This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Huy Binh - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.1. What is a perforated stomach ulcer?
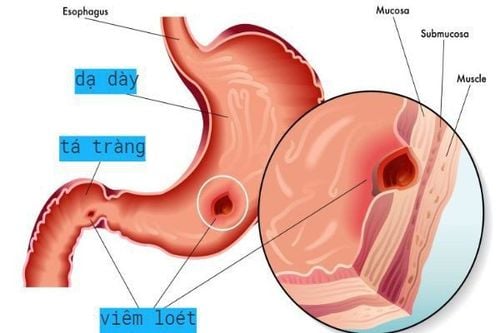
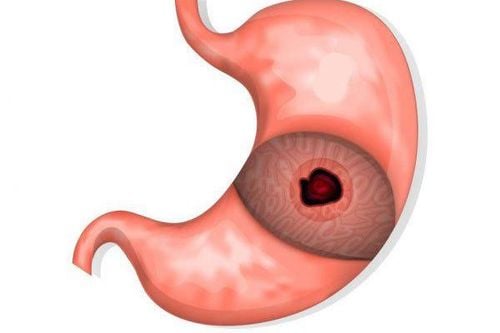
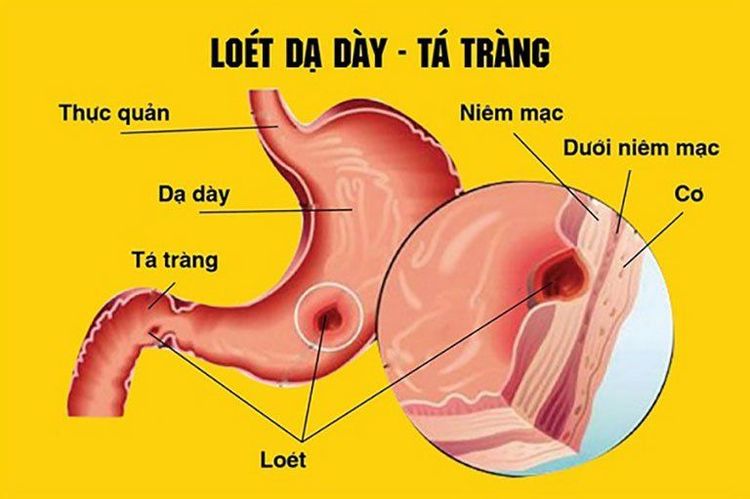
Gastric ulcers are lesions from the mucosal layer, through the muscularis mucosa to the muscle layer. Perforation of an ulcer is when an ulcerative lesion in the muscle layer continues to penetrate the serosa.Perforation peptic ulcer is common mainly in 1 hole, very rarely 2 or more perforations. Perforation is common on the base of a fibrous ulcer, which can be in a young ulcer or a perforation of a gastric tumor. Most of the perforations are in the anterior aspect of the duodenal bulb or the small curvature of the stomach, and the posterior perforation is less common.
But if the perforation is posterior to the duodenal bulb, the perforation is usually blocked by the pancreas and adjacent viscera. In the duodenum, the perforation is usually less than 1 cm. In the stomach, the perforation is usually larger, from 2-2.5 cm.
2. Causes of gastric ulcer perforation
Chronic peptic ulcer: This is the most common cause of gastrointestinal perforation Gastric cancer: less common, has a high postoperative mortality rate, gastric perforation is a manifestation. Late gastric cancer Perforation due to ulceration of the anastomosis after gastrectomy or gastrojejunostomy, this is a rare complication.3. Clinical symptoms of peptic ulcer perforation disease
3.1 Functional symptoms Sudden and severe abdominal pain: The patient feels a sudden sharp stabbing pain in the epigastrium, the pain may occur when the patient is working or lying down, the pain makes the patient unable to relax. dare to breathe. The pain then spread throughout the abdomen, the pain was continuous, the patient never felt comfortable, pain spread to the shoulder, chest, back. Vomiting: Not a specific symptom, usually in the early stage, the patient has no symptoms of vomiting, only when there is bleeding or in the late stage, vomiting when there is paralytic ileus. Constipation, defecation: This symptom is encountered in most cases, but when detected, it is too late and has little value.
4. Subclinical symptoms of peptic ulcer perforation
X-ray: Abdominal scan without standing position shows crescent below the diaphragm on one or both sides. If not clear, can be taken after gastric inflation (must rule out intestinal obstruction) Ultrasound: Abdominal fluid low Blood test: WBC increased , formula turned left, may show signs of acute blood loss In case the laboratory test is not clear, it is possible to conduct an abdominal puncture to diagnose: the abdomen has non-coagulated blood fluid.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.