This is an automatically translated article.
Sickle cell disease is one of the diseases with a high risk of serious consequences in people with the disease, especially young children and infants. So far, there is no cure for the disease, only methods to relieve pain and prevent the disease from getting worse. Therefore, early sickle cell testing is essential.
1. What is sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder that affects the red blood cells in the blood.
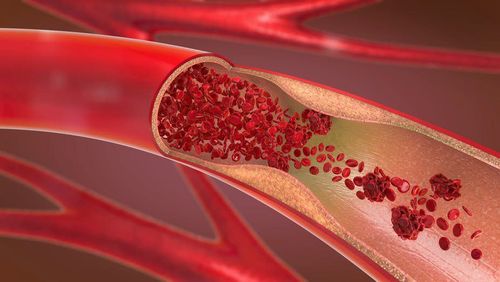
In normal people, red blood cells are round and have the ability to move flexibly in blood vessels with the task of carrying oxygen to other parts of the body. In people with sickle cell disease, their red blood cells take on a sickle-like shape and become sticky and stiff.
Abnormal shape of red blood cells makes it harder for cells to move through the blood vessels, slowing down and even blocking the flow of oxygen and blood to other organs. This damages tissues and organs by not getting enough oxygen and blood.
Sickle cell disease is a chronic disease that follows the patient for life and varies in severity.
Hồng cầu hình tròn có khả năng di chuyển linh hoạt hơn
2. What is a sickle cell test?
What is a sickle cell test? The sickle cell test is actually a type of blood test conducted with the purpose of checking for the sickle cell gene and diagnosing sickle cell disease.
Currently, the best method of diagnosing sickle cell disease is sickle cell testing through high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Through this test, the presence of pigments can be determined.
To strengthen and improve the reliability and accuracy of HPLC, the doctor may order genetic testing.
3. Indication for sickle cell test
Sickle cell testing is usually ordered in the following cases:
Diagnosis of sickle cell disease Sickle cell genetic screening and screening People at high risk for sickle cell disease, especially especially newborns Couples who are planning to have children but are at risk of carrying the sickle cell gene.
4. How is the sickle cell test done?
In order for the sickle cell test result to be accurate, if the patient has undergone a blood transfusion within the last 4 months, be sure to inform the doctor because this may affect the results. fruit.
The specimen used in the sickle cell test is usually venous blood or blood from the heel.

Sử dụng máu từ gót chân để xét nghiệm cho trẻ
4.1 Venous Blood The procedure for drawing venous blood in the sickle cell test is similar to that in other blood tests.
Tie the upper arm with an elastic band to stop the flow of blood, making the vein larger for easier collection; The blood collection site is disinfected with medical alcohol; The doctor inserts a needle into the vein and takes a sufficient amount of blood; Remove the bandage and withdraw the needle, then place a cotton ball or gauze pad over the site of blood collection. 4.2 Heel Blood Heel blood collection is usually done in neonates.
Clean the baby's heel before taking the blood; Use a small needle and gently poke the heel to get the blood out; Collect a few drops of blood on a special piece of paper; After taking the required amount of blood, use a small bandage to stick on the baby's heel where the blood is drawn.
5. Clinical significance of sickle cell test index
The sickle cell test returned to the patient can give results in 2 forms:
Normal: the person's hemoglobin is completely normal. Abnormal: hemoglobin has a certain abnormality. If a carrier carries the sickle cell gene, more than half of the hemoglobin is considered normal (hemoglobin A), otherwise less than half is abnormal (hemoglobin S).
For infants, the sickle cell test can be repeated at 6 months of age because infants under 6 months of age may give false negative results due to high levels of hemoglobin F in their blood. (fetal hemoglobin). Under certain circumstances, DNA genetic information testing may also be indicated.

Xét nghiệm tế bào hình liềm được chỉ định với trẻ từ 6 tháng trở lên
6. Some possible risks of sickle cell test
Sickle cell blood collection is very rarely problematic. The most common problem may be a small bruise at the site of the blood draw. However, the condition can be resolved by applying pressure to the area for a few minutes and will quickly disappear without serious effects.
In rare cases, phlebitis may be experienced, which means that a vein becomes swollen after blood is drawn.
In infants with bleeding-related problems may bleed more than usual. These problems will be detected during a sickle cell test.
According to research, patients with sickle cell disease often have a low life expectancy, about 40 years old. Early detection and proper medical care can help prevent disease progression and prolong life. Therefore, people should immediately go to reputable medical facilities to conduct a sickle cell test as soon as possible.
Vinmec International General Hospital owns advanced and modern equipment to bring the fastest and most accurate results to patients. A team of experienced and highly qualified medical doctors help the process of diagnosis and treatment to achieve the best results.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.