This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master. BSCK II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Gastrointestinal bleeding is a dangerous condition that can be life-threatening if not detected and treated promptly. Gastrointestinal bleeding is divided into upper gastrointestinal bleeding and lower gastrointestinal bleeding, of which the upper gastrointestinal bleeding is more common.
1. What is gastrointestinal bleeding?
Gastrointestinal bleeding is bleeding out of the blood vessels into the gastrointestinal tract. It is eliminated from the gastrointestinal tract by vomiting or passing blood or black stools. Bleeding can result from many different causes, each of which has a different treatment. There are causes of acute gastrointestinal bleeding, requiring emergency treatment if left untreated, can be life-threatening.
Xuất huyết tiêu hóa
2. Classification and causes of gastrointestinal bleeding
Based on the location of bleeding, it is divided into upper gastrointestinal bleeding and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Common causes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding and lower gastrointestinal bleeding include:Coagulation disorders: thrombocytopenia, hemophilia
Liver function impairment Vitamin K deficiency Taking anticoagulants Dengue fever 2.1 Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is bleeding from the esophagus to the upper part of the ligament of Treitz.
Causes of upper gastrointestinal bleeding:
Esophageal bleeding: The main cause is portal hypertension, causing esophageal varices, causing sudden rupture of esophageal veins. There are also other causes such as esophageal ulcers, HC Mallory weiss... Gastro-duodenal bleeding: Mainly due to gastric and duodenal ulcers. Gastric ulcers are often in the small curvature, the cardia, and the back of the stomach. The rate of bleeding in peptic ulcers is 15-16%. Duodenal ulcers are rarer, usually located in the duodenal bulb. The rate of duodenal ulcer with bleeding complications is 25%. Other causes such as stomach cancer, polyps of the stomach and duodenum. 2.2 Lower gastrointestinal bleeding Lower gastrointestinal bleeding is from below the ligament of Treitz down to the anus.
Causes of lower gastrointestinal bleeding:
Bleeding in the small intestine: There are many diseases that lead to gastrointestinal bleeding in the small intestine, including some common clinical diseases such as intestinal tuberculosis, intussusception, small bowel tumors, necrotizing enterocolitis... However, bleeding from the small intestine is rarer.
Colonic bleeding: It is the main cause of lower gastrointestinal bleeding.
Ulcerative colitis Crohn's disease Bacillary dysentery or amoebic dysentery Bleeding colon diverticulum Colorectal cancer Hemorrhoids cause bleeding, mainly fresh blood, which may flow as rays or drops. Colon polyps, often bleeding intermittently Anal fissure.
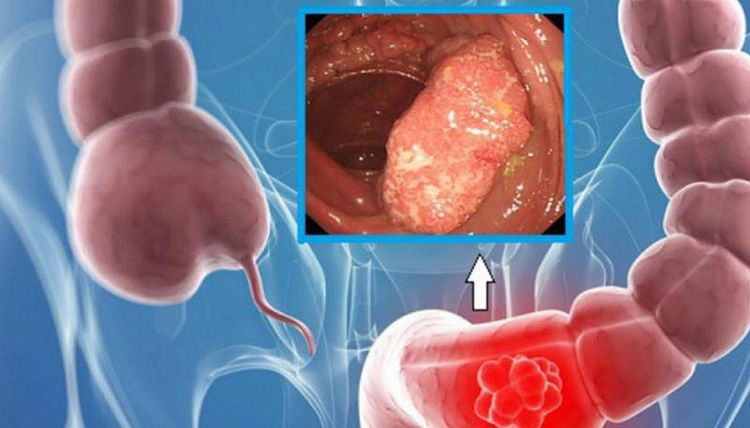
Xuất huyết tiêu hóa dưới do ung thư đại trực tràng
3. Symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding
3.1 Symptoms of upper gastrointestinal bleeding Vomiting blood Properties: The color can be red blood, clotted blood, black blood, in addition, it can be mixed with food. Quantity: Depending on the cause of bleeding, the number can vary from little to a lot. It is necessary to pay attention to the stool to know whether vomiting blood is really or because of eating blood pudding, coughing up blood, nosebleeds... Black stools: In many cases, there are no signs of vomiting blood, but the stools are black. . With the characteristics of black stools like coffee grounds, pungent smell. The nature of the stool depends on the transit time in the intestine and the amount of bleeding. In case of heavy bleeding, stools are usually thin, with red water mixed in. In case of small bleeding, stools are still molded, black like tar, sticky, with a pungent smell. Differentiate from the case of black stools due to the use of drugs such as iron, bismuth... Signs of blood loss: Depending on the amount of blood loss, the symptoms of blood loss range from mild to severe. In case of blood loss, many patients can go to a state of blood loss shock such as: dizziness, dizziness, thirst, oliguria, blue skin, viscous mucous membranes, fast and small pulse difficult to catch, low blood pressure. More seriously, the patient may fall into a state of fatigue, lethargy or coma. In case of small amount of blood loss: Patients may have no symptoms or have symptoms such as dizziness, headache. Other manifestations depend on the cause of the disease: In the case of esophageal bleeding due to esophageal varices, patients often have previous manifestations of portal hypertension such as: Jaundice, collateral circulation , fatigue... Due to peptic ulcer: Epigastric pain, vomiting, nausea, belching, heartburn, with a previous history of gastrointestinal disease. If due to malignant causes: The patient finds that the person is very tired, eats it quickly, loses weight for no apparent reason. Approximately 80% of patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding present with fever. Most of the cases of upper gastrointestinal bleeding lost a lot of blood, causing hemodynamic disturbances. Therefore, it is necessary to be treated quickly and find the location and cause of bleeding to take measures to treat the cause. 3.2 Symptoms of lower gastrointestinal bleeding Bright red blood in the stool: Blood may be mixed in the stool or after the stool. Black stools: If the bowel movement is enough, the stools will be black, possibly with blood. However, some cases of severe upper gastrointestinal bleeding also cause red blood in the stool. It is necessary to distinguish clearly, often to distinguish in cases where there is an indication for a nasogastric tube placement. Signs of blood loss: Depending on the amount of blood lost, the manifestations are different, mild, no symptoms, more severe symptoms such as dizziness, dizziness, thirst, oliguria, blue skin, etc. viscous mucosa, small fast pulse difficult to catch, low blood pressure; Very heavy, struggling, lethargic, comatose.
Đi ngoài ra máu là triệu chứng xuất huyết tiêu hóa dưới
Due to ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease causes abdominal pain, digestive disorders. Due to dysentery: If it is bacillus or gawoj in children with fever, frequent loose stools, with blood. Amoebic dysentery, abdominal pain, straining, bloody stools. Colon cancer: Diarrhea or bloody fish, thin stools, accompanied by unexplained weight loss, fatigue. Due to anal disease: Hemorrhoids bleed fresh, can flow into rays and hemorrhoids protrude. Anal fissure: Pain when defecating, bleeding after defecation, especially when constipated. The manifestations of lower gastrointestinal bleeding in about 80% of cases can be self-limited. However, it is still necessary to find the source of the bleeding for treatment. The above are possible symptoms of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Gastrointestinal bleeding needs to find out the location of the bleeding and the cause so that appropriate treatment measures can be taken.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.