This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Diabetes can cause many dangerous complications for the patient's body. One of the complications is an infection. When blood sugar rises, the patient is at risk of repeated infections, which is difficult to treat.
1. What are infectious complications in diabetics? Infection is a common complication in patients with diabetes, the course of the disease is often more severe and complicated than in the general population. An infectious complication is a condition in which a person with diabetes is infected with a certain microorganism, causing mild to severe infections. Often has a persistent or recurrent nature. It is estimated that nearly half of diabetics have at least 1 hospital admission or outpatient treatment for infections.
When having the above infection, if diabetic patients are not detected and treated early, there is a risk of serious development affecting the patient's health and life.
2. Why are people with diabetes prone to infections? The reasons that make patients with diabetes susceptible to infections include:
When you have diabetes, if your blood sugar is not controlled, high sugar levels create favorable conditions for bacteria to grow. Small scratches are favorable conditions for pathogenic bacteria to multiply.

Những vết trầy xước nhỏ khó lành do biến chứng của tiểu đường gây ra
3.1 Urinary tract infection This case is very common, more often in women than in men such as:
Cystitis : Manifestations of mild fever or no fever, painful urination, frequent urination, difficulty urinating. Urine is cloudy, cloudy, and sometimes bloody. However, nearly 90% of cystitis has no symptoms. Therefore, for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to rely on urine tests. Nephritis, pyelonephritis: Hip pain, high fever, chills, cloudy urine or possibly hematuria. 3.2 Lung infections The most common are pneumonia and pulmonary tuberculosis.
Pneumonia: High fever, cough, expectorated sputum that may be bloody, chest pain, shortness of breath... In patients with diabetes, damage to the lung parenchyma is common, easily leading to dangerous complications such as lung abscess. , sepsis . Pulmonary TB: Fatigue, loss of appetite, night sweats, rapid weight loss, mild fever in the afternoon, dry cough that may have persistent sputum or blood, accompanied by chest pain, difficulty breathing... Pulmonary tuberculosis in patients Diabetes is often severe and progresses rapidly, and if left untreated, can lead to exhaustion and death. 3.3 Skin and soft tissue infections Cellulitis: Appears painful red inflammatory patches on the skin, sometimes accompanied by swelling of adjacent lymph nodes. Foot and foot ulcers: Common in the toes, front legs, ankles and soles of the feet. Usually there is wet necrosis, rotten pus with local swelling, redness.
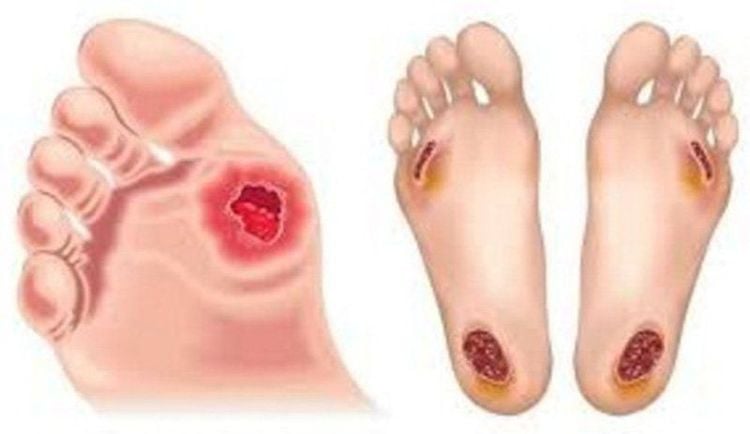
Loét lòng bàn chân có hoại tử là một trong những biến chứng nguy hiểm của tiểu đường gây ra
4. How to prevent infection complications? In order to prevent infectious complications in general, patients need:
Good control of blood sugar and accompanying diseases such as hypertension, dyslipidemia ... by using drugs as prescribed by the doctor, healthy diet and daily exercise. Proper oral hygiene, use soft toothbrushes, regular brushing and avoid causing damage in the oral cavity. Always wear a mask when going out in public. Get a seasonal flu shot every year. Clean the external genitals clean, wash the private area clean after sex, do not hold urine and drink a lot of water. Patients should always keep the skin clean, do not take hot baths (risk of burns due to sensory disturbances) and use mild moisturizing soap; keep skin dry in areas that rub together, such as armpits, groin, between toes; Trim toenails and fingernails regularly. For wounds, it is necessary to wash them with physiological saline or alcohol and bandage the skin scratches and lacerations as soon as they are discovered. Prevention of foot infection complications:
Check your feet daily, if it is difficult to see, use a mirror or ask someone for help. Keep clean, wash your feet every day with warm water: Do not soak your feet in water for too long, avoid too hot or cold, test the temperature of the water first and dry between your toes after washing.

Người bệnh lưu ý, không nên ngâm chân trong nước nóng quá lâu
At Vinmec International General Hospital, we always deploy a screening package for diabetes and dyslipidemia to help detect pre-diabetes early, accurately classify diabetes type, develop a nutritional regimen, monitoring to minimize the risk and complications caused by diabetes.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the national health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.