environments
2.2 Fetal arrhythmias
Fetal arrhythmia is a rare condition that often occurs at some point in pregnancy and does not last throughout the pregnancy. Fetal arrhythmia is temporary and usually benign, but in some cases, the fetus may die.
The fetal heart rate is usually higher than that of a normal person, around 120-160 beats/minute. The baby's heart rate may increase rapidly, slow down, or stop suddenly if there is a fetal heart disorder.
2.3 Faulty ultrasound equipment
An important factor helping you hear the fetal heartbeat clearly and accurately includes modern ultrasound equipment and a good stethoscope. However, you might mistakenly believe there is no fetal heartbeat or that there is a problem with the fetus if there is equipment error. This could be due to the device not being sensitive enough to detect when the fetal heart is still very weak, especially in the 6th to 8th weeks of pregnancy.
2.4 Miscalculation of gestational age
Due to miscalculations of gestational age, many cases of 7-week ultrasounds show no fetal heartbeat. At this time, the fetus is still small, and the gestational age may deviate by 1–2 weeks due to the mother and doctor calculating based on the ovulation day.
2.5 Types of ultrasound method
Ultrasound results can be affected by the type of ultrasound method chosen by the mother. When the fetus is still small and the heartbeat is not clear, abdominal ultrasounds are usually less sensitive, making it harder to detect the fetal heartbeat. Transvaginal ultrasounds provide more accurate results because the probe is closer to the uterus.
3. What to do when ultrasound shows no fetal heartbeat?
The mother should not worry too much if there is no fetal heartbeat on an ultrasound at 6–7 weeks, as it is likely due to late fertilization or irregular menstrual cycles leading to inaccurate gestational age calculations. At this time, the ultrasound may not detect the fetal heartbeat because your fetus may only be developing in the 4th–5th week of pregnancy.
In some cases, the embryo develops more slowly than normal, so the heartbeat may only be detected in the 8th–10th week. The doctor will perform tests to determine whether there are any abnormalities and assess the fetus's condition. Typically, you will be scheduled for a follow-up examination and ultrasound in 1–2 weeks if no abnormalities are detected.
If a 7-week ultrasound shows no fetal heartbeat due to external factors, incorrect gestational age calculation, or slow fetal development, the mother's HCG levels should be checked to confirm whether the fetus is still viable. If HCG levels are normal, the mother should wait 1 week before undergoing another ultrasound to check for the presence of a fetal heartbeat. To avoid health impacts, the mother should not worry excessively.
If a 7-week ultrasound shows no fetal heartbeat or the fetal heartbeat has stopped and the mother experiences abnormal symptoms such as severe lower abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, loss of morning sickness, notify your doctor immediately to check the fetus's condition.

To ensure a healthy pregnancy and good fetal heart development, mothers should consider the following:
- Mothers should limit alcohol consumption.
- Prevent congenital disabilities by supplementing with folic acid during this stage.
- Avoid smoking and minimize exposure to cigarette smoke as it can cause fetal birth defects.
- Maintain stable blood sugar levels, especially for mothers with gestational diabetes.
- Ensure a balanced and diverse diet and rest adequately.
If an ultrasound after 12 weeks still shows no fetal heartbeat, an HCG test should be urgently performed to determine whether the pregnancy is viable or if there is an issue with the fetus. In the case of a miscarriage, doctors will apply safe and appropriate methods to remove the fetus, ensuring the mother's safety. Family, relatives, and friends should support and comfort the mother in case of the worst scenario—no fetal heartbeat due to miscarriage—as this is a significant and painful loss. The most important thing for the mother right now is to overcome this great pain and regain her health. Wait at least 3 months before trying to conceive again after a miscarriage, giving yourself time to rest and recover.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.