This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Dr. Nguyen Manh Ha - Department of Radiation Therapy - Vinmec Times City International HospitalResearch purpose: "Comparing the dosage parameters of three techniques 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT in controlled breathing radiation therapy (DIBH) for left breast cancer" to select the superior radiotherapy technique. achieve optimal distribution to the therapeutic target while reducing the maximum dose to the surrounding critical organs such as lungs, heart, coronary arteries, ....
A. Make a problem
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women and the leading cause of cancer death in women globally [1]. In developing countries like Vietnam, breast cancer is also the most common disease in women, treatment methods usually include mastectomy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or targeted therapy. Multiple large randomized trials and meta-analyses have shown that radiotherapy after breast cancer surgery improves both local control and overall survival [2].
In breast cancer radiotherapy, groups of lymph nodes, axillary nodes, and/or internal mammary glands are also included in the treatment [3]. Radiation therapy to the chest wall is dosed from two-dimensional tangential photon beams, the lymph node region is irradiated using a direct field from the anterior neck combined with a magnetic field from the posterior axilla.
The 3-way compatible radiotherapy technique (3DCRT-3 Dimention Conformal Radiotherapy) was used in this case. According to the author [4,5], chest wall radiotherapy with such tangential beams will lead to high doses of lung and heart receiving lung cancer, which will increase the incidence of lung cancer on the radiation side, increasing the incidence of lung cancer. morbidity and mortality from cardiac damage, especially in patients with left breast cancer.
Today, with the development of radiotherapy techniques, new techniques are born to reduce high doses to the lungs and heart such as: Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT), radiotherapy Volume Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) combined with controlled breathing by deep inspiration breath hold (DIBH). In particular, VMAT is one of the most advanced radiotherapy techniques today, with the outstanding advantage of being able to modulate the dose rate, gantry rotation speed and the collimator leaves to move continuously during radiation to help achieve coverage of high dose to therapeutic volumes (PTV) while reducing dose to risk organs (OARs) such as the patient's lungs and heart.
In Vietnam, there are very few studies comparing radiotherapy regimens in breast cancer in combination with respiratory control. In order to help doctors and patients (NB) have a basis to choose radiotherapy techniques suitable to the economic and technical conditions of each radiotherapy unit. Therefore, we conducted the study: "Comparison of dose parameters of three techniques 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT in controlled breathing radiation therapy (DIBH) for left breast cancer". From there, select the most superior radiotherapy technique, obtain the optimal distribution to the treatment target and reduce the maximum dose to the surrounding vital organs such as lungs, heart, coronary arteries, etc.
.
B. Research object and method
1. Objects
Data of 20 patients who had surgery on the left breast with indications for radiation therapy for left breast cancer with controlled breathing at the radiation therapy department of Vinmec Times City International Hospital from January 2018 to March 2020. selected for this study. A total of 60 3DCRT, IMRT and VMAT plans were established to compare dose parameters with each other. The plans are made on Eclipse version 13.0 planning system of Varian (USA).2. Research Methods
Descriptive study of dose index.
2.1 Research procedure The patient was assigned to have 4D-DIBH simulation CT scan (combined with DIBH breathing control during the CT scan). Before the simulation, the patient was trained to inhale and hold the breath with a breath-holding cycle of 20 seconds or more. It is important to ensure that the interval between breath-hold amplitudes is stable between inhalations of the open-breath that qualifies the 4D-DIBH simulation for breast cancer (Figure 1).
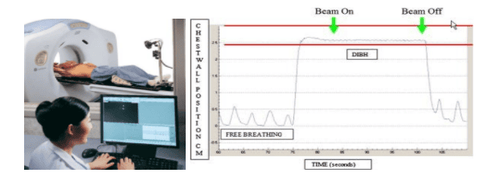
Hình 1. Chu kỳ và biên độ nhín thở trong mô phỏng 4D-DIBH
The patient is placed in a supine position on the breast table (Qfix, USA) made of carbon, with both hands on the head, the body is fixed by a vacuum bag Vacklog, helping to shape the position transparently. treatment session.
The simulation CT scan was performed on GE's optimal 580-16 series CT machine, the image section was selected from the C3 vertebral body to the L2 vertebral body level using a 2.5 mm slice thickness.
The planned volume was determined by contour physicians based on the Radiotherapy Society's Guided Atlas (RTOG) [6]. The PTV consists of the chest wall with pectoralis, anterior, rib, and intercostal muscles and ganglion groups. If the skin is not involved in the tumor, the contour is cut 3mm from the skin surface. Skin is included in case of pathological involvement of the skin.
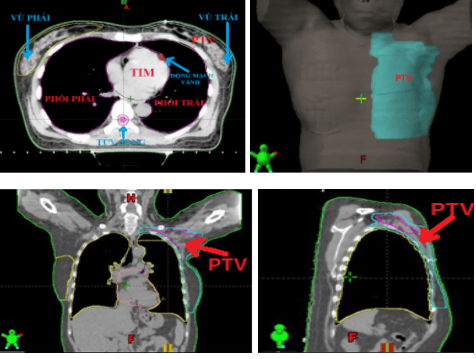
Hình 2. Xác định các thể tích trong lập kế hoạch xạ trị
PTV is marginally opened 5 mm in the medial, anterior, posterior and inferior directions from the CTV. The lateral border of the CTV is taken as the anterior most part of the latissi dorsi. This is almost 1 cm below the mid-axillary line.
Therefore, the PTV must not open the edge in the lateral direction. Organs at risk (OAR) were also identified including: lung, heart, right breast and spinal cord, coronary artery (Coronary atery), humerous head. In addition, contour identification and delineation of individual coronary vessels and its branches is also performed (Figure 2). Indicated dose: 50Gy/25 fractions, 2Gy/day, 5 days/week.
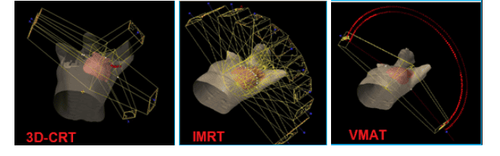
Hình 3. Thiết kế trường chiếu trong 3 kế hoạch: a) 3D-CRT, b) IMRT, c) VMAT
2.2 3D-CRT Plan 3D-CRT plans are set up by us on Eclipse planning software version 13.0 of Varian (USA). The 3D-CRT plans include 5 projection fields with 6 MV photon energy, 600MU/min dose rate, AAA algorithm. In which 2 symmetric diagonal fields for the chest wall (310o and 130o) and 3 projection fields for the lymphatic part around the scapula (310o, 45o, 160o). Customized projection fields avoid spinal cord and minimize lung projection.
2.3 IMRT Plan The IMRT plans we set up include 9 coplanar fields (300°, 330°, 0°, 30°, 60°, 90°, 120°, 120°, 150°, 180°) ), using dynamic MLC technique with 6M photon energy, 600MU/min dose rate, AAA algorithm.
>>> Dose Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
2.4 VMAT Plans The VMAT plans designed in the study consisted of 2 semitones from 300° to 179° clockwise and counterclockwise 179 to 300°. clockwise. The two semitones use a 6M photon energy level, a maximum dose rate of 600 MU/min, and the algorithm is AAA.
>>> Volume Modulated Radiation Therapy (VMAT)
3. Evaluate and compare plans
The plan quality index of all 3 plans 3DCRT, IMRT and VMAT was analyzed using a dose-volumetric (DVH) plot. The DVH histogram represents all dose information in a two-dimensional curve. Coverage of planned volume (PTV) and mean dose to organs of risk (OAR) mean (Dmean) and maximum dose (Dmax), Concordance Index (CI) and index Homogeneity (HI) was analyzed for all plans [7]. For all patients, the total number of MUs per dose fraction and the exposure time for each plan were compared.
Criteria to approve the plan with PTV : At least 95% of the PTV volume received 95% of the indicated dose (47.5Gy) (we chose the criterion for the plans to be 99% of the PTV receiving 95% of the indicated dose). For risk organs (OARs): V20<25% for bilateral lungs, Spinal cord: Dmax<4500 cGy, Heart: V40<30% and dose to right breast, as little as possible. The parameters evaluated for PTV include: CI, HI, D2, D98, D50, CI, HI (according to ICRU83[13]).
The index of relevance (CI) is determined: CI = Vref/VPTV. Where: Vref = receiving dose 47.5 Gy (95% of the indicated dose).
The homogeneity index (HI) is determined: HI= (D2%-D98%)/D50%. In which: D2%, D98% of the dose that 2% and 98% of the treatment volume (PTV) received. D50% of the dose that 50% of the therapeutic volume (PTV) received.
Dose parameters to organs OARs include : Bilateral lung dose (Mean, V5, V10, V20, V30, V40); Dose to the left lung (Mean, V5, V10, V20, V30, V40); Dose to the right breast (Mean); Irrigation dose to Heart (Mean, V20, V30, V40), Dose to coronary (Mean, V20), Dose to humerus cap (Dmean), Dose to spinal cord (Dmax).
All data in this article use SPSS15.0 for statistical analysis. We passed the T-test of paired samples to compare the difference in dosage between the 3 alternatives, the significance level P < 0.05.
C. Results and discussion
The 3D-CRT, IMRT, VMAT plans are all assessed against the plan approval criteria before being compared with each other. The results in Table 1 show that the V95% volume of PTV in the VMAT plan (99.8±0.2%) and IMRT (99.7±0.1%) was better than that of 3DCRT (99.1±0.5%, p<0.01). VMAT had better CI (0.998±0.01), HI (0.094±0.02) than 3DCRT (CI=0.991±0.01; HI=0.116±0.02), and IMRT (CI=0.997±0.01; HI=0.110±0.02) ) (p<0.01).
The average number of MUs of the IMRT plan is the largest (2115±239 MU) compared to that of 3DCRT (550±45MU) and VMAT (565±71 MU). The treatment time of 3DCRT (3.3±0.2 min) and VMAT (3.4±0.1 min) was less than that of IMRT (6.1±0.5 min) (p<0.01).
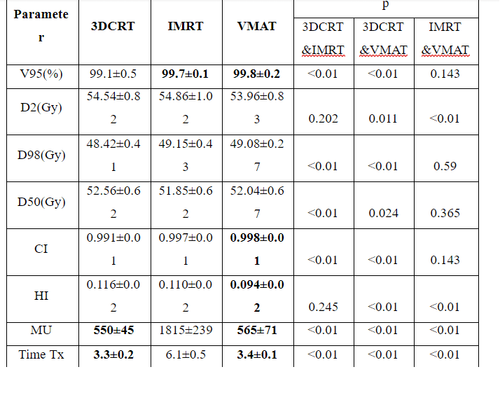
Bảng 1. Thông số liều tới thể tích điều trị PTV
1. Discussion
In our study, the difference in CI between VMAT plan (0.998±0.01) and IMRT (0.997±0.01) versus 3DCRT (0.991±0.01) was statistically significant (p<0.01). The HI score of VMAT (0.094±0.02) was better than that of 3DCRT (0.116±0.02) and IMRT (0.110±0.02) plans (p<0.01). Our study also shows that the coverage rate of V95% of PTV in the VMAT plan is the best (P<0.01), quite similar to the studies of Ma et al. [8]; According to author Liu [9], dose coverage in VMAT plans (97.44±1.21%) was better than IMRT (96.05±0.77%) and 3DCRT (90.22±1.20, p<0.05).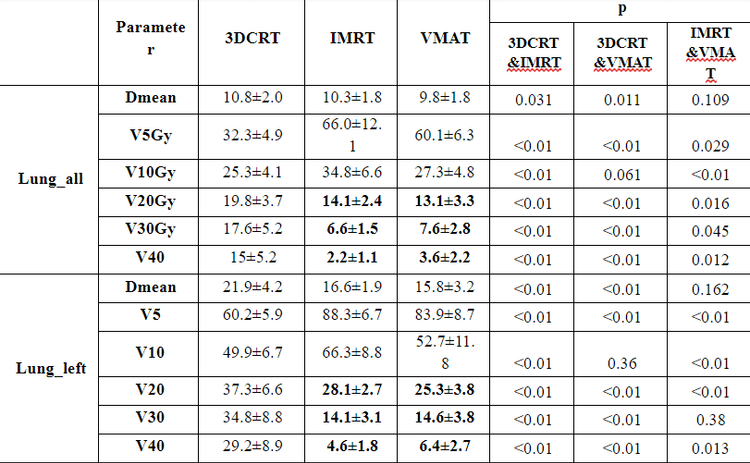
Bảng 2. Thông số liều tới các cơ quan nguy cơ
The CI and HI values of the 3DCRT plan are reduced compared with IMRT, VMAT is explained by the junction between the chest wall projection fields and the upper lymph node groups, which easily leads to dose missed. Figure 5a is the dose-volume histogram (DVH-Dose Volume Histogram) of PTV, showing that the D2% curve of the VMAT plan is the smallest.
In Figure 4 and Figure 5d, it is shown that at V20Gy, V30Gy, V40Gy and mean doses in both lungs and left lung of the IMRT plan, the VMAT is lower than that of the 3DCRT plan which is explained by the number of The radiation field of both IMRT and VMAT is larger, so in the modulation process, avoiding high dose will be better, and at the same time will pass through more volume of healthy tissue, leading to larger V5Gy, V10Gy volume for the plan. 3DCRT. In the left lung, the dose levels V20Gy, V30Gy, V40Gy of 3DCRT (37.3±6.6; 34.8±8.8; 29.2±8.9%) when compared with IMRT (28.1±2.7; 14.1±3.1; 4.6±1.8) were higher, respectively. is 24%, 29%, 86%, and compared with VMAT (25.3±3.8; 14.6±3.8; 6.4±2.7) is 32%, 28%, 78%, respectively. This result is similar in the study of Liu [9], V20Gy, V30Gy of 3DCRT (29.45±2.46; 28.14±1.34) when compared with IMRT (24.46±2.05; 15.95±1.27), respectively, 17% higher, 43% and compared with VMAT (25.41±1.98; 16.17±0.88) higher by 14%, 43%, respectively.
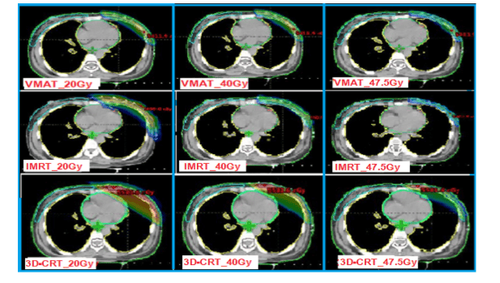
Hình 4. Phân bố liều trên PTV ở 20Gy, 40Gy, 47.5Gy của 3 kỹ thuật xạ trị
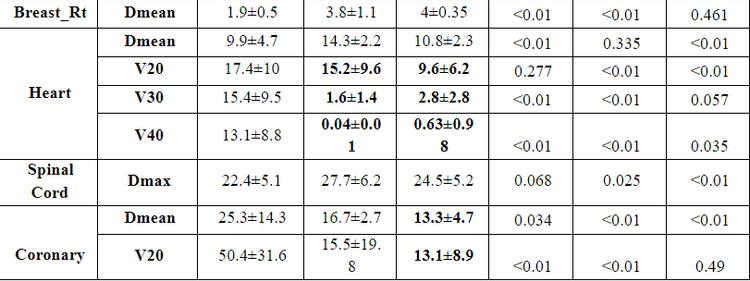
Our study also showed similar results when compared with Liu's report [9], the mean dose to the right breast and heart in the 3DCRT plan (1.9±0.3 and 25.3±14.3) was the smallest when compared. with IMRT (3.8±1.1 and 25.3±14) and VMAT (4±0.35 and 10.8±2.3), which can also be explained by the large number of radiated fields of these two techniques, thus in the modulation of the possible region. much more irradiated area with low dose. This is also a point to improve in the future of radiation therapists in the process of optimizing IMRT, VMAT.
The VMAT and IMRT plan avoids high cardiac doses better than the 3DCRT plan shown on the DVH chart figure 5b. Cardiac high dose levels such as V20Gy, V30Gy, V40Gy of the IMRT plan (15.2±9.6; 1.6±1.4; 0.04±0.01) and VMAT (9.6±6.2; 2.8±2.8; 0.63±0.98) when compared with 3DCRT ( 17.4±10; 15.4±9.5; 13.1±8.8) were reduced by 12%, 92%, 97% and 39%, 82%, and 93%, respectively.
On Figure 5c is a DVH chart showing the dose to the coronary artery in the 3 plans: mean dose (Dmean) and maximum dose (Dmax) of VMAT (13.3±4.7; 17.5±2.6) is the best in comparison. with IMRT (16.7±2.7; 23±2.4) and 3DCRT (25.3±14.3; 23.1±8.7).
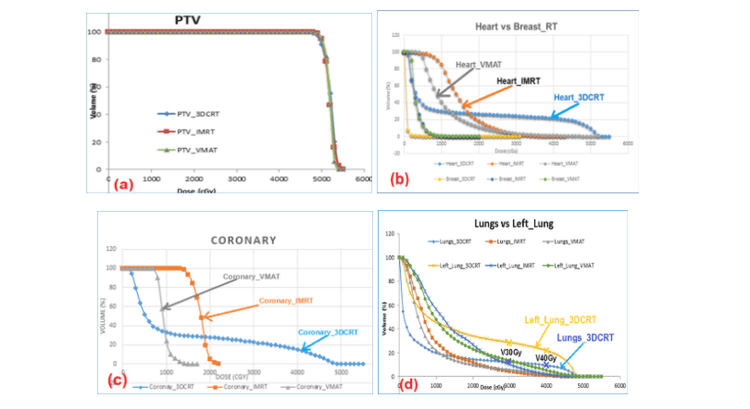
Hình 5. Biểu đồ DVH của PTV và OARs trong kế hoạch 3DCRT, IMRT và VMAT PTV; (b) Heart vs Breast_RT; (c) Coronary; (d) Lungs vs Left_Lung
2. Conclusion The VMAT plans have better index matching, homogeneity, dose-to-volume distribution, and high dose reduction in healthy organs than the 3D-CRT and IMRT plans. VMAT and 3D-CRT plans have less treatment duration and number of MUs than IMRT plan
3. Recommendations IMRT and VMAT radiotherapy techniques have a complex number of fields and intensity modulation due to their complexity. Therefore, strict pre-treatment dosage verification is required. It is necessary to study the breathing amplitude and the distance of the heart to the treatment area to be able to set criteria in the selection of patients for radiotherapy to control breathing.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:
[1] . Available from: http://www.globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_ population.aspx [2015].
[2] . Overgaard M, Nielsen HM. Is the benefit of postmastectomy irradiation limited to patients with four or more positive nodes, as recommended in international consensus reports? A subgroup analysis of the DBCG 82 b&c randomized trials. Radiother Oncol 2007; 82:247-53.
[3] . McGale P, Taylor C, Correa C, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet 2014;3 83:2127-35.
[4] . Zablotska LB, Neugut AI. Lung carcinoma after radiation therapy in women treated with lumpectomy or mastectomy for primary breast carcinoma. Cancer 2003; 97:1404-11.
[5] . Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P, et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2013; 368:987-98.
[6] . Guideline contouring: breast cancer atlas for radiation therapy planning (RTOG).
[7]. Van't Riet A, (1997): A conformation number to quantify the degree of conformality in brachytherapy and external beam irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 37, 731-6.
[8] . Ma C, Zhang W, Lu J, et al. Dosimetric comparison and evaluation of three radiotherapy techniques for .... Sci Rep 2015; 5:12274.
[9] . Haiyun Liu, Xinde Chen, et al. Evaluation of 3D-CRT, IMRT and VMAT radiotherapy plans for left breast cancer based on clinical dosimetric study, Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics (2016).
[ten] . Christer Andre Jensen, et al. Robustness of VMAT and 3DCRT plans towards setup errors in radiation therapy of locally advanced left-sided breast cancer with DIBH. Physica Medica (2018).
[11] . Swamy ST, Radha CA, et al. Feasibility study of DIBH based VMAT for left Breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014; 15:9033-8.
[twelfth] . Shyama P, et al. Comparison of dosimetric parameters of VMAT and 3DCRT in breast carcinoma, Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics 2016; 1005:1009.