This is an automatically translated article.
Iron overload is a disorder of iron storage leading to increased intestinal absorption of iron causing iron deposition and multiple tissue damage. The classic clinical manifestations of iron overload are patients with bronze skin, liver disease, diabetes, joint disease, cardiac conduction disturbances, and hypogonadism.
1. Causes of iron overload in the body
Iron overload is a phenomenon where the amount of iron in the body exceeds the required level. The body's intestines are unable to regulate iron levels unnecessarily, and iron is also accumulated in the liver causing iron infection, and eventually damage to other organs. The amount of iron that people with iron overload absorb is 3 times more than the amount of iron absorbed by people without the disease.
Causes of iron overload are due to:
Genetic mutations: Mutations in the HAMP, HFE HFE2, SLC40A1 and TFR2 genes are responsible for the disease that reduces the control of iron absorption in the digestive process and alters distribution of iron to parts of the body. Excessive iron supplementation: Overdosing on iron due to excessive iron intake. Or due to a large blood transfusion also causes an excess of iron. Acquired iron overload: An opportunistic disease, accompanied by other diseases such as anemia, liver disease, disease related to iron absorption or alcoholism, will suffer from this disease. Symptoms of iron overload include:
Joint pain is the most common symptom of people with iron overload disease. Other early symptoms include weakness, fatigue, weight loss, bronze or darker skin, abdominal pain, and loss of sex drive. Enlarged liver and heart-related diseases are common. Other manifestations include pigmentation (bronze color), diabetes mellitus, joint disease, arrhythmia or heart failure, hypogonadism due to hypogonadism. Typical late signs are increased venous pressure and decompensated cirrhosis. Adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, hypoparathyroidism rarely occur.
2. Complications of iron overload in the body

Khi cơ thể bị quá tải sắt sẽ dẫn đến bệnh Parkinson
Iron overload can cause serious, even life-threatening complications:
Iron overload can cause liver failure, heart failure (stroke) and these are the main causes of death from iron overload. iron load. Heart failure can lead to leg swelling, shortness of breath, limited physical activity, fatigue, rapid heart rate, and nausea. Iron overload damages the pancreas which can lead to diabetes. Excess iron accumulated in the body for a long time will put pressure on the spleen, leading to spleen failure in the long run. Your skin color is changed to bronze or gray. Create favorable conditions for the growth of bacteria. This is also the reason why patients with iron overload also suffer from chronic infectious diseases. Some neurological diseases caused by excess iron such as Parkinson's, Alzheimer's. Iron overload causes fatigue, stress, anger, fear, antisocial and violent behaviors. Erectile dysfunction (impotence), loss of sex drive in men, and absence of menstruation in women are complications of iron overload. For pregnant women, iron overload makes it difficult to transport blood and oxygen from mother to fetus. Babies are born with low birth weight, premature birth, and even death.
3. Diagnosis and treatment of iron overload
3.1. Diagnosis of iron overload
From the above clinical symptoms, the following tests and techniques are usually performed to make the diagnosis:
Serum transferrin saturation test: Measures the amount of iron bound to iron-carrying proteins in the blood. Serum ferritin test: used to measure the amount of iron in the liver. Liver function tests to check for liver damage. Magnetic resonance imaging to determine the degree of iron overload in the liver. Genetic testing: look for HFE mutations if the blood iron test is high. Liver Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken from the liver to test for liver damage.
3.2. Iron overload treatment
Treatment of iron overload is mainly to remove the excess iron. Currently, the following methods are commonly performed such as:
Blood collection: A method of iron chelation is performed continuously by taking venous blood (after venous blood collection, it is necessary to add plenty of water and avoid exercise). exercise within 1 day). This method is evaluated as a safe and effective treatment for iron overload. Initially, the patient had about 470ml of blood drawn, drawn once or twice a week. Then, when the patient's iron levels returned to the normal ratio, blood draws were performed less frequently and subsequently iron chelation was not required. Open vein : This procedure is used when the patient already has liver disease, heart disease and diabetes. Drug treatment of iron overload: Medicines used to treat iron overload can be taken orally such as deferiprone, deferiprox or injected as deferioxamine. However, the ability of each drug to eliminate iron from the body is different.
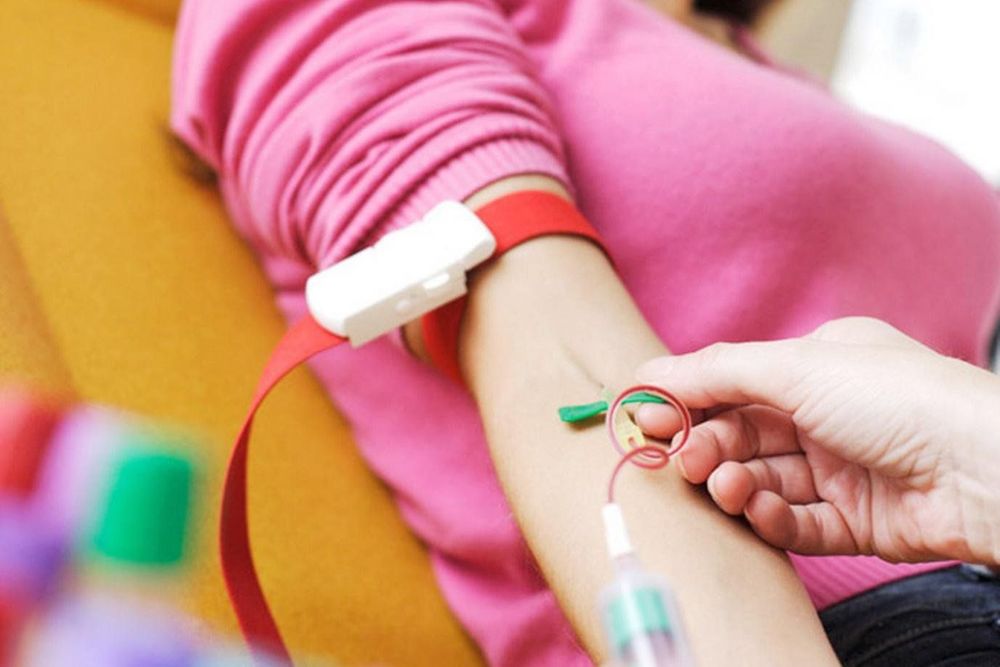
Một trong những cách điều trị việc quá tải sắt là lấy máu
4. Prevention of iron overload
If you are taking iron tablets stop taking iron tablets completely. Stopping iron tablets reduces iron intake. People with excess iron should eat more vegetables. Eat as many vegetables as possible because vegetables with fiber reduce iron absorption relatively effectively. At the same time use foods with diuretic effect to quickly eliminate iron out. For example: vegetables, squash, gourds, purslane, drink green tea, coffee, tea, gotu kola, corn silk juice. As for the protein, you should choose foods low in iron such as goat meat, poultry, pork. Patients should avoid foods rich in iron such as beef, beef jerky, pate, animal organs such as liver, heart, and lungs. Patients with severe or ongoing joint disease, heart disease, elevated liver enzymes, impotence, and diabetes should also be tested for iron overload for early treatment. People who are related by blood to people with iron overload need blood tests to see if they have the disease. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
MORE:
Disorders of iron metabolism in the body How is iron metabolized in the body? Harm if the body has too much iron