This is an automatically translated article.
Sepsis or sepsis is a serious systemic disease, threatening the life of the patient. Clinical manifestations of sepsis are quite diverse because it affects many organs in the body.
Diagnosis of the disease requires many tests for sepsis , in which blood culture test is the gold standard. A positive blood culture test result allows for the conclusion that the patient is suffering from sepsis. However, the positive rate of blood culture tests is not high and inconsistent among laboratories. Therefore, a negative blood culture test cannot rule out sepsis.
1. Learn about bacteremia
Sepsis is a serious disease that threatens the life of the patient. It is a systemic infection caused by the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the bloodstream, causing impairment of the function of various organs in the body. Disease-causing microorganisms can originate from infections from organs in the body that are not well controlled, so they spread into the blood or microorganisms when entering the body directly attack the blood, multiply and develop. and carried by the blood to other organs in the body. Patients are therefore vulnerable to multiple organ failure and septic shock, which can eventually lead to death. Clinical manifestations of multi-organ failure are:
Acute respiratory failure or ARDS syndrome (English name is Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome); Acute liver failure ; Acute renal failure ; Myocardial necrosis; Coagulation dysfunction, internal bleeding; Necrosis of organs such as liver, kidneys, intestines.
Tình trạng suy hô hấp cấp
Besides sepsis, another medical condition that is often mentioned is bacteremia. Bacteremia is defined when there is evidence of the presence of bacteria in the patient's blood, such as a positive blood culture test, but no clinical manifestations.
According to data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (the English name is Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), every year there are more than 20,000 cases of bacteremia patients over 65 years old. memory . Sepsis is believed to be the 11th leading cause of death.
Certain people are considered at risk for sepsis to be aware of, including those with underactive immune systems, susceptible to pathogenic microorganisms or those with infectious diseases heavy in the organs. Some cases are listed as follows:
Infants, young children; Elder; People with weakened immune systems such as HIV/AIDS patients; Patients with long-term chronic diseases such as diabetes, malignancy, using immunosuppressive drugs, anti-rejection drugs continuously for a long time; People with acute infectious diseases: Pneumonia patients have a 12% risk of bacteremia, urinary tract infections have a 17% risk of bacteremia, while the risk of bacteremia of patients infected with intra-abdominal viscera about 5%; Acute osteomyelitis; Widespread cellulitis; Patients have to undergo major surgery, stay in one position for a long time; People carrying many instruments that can penetrate the body such as endotracheal tubes, urinary catheters, and gastric tubes.
Người có hệ miễn dịch suy giảm
2. Test for bacteremia
Sepsis is a serious disease with diverse and critical clinical manifestations, however, the definitive diagnosis of a case of sepsis should be based on laboratory tests. Some basic bacteremia tests commonly used in clinical practice are:
Blood culture test; Peripheral blood cell analysis; Quantification of inflammatory markers such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (VS), CRP, procalcitonin; Quantification of blood lactate levels; Test kidney and liver function; Tests to assess liver and kidney function.
Xét nghiệm cấy máu được sử dụng
In which, blood culture test is the gold standard for diagnosing sepsis. The patient's blood should be drawn at the time of high fever or chills, before antibiotics are administered. However, that does not mean that the appointment of antibiotics is delayed in severe cases. In case the patient has been treated with antibiotics, and wants to have blood taken for blood culture test, antibiotics need to be stopped for at least 24 hours. Blood samples taken for testing are venous blood, the process of taking samples should ensure absolute sterility to avoid contamination of bacteria from the environment or surrounding items. The amount of blood required for each blood culture test is about 20 to 30 ml. Obtaining the necessary blood volume plays a role in increasing the detection rate of pathogenic microorganisms. In addition to blood, a case of suspected sepsis should be taken from the primary infection sites such as respiratory fluid, pus, and urine for testing for bacteria. The result of blood culture and patient culture being positive for the same pathogen increases the accuracy of the test. Blood culture test, in addition to helping to identify pathogenic microorganisms, also supports the implementation of antibiogram tests, finding out which antibiotics the bacteria are sensitive to, which should help increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Currently, the emergency dialysis technique for multi-organ failure patients is being applied at Vinmec International General Hospital. With a system of modern machinery and a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors and nurses, Vinmec is committed to the best protection for patients' health.
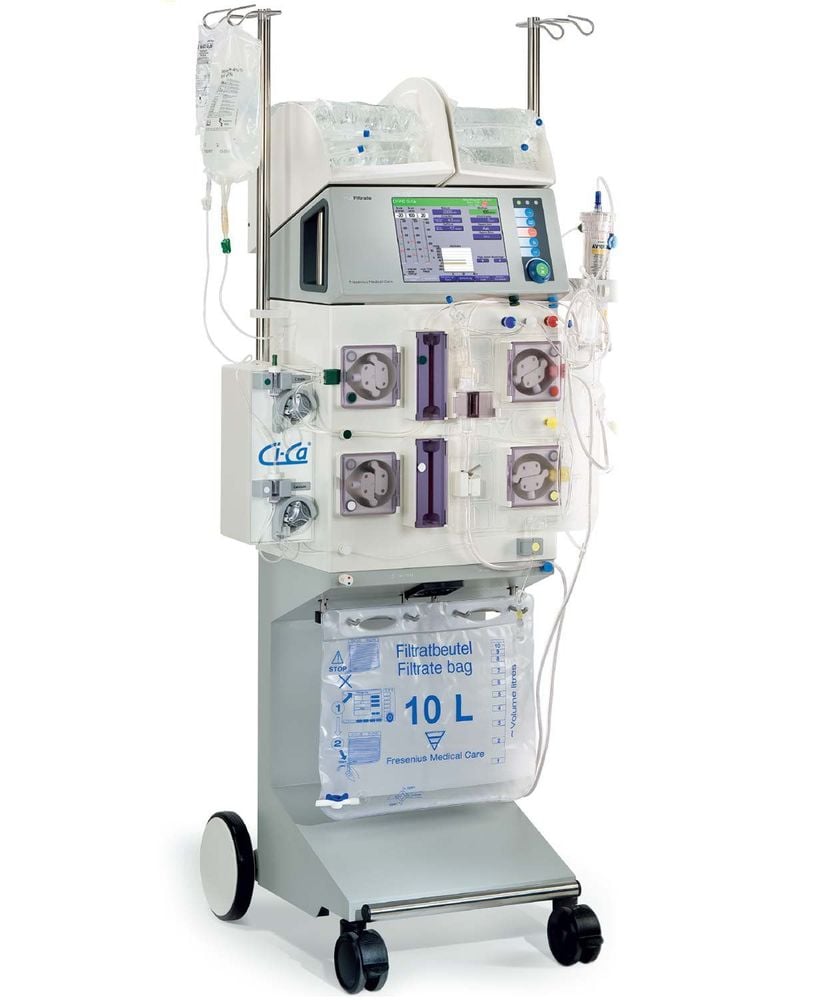
Máy lọc máu liên tục multiFiltrate tại Bệnh viện Vinmec
Vinmec uses a modern, new, multi-featured machine system. Fresenius multiFiltrate continuous dialysis machine with many outstanding advantages. The team of doctors and nurses are skilled people, have experienced technical mastery and have been trained in this technique very intensively, have a lot of experience in handling critical patient cases, support and coordinate with departments in the hospital to treat severe and complicated patient cases.
Customers who need medical examination and treatment at Vinmec Health System can go directly to facilities nationwide or contact to book an appointment online HERE.
MORE:
What is sepsis? Stages of sepsis Sepsis: Dangerous, silent symptoms