This is an automatically translated article.
Polycystic kidney disease is a common and relatively dangerous hereditary cystic kidney disease, potentially leading to kidney failure, kidney cancer, but so far there is no specific treatment for polycystic kidney disease.1. Is polycystic kidney disease dangerous?
Polycystic kidney disease is an inherited disease and is divided into 2 types: recessive inheritance (usually onset in adolescence) and dominant inheritance (usually onset in middle age). However, signs of disease onset usually appear in adults between 30 and 40 years old, rarely appear when the patient is young. Therefore, family members with polycystic kidney disease should be screened to assess the risk of disease, thereby guiding marriage and childbearing counseling.
The danger of polycystic kidney disease no longer depends on the time of detection and complications of the disease. Cystic kidney disease can be associated with liver cysts and cardiovascular abnormalities, leading to end-stage renal failure, a very dangerous complication. Therefore, knowing the signs of the disease and knowing how to prevent dangerous complications is extremely important.
2. Signs to recognize polycystic kidney
Polycystic kidney disease is characterized by the presence of many cysts in both kidneys. The initial symptoms are often non-specific, and the disease is discovered incidentally during routine physical examination or abdominal ultrasound. Some patients only show clinical symptoms when the cyst is large and accompanied by complications. Approximately 20-30% of patients with polycystic kidney disease are found to increase with age and size of the cyst. Patients present with pain in the right lower quadrant or pain on both sides of the kidney, dull pain, severe pain. In addition, patients with polycystic kidney also have signs of urinary disorders, may have urinary tract infections upstream, causing painful urination, urinary frequency or blood in urine due to cyst infection or cyst bleeding or stones.
Biểu hiện đau dưới hạ sườn
3. Polycystic kidney causes many dangerous complications
3.1. Kidney failure Dangerous polycystic kidney disease is due to the possibility of progression to kidney failure. This is the most common complication of polycystic kidney disease. The percentage of patients who are able to maintain kidney function (without cyclic dialysis) by age 50 is 78%, by age 70 is 50%. However, many patients can live normally until the age of 80 without detecting the disease, when death is performed autopsies to find out the cause of polycystic kidney.In addition, complications of kidney failure often combine with clinical symptoms such as decreased urine concentration, anemia, and increased uric acid in the blood.
3.2. Kidney and urinary tract infections Kidney and urinary tract infections are often the reason for hospitalization. Urinary tract infections are more common in women. Renal infections are common in patients with renal failure and in patients with normal renal function. In particular, kidney infection complications can be very dangerous, causing septic shock or abscess around the kidney.
3.3. Hemorrhage in the cyst Intracystic hemorrhage causes gross hematuria, occurring in 15-20% of patients with polycystic kidney disease, of which occurs at least once in 30-50% of cases. Gross hematuria usually occurs after trauma, even minor trauma, but can also occur randomly. The proportion of patients with intracystic hemorrhage increases with the degree of renal enlargement. If the longitudinal diameter of the kidney is less than 15 cm, the probability of occurrence is about 14%, if the longitudinal diameter of the kidney is more than 15 cm, the probability of occurrence can reach 43%.
3.4. Hypertension Polycystic kidney disease can lead to high blood pressure and fever, often accompanied by other complications such as infection, kidney stones, kidney failure. Hypertension can occur early, with a complication rate in 13-20% of patients, even in the absence of renal failure.
3.5. Kidney stones Kidney stones often occur in patients with polycystic kidney disease inherited by the dominant gene (accounting for 11-34% of cases). However, most cases of small kidney stones go undiagnosed and go undiagnosed. The rate of kidney stone complications is equal between men and women, in which 50% of patients with kidney stones have no clinical symptoms.
3.6. Kidney cancer Nearly 50% of kidney cancer patients are related to polycystic kidney disease inherited in a dominant gene, mainly renal cell cancer, a few cases of renal papillary cancer. The reason for the high cancer rates in these patients is currently unknown. The diagnosis of kidney cancer in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is usually based on symptoms including: erythrocytosis, low back pain, enlarged kidneys, along with symptoms of bleeding in the cyst. In terms of facilities, CT-scan or renal MRI are the two best methods to help differentiate this complication.
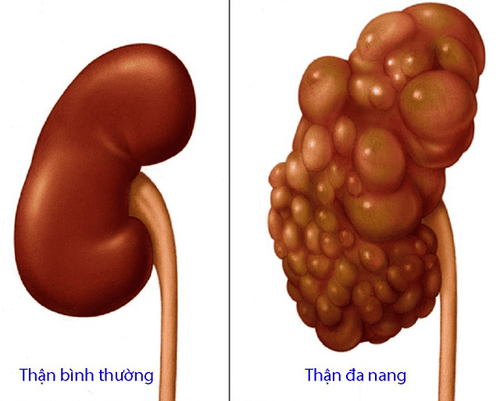
Hình ảnh thận đa nang và thận bình thường
3.7. Effects of polycystic kidney on other organs Liver: About 50% of patients with inherited polycystic kidney disease have cysts in the liver. The incidence of liver cysts usually increases with age, more so in women, but progression to end-stage renal failure in female patients is slower than in male patients. Intracranial aneurysms: When performing cerebral angiography of patients with polycystic kidney disease, about 10 - 30% of patients with intracranial aneurysms are detected. Heart valve abnormalities: Abnormalities in the heart valves appear in 18% of cases of polycystic kidney disease inherited in a dominant gene. Signs of disease in other organs: Cysts can be found in several other organs, especially in the pancreas and spleen, the incidence is 10% and 5%, respectively. Occasionally, cysts are found in the esophagus, ureters, ovaries, and in the brain. However, when cysts appear in the above organs, they generally do not cause clinical symptoms. For patients with polycystic kidney disease, prevention of complications such as recurrent infections, bleeding in renal cysts, and kidney stones to prolong the progression of kidney failure is essential. Patients need to adhere to the treatment schedule and follow-up appointments as scheduled. Besides, it is necessary to pay attention to the diet, add more fruits and vegetables, limit salt, drink a lot of water. When you notice unusual manifestations or signs of severe abdominal pain, it is necessary to promptly seek medical attention.
4. L-FABP test detects the risk of kidney disease early
Early detection of the risk of kidney disease is extremely important, helping to prevent dangerous complications, avoiding affecting health and life. Urine test L-FABP helps to check kidney function, is indicated when the doctor suspects that the patient has renal dysfunction, in addition, it is also used to monitor kidney complications in those patients. patients with diabetes and hypertension.

Với kỹ thuật L-FABP, bệnh nhân chỉ cần lấy nước tiểu xét nghiệm bất cứ lúc nào trong ngày, cho kết quả chính xác chỉ sau 30 phút.
So far, Vinmec Times City is the first medical facility in Vietnam to apply urine L-FABP test according to Japanese technology on a modern automatic AU 680 testing machine, giving quick and accurate results. corpse.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.