This is an automatically translated article.
Traumatic brain injury is a term that is no longer strange to everyone, but the complications of traumatic brain injury such as unconsciousness, loss of consciousness and forgetfulness are called traumatic brain injuries although they are not. there are physical lesions on pathology.
1. Traumatic brain injury
The cause of traumatic brain injury is mainly traffic accidents and occupational accidents. Traumatic brain injury is a condition in which a person has a head injury that damages the skull and other structures inside the skull.
Diseases with manifestations of disruption of high-grade nerve activity such as: Unconsciousness, loss of consciousness and forgetfulness is called traumatic brain injury even though there is no physical damage on pathology.
Traumatic brain injury can occur at any age and the damage caused by the disease has the potential to lead to death for the patient, especially for children.

Chấn thương sọ não có nguy cơ dẫn đến tử vong đối với người bệnh, đặc biệt với trẻ em
2. Injuries caused by traumatic brain injury
Primary injury and secondary injury are the two main injuries caused by traumatic brain injury. In addition, traumatic brain injury also causes some late complications such as epilepsy due to brain scarring.
2.1 Primary lesions Primary lesions that form immediately after traumatic brain injury usually include cranial vault lesions, skull floor fractures, brain contusions, cranial concavity in children, and craniofacial concavity in adults. Specifically:
Skull fracture: Only when the patient is X-rayed can the crack in the brain be detected. However, brain fissures may not require treatment but should be monitored further for progress to another stage of disease. Concave skull in children: Mainly concentrated in young children and infants, the reason is that when children are young, the brain is not yet complete and very fragile. The cranial concavity is mostly noted in the convexity of the parietal bone, and the outer skin is usually intact. In this case, usually the meninges and underlying brain tissue are not damaged. Cranial depression in adults : It is very dangerous and there is a risk of cranial osteomyelitis and meningitis . The reason is that the skull bones are often broken into many pieces that are interlocked. Brain concussion is a very dangerous condition and has a mortality risk of up to 70%. This case occurs mainly due to strong trauma causing injury such as traffic accidents. Contusion state includes damage to brain cells such as necrosis and in cerebral blood vessels such as rupture, contusion, thrombosis leading to cerebral infarction, cerebral hematoma; Blood normally flows into the cerebrospinal fluid. If the contusion spreads deep into the brain, a hematoma can form in the brain tissue, which is a secondary lesion. When an accident occurs, direct damage occurs at the base of the frontal lobe, at the temporal pole, the brain will be crushed due to a strong impact on the ceiling of the orbit and on the small wings of the butterfly chorus. In many cases there will be rapid formation of a subdural hematoma in that area, which is a secondary lesion. Later, around the concussion area, there is obvious cerebral edema and is also a secondary lesion.
Fracture of the skull floor: Usually the craniofacial fissures will spread to the base of the skull. The majority of fractures are usually in the middle layer and involve the stony bones and adjacent cranial nerves such as: nerves III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII; Sometimes cerebrospinal fluid or blood is drained into the outer ear. 2.2 Secondary lesions Secondary lesions are not present immediately after traumatic brain injury, but they develop gradually later including cerebral edema, various types of intracranial hematoma, and other late lesions.
Cerebral edema: A common consequence of all severe traumatic brain injuries, the cause is vascular damage in the blood-brain barrier. The condition is further aggravated when cytotoxicity is caused by disturbances in the exchange of electrolytes between, inside and outside the cell. The brain volume in this case increases, cerebral edema is often severe in the area of the concussion. Therefore, there is one more reason that makes the cranial pressure increase, until this pressure is higher than the systolic blood pressure, the blood supply to the brain decreases, the brain becomes more severe because of ischemia.

Phù não là hậu quả chung của tất cả mọi chấn thương sọ não nặng
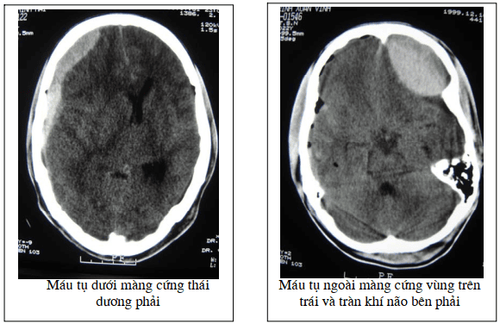
Epidural hematoma: The source of bleeding usually originates from a craniocervical fissure, especially in children, or from a ruptured meningeal artery when trauma causes it to dislodge from the sulcus on the inner surface of the skull. which is still close to the former. In fact, in the total number of cases of traumatic brain injury, there are about 1 to 3% of epidural hematomas, if only the number of severe traumatic brain injuries is about 10% of the cases of hematoma. this. Acute subdural hematoma: Symptoms of an acute subdural hematoma usually appear soon after a head injury. It can be after a few minutes to 24-48 hours. You may be unconscious at the time of the head injury, but this does not always happen. You may have a few hours of alertness after the injury, but then become unwell. You may pass out or go into a coma when the hematoma forms. If you don't faint, you may feel groggy or have a lot of headaches. You may also experience discomfort or vomiting, may be confused, have weakness on one side, and have difficulty speaking. Sometimes convulsions may occur. Chronic subdural hematoma: Symptoms of a chronic subdural hematoma usually don't appear until about two to three weeks after a head injury and, in some people, months after injury. In practice, it is often the injury that is minor or the patient forgets to have had a head injury. More specifically, this disease can occur in older people taking anticoagulants, or people who drink alcohol.
Symptoms tend to increase gradually. Common are loss of appetite, nausea and/or vomiting. Headaches are very common and get worse.
2.3 Other Late Lesions Purulent Meningitis : Bacteria penetrate the cerebrospinal fluid causing the number of neutrophils to increase to hundreds, thousands and later uncountable per mm3. These white blood cells degenerate and pus cells appear. In some cases, surgery is indicated to seal the fistula in the floor of the skull, but it often fails with a high rate. Therefore, antibiotic treatment when the fistula is not sealed will be ineffective, the skull floor will be filled with pus covering the brain stem, which can be fatal. Carotid-cavernous fistula: this is a rare but easy to diagnose complication. In surgical treatment, sometimes it is successful and easy, but there are also some cases where multiple operations can't seal the fistula because the floor of the skull is broken in the middle layer and involves the passage of the internal carotid artery. cavernous sinus and cause a fistula there. Intracranial pressure: In traumatic brain injury, secondary injuries such as cerebral edema, cerebral contusion, and hematoma are new foreign components that appear and compress the other three components, which divide and occupy the intracranial volume and now The ability to self-regulate blood in the brain is also lost. That serious consequence is manifested by symptoms collectively known as acute cranial hypertension syndrome. Two types of symptoms are evident: diminished consciousness and altered vital signs. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.