This is an automatically translated article.
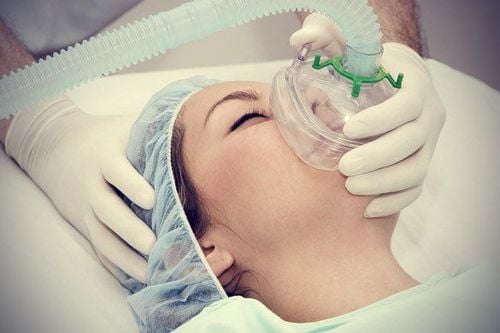
Before some types of surgery, the patient will be given a medicine to help them sleep and not feel pain. This drug is called general anesthetic, given into the patient's body in two ways: intravenous injection and aerosol.
1. Composition of anesthetics
Today, the most common anesthetics are made from a mixture of inhaled gases, including nitrous oxide (N2O or laughing gas) and various ether derivatives such as Isoflurane, sevoflurane, and desflurane.
General anesthetic drugs have two routes into the body:
Inhalation form: Desflurane, Isoflurane, Sevoflurane, Ethyl Ether Intravenous form: Propofol Intravenous drug Propofol has the chemical formula C12H18O. After intravenous injection of Propofol, this drug enters the blood circulation of the whole body and works in the brain, because the brain has a good blood supply. Propofol enters the brain and stimulates GABA receptors (This is an amino acid as well as a neurotransmitter widely distributed in the central nervous system), producing a sedative effect. Propofol affects the central nervous system by drastically reducing gamma-band chains across cell membranes, causing extreme levels of loss of consciousness in patients.
Sevoflurane inhaled drug with the chemical formula C4H3F7O acts mainly at the spinal cord and central nervous system, as well as at GABA receptors. Sevoflurane is a highly fluorinated Ether, commonly used in not-so-long surgeries. This drug is an antagonist acting on glycine receptors (the amino acid neurotransmitter glycine) reducing mitochondrial connectivity, decreasing arterial pressure, and increasing respiratory rate.
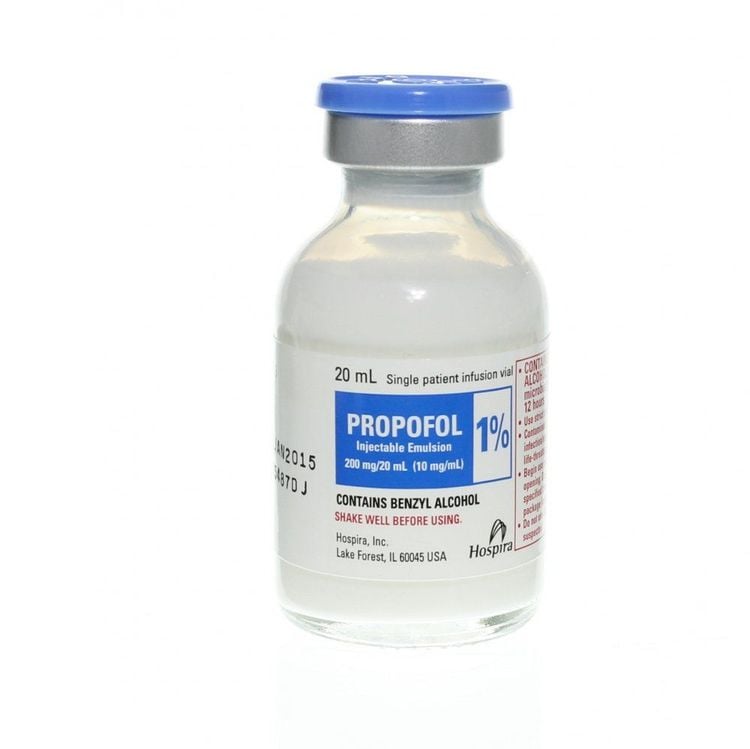
Thuốc mê Propofol dang tiêm tĩnh mạch
2. Why do patients need anesthesia?
The treating doctor will give you the best anesthetic plan for you based on the type of surgery that the medical facility is having, the health status, the disease/injury status and the patient's wishes. For certain medical conditions, the patient will definitely need general anesthesia such as:
The surgery takes a long time Expected to lose a lot of blood Lowering the patient's temperature The surgery has an impact to the airways such as thoracic or upper abdominal surgery Other forms of anesthesia, such as mild sedation combined with local anesthesia (for a small area of the body) or regional anesthesia (for an area) larger areas of the body), may not be suitable for the above conditions.
Thuốc gây mê được dùng trong những ca phẫu thuật kéo dài
3. Side effects of anesthetics
In general, general anesthesia is very safe for most patients, even if the patient has a serious medical condition and can still perform general anesthesia without serious problems.
In fact, the risk of complications is more closely related to the type of surgery a patient needs to have to treat the illness/injury than with the type of anesthetic.
Older adults or people with serious medical problems, especially those with long-term surgery, may have an increased risk of pneumonia or even stroke and heart attack. Specific factors that may increase a patient's risk of complications during surgery with anesthetics include:
Smoking Convulsions Sleep apnea Obesity

Béo phì làm tăng nguy cơ biến chứng
High blood pressure Diabetes Stroke Other conditions related to the heart, lungs, or kidneys Use of medications, such as aspirin, which can increase bleeding History of heavy alcohol use Drug allergies History of allergies with anesthetics
4. The process of using anesthetics
4.1 Before surgery Before the patient is under general anesthesia, the anesthesiologist will talk and may ask some questions about:
Medical history What medications are you currently taking including prescription and Over-the-counter, dietary supplements... Allergies History Have you ever used anesthetics before and had any problems providing the above information accurately will help the anesthesiologist choose Choose the safest anesthetic for the patient.
4.2 During surgery Anesthesiologists usually give anesthetic drugs through a vein in the arm and sometimes the drug is given into the body by aerosol.

Gây mê bằng khí dung
While the patient is asleep, the anesthesiologist can insert a breathing tube into the mouth and push it down to the trachea in the lungs to ensure that the patient receives enough oxygen during surgery, and at the same time protect the patient's lungs during surgery. where blood or other fluids, such as stomach fluid, have leaked into the lungs.
During the surgery, there will be a medical staff to continuously monitor the patient to adjust medication, monitor vital signs, add fluids when necessary. Any problems that occur during surgery are treated with additional medications, fluids, and sometimes blood transfusions.
After surgery
When the surgery is over, the patient will slowly wake up in the operating room or recovery room. Some common side effects may be experienced after the patient wakes up such as:
Nausea Vomiting Dry mouth Sore throat Muscle pain Itching Drowsiness Mild hoarseness

Người bệnh có thể cảm thấy buồn nôn
The medical staff will ask the patient about the pain and side effects that the patient is experiencing. In addition, the side effects that occur depend on the individual's condition and the type of surgery. If side effects are severe, your doctor may give you medication after the procedure to reduce pain and nausea.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article reference source: mayoclinic.org, livescience.com