This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by MSc, BS. Mai Vien Phuong, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalEosinophilic esophagitis is a dangerous disease that, if not treated promptly, will cause many complications such as esophageal stricture, choking on food, perforation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a muscular tube that helps the body push and swallow food from the mouth into the stomach. Esophagitis has several causes: the most common cause is acid reflux, which leads to a burning sensation in the throat, although acid reflux can cause ulcers on the inner lining of the esophagus. Other, rarer causes are viruses (herpes simplex), fungi (candida), drugs (tetracycline), radiation (lung cancer treatment). Eosinophilic esophagitis (VTQDBCAT) is an inflammatory condition in which the wall of the esophagus is infiltrated with large numbers of eosinophils. The hallmark of eosinophilic esophagitis is the presence of large numbers of eosinophils in the tissue underlying the lining of the esophagus.
This disease can cause some of the following complications:
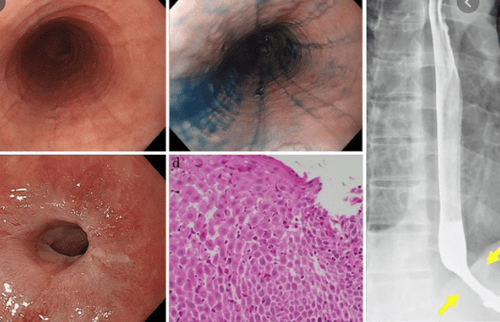
1. Esophageal stenosis/ring
In adults, esophageal stricture lesions are uncommon but can progress to different degrees with two main forms, narrowing at one location or narrowing over a long segment. According to several case series reports, the incidence of focal narrow lesions is <10%. Patients with this complication usually progress slowly and the patient adapts by changing the solid diet to liquid foods and eating them slowly. Treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs such as topical steroids can help reduce fibrosis in the lining and submucosa of the esophagus. Systemic steroids can affect the fibrosis process in the esophageal muscle layer, but they can only be used for a short time because of undesirable effects when used for a long time.2. Choking on food
Sometimes this is the first symptom of the disease and can be of varying degrees. Patients often find themselves choking after swallowing food and try to let the food down by drinking more water, getting up or sitting down, or doing some strenuous movements. In the early stages, when using these methods, the patient can stop choking, but there are a few cases where the patient has to go to the hospital when the food does not come down.One study found that 54% of hospitalized patients with choking were diagnosed with VTQDBCAT. This condition can also occur in patients who have been diagnosed but are not treated and monitored regularly. The mechanism of choking is not fully understood, but it may be due to focal or diffuse narrowing of the esophagus or transient contraction of the esophageal muscularis. This second hypothesis is proposed because in some cases, after removal of food from the esophagus, no actual narrowing site or lesion was found.
3. Esophageal perforation
Esophageal perforation is a rare but possible complication due to the thin and fragile esophageal wall and can range in severity from minor lacerations, perforation due to separation of layers in the esophageal wall, to actual perforation. into the mediastinum. Esophageal perforation into the mediastinum is a very serious complication in patients with this pathology. If diagnosis and treatment are delayed, the mortality rate will be very high. Special attention should be paid to this complication when the patient has swallowed food or is secondary to taking the drug. A study has recorded cases of VTQDBCAT with esophageal perforation due to drugs in which paracetamol is the most common.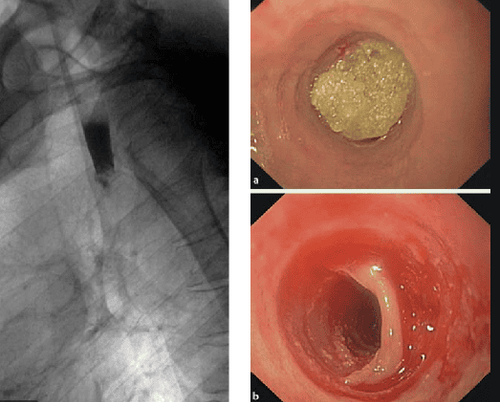
4. Complications related to treatment
In the process of monitoring and treating patients with VTQDBCAT, it is necessary to pay attention to complications related to the use of drugs or procedures. In patients on long-term use of topical steroids, candida and herpes infections have been reported. In patients with indications for endoscopy or endoscopic balloon dilation, attention should be paid to the risk of erosions, esophageal wall separation, or esophageal perforation.5. Malnutrition
Reducing food intake for a long time will lead to malnourishment, the patient will be exhausted, anemic, easy to infection, difficult to heal.
Conclusion: Patients with symptoms of difficulty swallowing, choking, discomfort behind the sternum, should be diagnosed and treated early to avoid the above complications. Counseling patients on pathology and treatment adherence also contributes significantly to the treatment of diseases
Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious address trusted by many patients in performing diagnostic techniques digestive diseases, especially diseases of the esophagus... Along with that, at Vinmec Hospital, the diagnosis of these diseases is made through gastroscopy with an Olympus CV 190 endoscope, which has NBI function (Narrow Banding Imaging - endoscopy with narrow light frequency band) results in clearer mucosal pathological analysis images than conventional endoscopy, detection of vascular lesions, atrophic gastritis , esophagus, early stage gastric and esophageal mucosal lesions. Vinmec Hospital with modern facilities and equipment and a team of experienced experts who are always dedicated in medical examination and treatment, customers can be assured of gastroscopy and esophagoscopy services at Vinmec Hospital. Vinmec International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
ReferencesSchoepfer AM, Gonsalves N, Bussmann C, et al. Esophageal dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis: effectiveness, safety, and impact on the underlying inflammation. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2010;105(5):1062–1070. [PubMed] Jung KW, Gundersen N, Kopacova J, et al. Occurrence of and risk factors for complications after endoscopic dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 2011;73(1):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] Ally M, Dias J, Veerappan G, et al. Safety of dilation in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Diseases of the Esophagus. 2013;26(3):241–245. [PubMed] Dellon ES, Gibbs WB, Rubinas TC, et al. Esophageal dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis: safety and predictors of clinical response and complications. Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 2010;71(4):706–712. [PubMed]