This is an automatically translated article.
Abdominal esophageal foreign body removal is one of the procedures applied when endoscopic intervention fails. Surgery to remove esophageal foreign bodies and resolve complications such as mediastinal abscess, esophageal fistula when endoscopic intervention is no longer indicated. The following is the procedure to guide the removal of esophageal foreign bodies through the abdomen.1. Indications and contraindications
Indications:Abdominal esophageal foreign body removal is indicated when the foreign body in the esophagus is complicated by damage to large blood vessels, mediastinal abscess but endoscopic intervention fails or there is no indication for endoscopy. Contraindications:
There are no absolute contraindications.
2. Prepare for the procedure to remove the esophageal foreign body through the abdomen
2.1. Executor
01 gastroenterology or general surgery surgeon 02 surgical assistants Anesthesia team: 1 anesthesiologist, 1 anesthesiologist assistant Tool kit: 1 instrument, 1 running staff2.2. Patient
Patients are assigned to do tests, diagnose the disease, and assess the overall condition of the disease. Be treated, cared for, nourished, balanced, and improved enough to ensure the expected surgery. Overcoming and balancing disorders caused by the consequences of the disease or due to the patient's physical condition, chronic disease, age, etc. Before surgery to remove esophageal foreign body, the patient and the patient's family are clearly explained by the doctor about the condition as well as the possibility of surgery, complications, complications, and possible sequelae. Fasting, enemas, cleaning the whole body, especially the surgical area to avoid infectious bacterial agents into the lesion.
Người bệnh tiến hành xác xét nghiệm về dị vật thực quản
2.3. Vehicle
To remove the esophageal foreign body, the following means and tools are needed:Major surgery kit Ligasure Ultrasonic knife Surgical only Medicines, fluids, scissors,.....
2.4. Estimated time of surgery
Estimated surgery time is about 90 minutes.3. Steps to take the esophageal foreign body through the abdomen
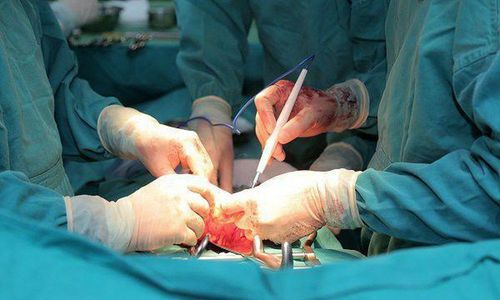
Insert nasogastric tube for the patient if possible. Position of patient with foreign body: Place patient on back with pillow under shoulder if foreign body is in cervical esophagus. The patient should lie on the left side if the foreign body is in the thoracic esophagus. Have the patient lie on his back with a pillow under his back if the foreign body is in the oesophagus. Perform endotracheal anesthesia for the patient and have all equipment and facilities ready in case of atelectasis. Using a scalpel, make an incision along the white line in the middle of the abdomen, from the sternum toward the navel, through the muscle fascia and into the abdominal cavity. Dissection of the abdominal esophagus and stomach bulge, abdominal esophagus. Expose the abdominal esophagus to find foreign bodies, remove esophageal foreign bodies. Use surgical sutures or appropriate tissue to close the esophageal opening. Note, it is possible to suture the lower thoracic esophagus from the abdomen through the diaphragmatic hole to the mediastinum. It is possible to suture the central angle of the gastric aneurysm or add surgery to create an anti-gastroesophageal reflux valve, possibly placing an abdominal drainage. Close the abdominal incision according to the standard.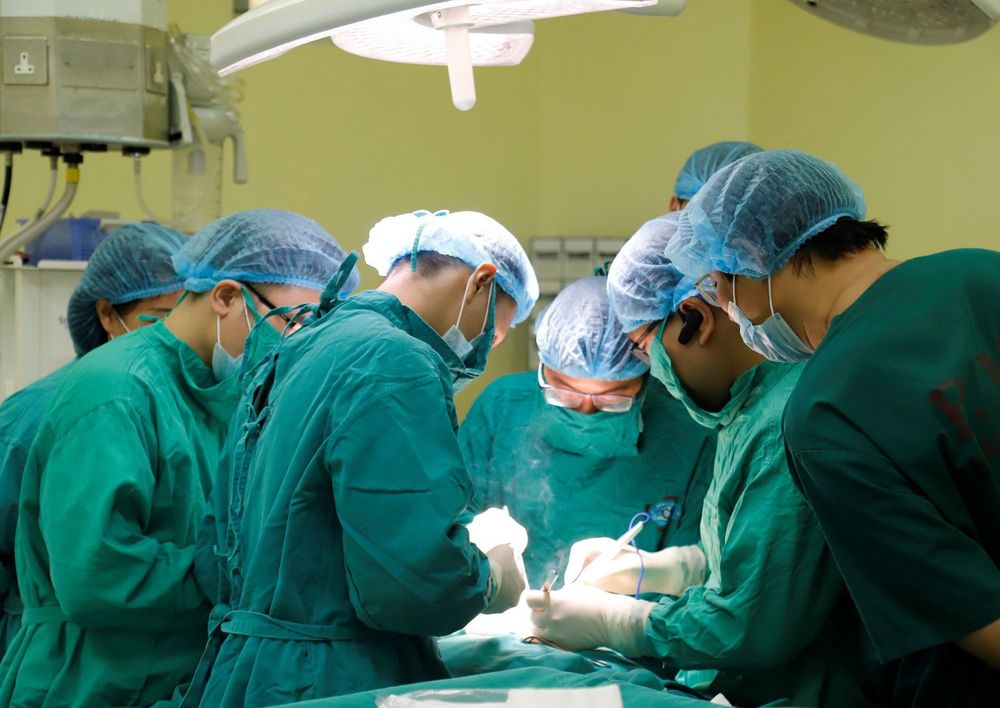
Tiến hành lấy dị vật thực quản qua đường bụng
4. Some complications and principles of management
During or after surgery to remove esophageal foreign bodies through the abdomen, some complications may appear as follows:Bleeding complications: If bleeding is detected at the surgical site or there is anemia. Do exploratory tests to determine if there is bleeding and how much bleeding is present. Treat with conservative treatment or surgical hemostasis. Complications of perforation and re-infection: If perforation and infection are detected at the surgical site or acute infection is present after an esophageal foreign body is removed through the abdomen, definitive investigations should be performed. Manage with conservative treatment, drainage or anti-infective surgery as well as a combination of other appropriate measures. Respiratory complications: If after removing the esophageal foreign body, the patient appears to have respiratory failure, atelectasis, pleural deposits, respiratory obstruction, pneumothorax, it is necessary to identify, find and overcome by cause. Above are the contents guiding the procedure to remove the esophageal foreign body through the abdomen and some complications during and after surgery as well as how to manage. Therefore, if you choke on a foreign object, immediately go to a medical facility for timely treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.