This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Tran Hong Nhat - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Coronary fistula into the chambers of the heart is a rare congenital heart disease that accounts for 0.2 to 0.4% of all congenital anomalies. The disease has an unclear presentation, in some cases presenting with a state of heart failure. Congestive heart failure often goes undetected.
1. Coronary artery fistula
The coronary artery is the vascular system of the heart, divided into branches including the left coronary artery (divided into the anterior interventricular artery, the circumflex artery) and the right coronary artery, which is responsible for bringing oxygen-rich color to the blood supply. heart cells.Coronary artery fistula is a congenital malformation in which the coronary arteries are anatomically abnormal, with abnormal vascular branches protruding into the heart chambers or large blood vessels near the heart (pulmonary artery, vena cava, vein). lung ...). Incidence is low with equal incidence in men and women. Arterial fistula is mainly found in the right coronary artery, the rate of fistula in both right and left arteries is low.
Leakage of coronary arteries into the heart chambers causes the amount of blood in the coronary vessels to decrease, not supplying enough demand for the heart muscle and increasing the flow to the heart chambers, so symptoms such as shortness of breath may appear on exertion. strength, chest pain, auscultation, abnormal heart sounds, and a continuous murmur on the left side of the sternum.
2. Diagnosis of coronary artery fistula
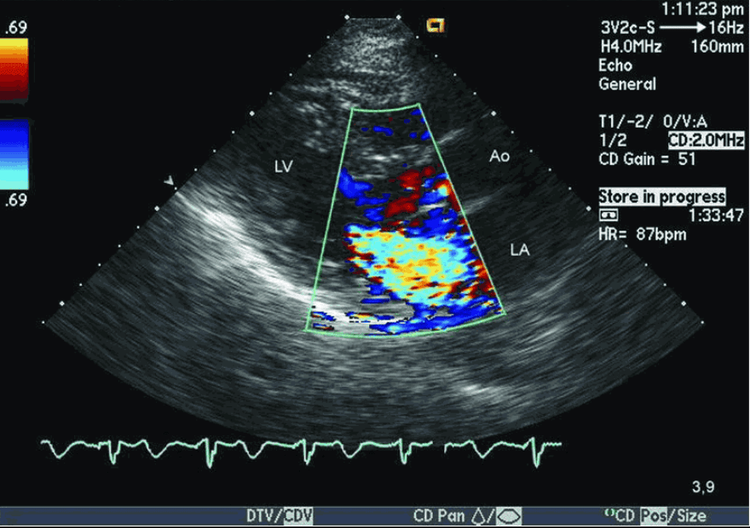
- Echocardiography: Has high diagnostic value in identifying coronary artery disease. Most of over 90% of patients are diagnosed with coronary artery disease by this method:
On ultrasound, there are signs such as coronary artery diameter at the great dilatation, the ratio of coronary artery to aorta at the origin of the artery increases. , there is a strong eddy blood flow into the chamber of the heart with the coronary artery entering. In addition, ultrasound has prognostic value, indicating surgical intervention. Ultrasound findings that help indicate interventional therapy include coronary artery size at the base of dilation, chamber dilation, pulmonary hypertension, left ventricular systolic dysfunction, and other associated heart disease. Coronary angiography and CT coronary angiography: In some people, when cardiac abnormalities are seen but are difficult to detect and cannot be definitively diagnosed by echocardiography, angiography should be performed to definite diagnosis of the disease.
3. Treatment of coronary artery fistula
Surgical method:
Surgery is indicated for the following patients
Coronary artery leak and symptoms of heart failure (dyspnea on exertion, chest pain...) have heart failure but have high cardiac output on echocardiography. Surgery has no absolute contraindications but there are relative contraindications such as:
Severe heart failure, no response or very little response to aggressive medical treatment or prolonged heart failure, poor patient condition. exhaustion, impaired liver and kidney function. Left ventricular function severely reduced on echocardiography showed ejection fraction (FE) less than 40%, contraction fraction less than 25%. Objectives of coronary artery fistula surgery:
Determine the location of the fistula into the heart chamber, then tie the fistula around 15 minutes. After ligation, check the electrocardiogram, if there is no myocardial ischemia, close the fistula with sutures.
Bleeding, pericardial effusion, cardiac tamponade Acute heart failure Mediastinitis, sternal inflammation. Vascular thrombosis, myocardial infarction Hemolysis. Follow up after surgery
Do blood gas, electrolytes, liver and kidney function tests, blood count immediately after returning to the monitoring room for 15-30 minutes, chest X-ray at bed. Monitor hemodynamics, respiration, drains, urine every 30 minutes to 1 hour, in the first 24 hours or longer depending on hemodynamic status. Monitor possible complications after surgery. To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for the Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital. The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.