This is an automatically translated article.
Cholesterol is not bad, because the body still needs cholesterol to synthesize hormones, vitamin D and digestive fluids. Cholesterol also creates a metabolic environment for the organs to function smoothly. However, high cholesterol levels cause many dangerous diseases. Therefore, understanding about dyslipidemia and its complications helps us to take early measures to regulate blood fat levels, prevent diseases, ensure quality of life and prolong life in the future.
Complications of dyslipidemia on organ systems are as follows:
1. Cardiovascular system
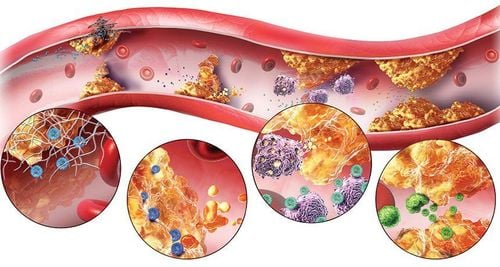
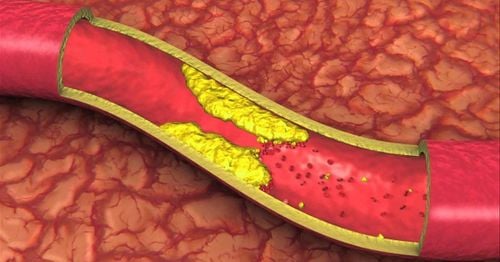
When blood cholesterol levels are too high, they form plaques, which build up on the artery walls. The consequence is on the one hand to block the blood circulation in the vessel lumen, on the one hand to make the vessel wall become stiffer. This condition is commonly known as atherosclerosis. This is the most common and also the most worrisome manifestation of hyperlipoproteinemia.
Arterial damage in any organ will cause symptoms in that organ. If the artery damage in the heart is acute, it will cause a myocardial infarction, the patient suddenly has severe chest pain, sweating, shortness of breath and must be hospitalized. In the case of long-term progression of the blood vessels supplying the heart, the patient often has a significant reduction in exercise capacity, walking or climbing stairs often has chest tightness, requiring sitting to reduce it.
If the artery in the brain is blocked, it will cause cerebral infarction, the patient is admitted to the hospital in the sudden situation of speech, weakness, paralysis of limbs, ... When taken to the hospital to revascularize in time, the brain parenchyma With limited damage, the patient can partially recover organ function. If left late or the area of cerebral infarction is too large, the sequelae will be very heavy, the patient may have a stroke, be bedridden, depend on others for all activities, and reduce the quality of life.
Plaque caused by atherosclerosis can also restrict blood flow to the arteries that supply blood to distant organs such as the legs and feet. This is the basis of peripheral artery disease. Initially, the patient had symptoms of limping, intermittent pain, and had to sit and rest before continuing to move. After that, the distance will gradually shorten, the feet feel cold to the touch, the sensation decreases, the pulse is not seen; More severe is necrosis due to lack of blood supply, sometimes requiring amputation.
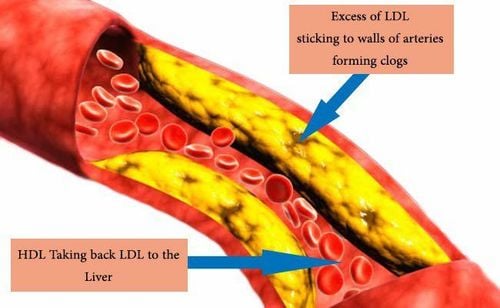
Các mảng xơ vữa tích tụ trên các thành động mạch làm mạch trở nên xơ cứng
2. Endocrine system
Some endocrine glands produce hormones that tell the body to use cholesterol such as estrogen, testosterone and cortisol. So hormone levels in the blood also interact with cholesterol levels.
Indeed, many studies have shown that as estrogen levels increase during a woman's menstrual cycle, HDL cholesterol levels also increase and LDL cholesterol levels decrease. In contrast, as menopause approaches, estrogen levels drop and the amount of unused blood lipids increases. This is why middle-aged women have a similar increased risk of cardiovascular disease as men.
3. Nervous system
Cholesterol is an essential component of the human brain. In fact, the brain contains about 25% of the total body's supply of cholesterol. This fat is essential for the development and protection of nerve cells, allowing the brain to work and control life activities.
Although the body always needs some cholesterol for the brain to function optimally, too much cholesterol can be harmful. Excess cholesterol creates plaque in the artery walls that can lead to stroke, ischemic stroke, leading to memory loss, reduced mobility, difficulty swallowing, difficulty speaking and affecting other functions.
In addition, many studies have also shown a link between high blood cholesterol levels and memory loss and mental function. That's because high blood cholesterol can accelerate the formation of beta-amyloid plaques that cause brain damage in people with Alzheimer's disease.
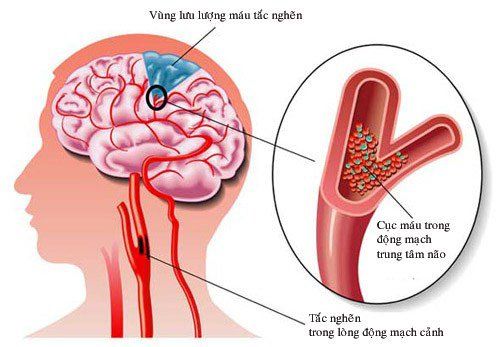
Các mảng xơ vữa trong thành động mạch có thể dẫn đến đột quỵ gây nhồi máu não
4. Digestive system
In the digestive system, cholesterol is the main raw material for the liver to produce bile - a digestive fluid that helps the body break down food and absorb nutrients through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream. However, when there is too much cholesterol in the bile, the excess will promote the formation of crystals, which in the long run will form hard stones in the gallbladder, bile ducts in the liver. As a result, it will cause obstruction, causing the patient to have intermittent cramps or high fever due to infection - poisoning from the biliary tract. Because of the dangerous dyslipidemia complications mentioned above, the treatment of lipid reduction is extremely necessary. A healthy diet and active exercise habits will help people avoid cardiovascular diseases as well as the bad consequences caused by hyperlipidemia.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.