This is an automatically translated article.
Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration (SCUF) is one of the techniques of continuous renal replacement therapy. This is a simple, safe, and beneficial technique for the active treatment of patients with severe overhydration due to various causes.
1. What is continuous slow ultrafiltration?
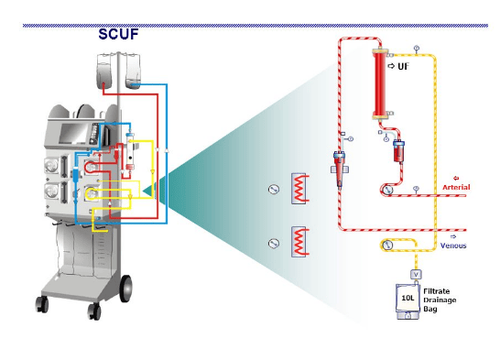
In this technique, the amount of water is removed from the body simply by convection mechanism based on transmembrane pressure, so the excess water is removed mainly, with water-soluble substances that are removed. The molecular weight is small enough to pass through the membrane pores. Normally, the amount of water removed is only about 4-5 liters/24 hours and there is no need for replacement fluids.
Quy trình siêu lọc máu chậm liên tục (SCUF)
2. Renal replacement therapy
2.1 Intermittent dialysis
This method has the advantage of filtering out dissolved substances. The new generation machines have many modern and safe equipment for patients.
However, this method only removes water-soluble toxins, with a small molecular weight of less than 30,000 daltons, and is not effective for protein-bound toxins or medium and large molecular weight toxins.
This method has the disadvantage of causing hemodynamic changes and can cause new lesions due to ischemia, prolonging the recovery of renal function and imaging., and it is not applicable in patients with bleeding unstable movement, heart failure, liver failure. When using this method requires a source of treated water.
2.2 Intermittent peritoneal dialysis
This method has poor performance, the elimination of water and solutes is not much, but it can be applied at home, does not require the patient to visit the hospital many times a week and does not need a source of treatment water. physical.

Phương pháp lọc màng bụng ngắt quãng có thể được thực hiện tại nhà
2.3 Continuous renal replacement therapy
Slow continuous hemodialysis occurs slowly, can eliminate water and remove most endogenous and exogenous toxins, toxins with molecular weight from 30,000 to 40,000 daltons, cytokines, internal toxic, has little effect on hemodynamics and the patient can adapt, this method also does not need treated water.
3. Indications and contraindications for continuous slow ultrafiltration
3.1 Designation
Excess water due to kidney failure or nephrotic syndrome. Excessive water intake due to severe heart failure. Excessive fluid retention but unresponsive to conventional treatment measures the risk of complications of acute pulmonary edema.
3.2 Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications.
Relative contraindications:
Coagulation disorder, ongoing bleeding. Lack of intravascular fluid volume. Low blood pressure has different causes.

Phương pháp này chống chỉ định cho bệnh nhân mắc rối loạn đông máu
4. Continuous slow ultrafiltration preparation
4.1 Executor
02 doctors: 01 main specialist and 01 auxiliary doctor. 01 specialist nurse.
4.2 Vehicles and consumables
Machine for slow ultrafiltration. Set of filter wire: 01 set. Catheter 2 barrel for dialysis: 01 set or large needle (size 17 - 15 G): 02 pieces (if there is no catheter). Catheter set: 01 set.
4.3 Patients
Patients are carefully explained about the technical process, purpose, and complications when performing the technique and signed a commitment letter.
4.4 Clinical assessment
Height, weight, temperature, pulse, blood pressure, cardiovascular, respiratory, edema...
4.5 Paraclinical assessment
Blood count, blood group. Basic coagulation. Anti-HIV, HBsAg, anti-HCV. Blood chemistry: urea, creatinine, glucose, protein, albumin, GOT, GPT, electrolytes, calcium. Urine analysis.

Tổng phân tích nước tiểu được thực hiện trước khi thực hiện thủ thuật
5. Steps for continuous slow ultrafiltration
5.1 Preparation
Check records and medical records: Check the patient's name and age... Check and examine the patient Technical implementation: The technique should be carried out in a sterile room with adequate equipment. assist. The person performing the procedure needs to wear a hat, mask, wash hands according to the procedure, wear a surgical gown and wear gloves.
5.2 Intake of blood vessels
Place a double-bore catheter into the femoral vein, internal jugular vein, or subclavian vein. If a double-bore catheter is not available, two large needles can be used: one is placed in the femoral vein to remove blood and the other is placed in the forearm vein to return blood. Note: It is necessary to test lidocaine before using for local anesthesia.
5.3 Establish extracorporeal circulation
Step 1: Prepare the machine.
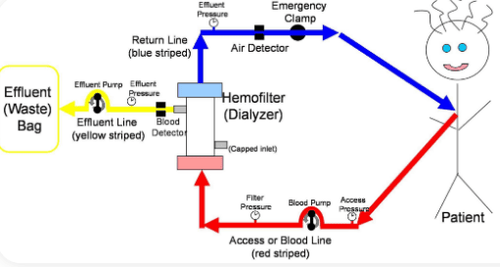
Start the dialysis machine, install the filter and wiring as directed. Evacuate with 2000 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution with heparin phase 1000 units/litre. Check the machine's safety system: safety locks, connectors. Initial setting of parameters: Bilan translation, blood volume, procedure time. Step 2: Connect the lead - filter system to the needle or catheter in the vessel to form a closed circulatory system.
Connect the blood line (red barrel of the catheter) to the extracorporeal circulation (red tip), turn on the blood pump (initial speed about 50 ml/min), when the blood begins to reach the membrane, pump the heparin dose. Initially (2000 units), when the blood passes through the membrane, stop the pump, connect the circulatory system (blue end) to the return blood line (blue) of the catheter.
Hình ảnh máy lọc máu trong siêu lọc máu chậm liên tục (SCUF)
Blood rate: gradually increase to 80-100 ml/min. Temperature: 37oC. The average ultrafiltration rate is 500 - 800 ml/hour. Average dose of heparin 500 units/hour On average, about 4 - 5 liters are removed during a filtration period of about 6 - 8 hours. Step 4: At the end of the procedure, collect the blood at the end of the ultrafiltration time. If the catheter is saved, it is necessary to clean the two catheters with 0.9% sodium chloride and inject an amount of heparin into each barrel to prevent blood clots causing catheter occlusion, the amount of heparin depends on the type of catheter. If a catheter is used, withdraw the needle after the procedure is completed, with a tight bandage to stop the bleeding.
6. Follow up
Monitor the patient: make a table to monitor consciousness, pulse, electrocardiogram, blood pressure, central venous pressure (CVP), respiratory status. Machine parameters: Inlet - outlet pressure, transmembrane pressure... Record medical records or monitoring sheet: Type of machine, vascular access, type of dialysate, filtration time, anticoagulant dose, speed blood draw rate, total amount of fluid drawn; blood pressure before, during and after dialysis; Abnormal handling (if any). After the dialysis session: Continue to monitor pulse, blood pressure, temperature, urine, bleeding for at least the next 8 hours. Monitor catheter status if catheter remains. Post-procedure tests: Electrolyte, blood count, coagulation.
Sau khi thực hiện thủ thuật, người bệnh cần xét nghiệm công thức máu
7. Complications and treatment
Related to vascular access procedure:
Local hematoma, pneumothorax - hemothorax, mediastinal bleeding. Requires specialist consultation for treatment. Infection at the puncture site and sepsis: It is important to ensure that the procedure is as sterile as possible, possibly requiring removal of the catheter, blood culture, catheterization, and antibiotics (preferably according to an antibiogram if available). . Low blood pressure due to rapid ultrafiltration:
Reduce the rate of ultrafiltration, can add colloidal solution or albumin if necessary. Hemorrhagic complications: can be used to neutralize heparin (protamine sulphate). Need to find the cause to treat. Coagulation in the set of tubes and filters:
Need to recalculate the anticoagulation dose. If necessary, the fluid can be flushed with 0.9% sodium chloride; If the blood clots a lot, the procedure must be stopped. Allergic condition or shock due to allergy to wire or membrane filter, or allergy to plasma: use dimedrol, methylprednisolone... according to the protocol. Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed in a modern way, but still gives patients the comfort, friendliness and peace of mind as if they were at home.
For detailed information, please contact the hospitals and clinics of Vinmec health system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
READ MORE
Dialysis techniques in resuscitation Role of dialysis in poisoning Indications for dialysis in acute renal failure