This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.The BIRADS classification aims to standardize the diagnosis, predict the risk of malignancy, and help have an appropriate management attitude. Combined ultrasonography after mammogram is always necessary in difficult to see lesions on the background of dense breasts that are easy to miss.
1. What is BIRADS?
BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) is a system that classifies mammography results according to a score from 0 to 5 as follows:0 - The information is not enough to be conclusive. 1 - Nothing out of the ordinary. You should continue to check periodically. 2 - Detects a benign cyst (which is a tumor but not a cancer). You should continue to check periodically. 3 - Detected abnormality but not necessarily cancer. A mammogram should be performed within the next 6 months. 4 - Detecting risk factors for cancer. Your doctor may perform a biopsy to confirm. 5 - Detecting a high risk of cancer occurring. You need a biopsy to confirm.
2. What is mammary gland?
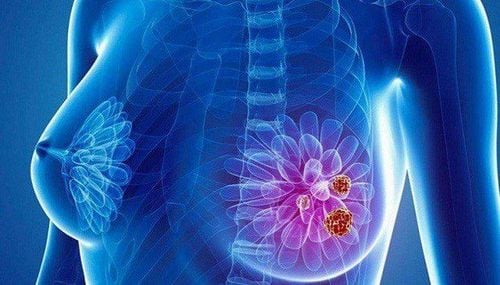
The mammary gland is made up of many lobules, each of which has a lobular duct, which gradually divides until the final point is the milk glands. Each lobule has 3 to 100 milk glands. The lobes are not evenly distributed, but are concentrated in the upper 1⁄4 of the breast. This is the area that contains more breast tissue, so it is more prone to cancer.Breast cancer is a malignant form of cancer. A y mass can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Most cancers start in the milk ducts, with a small percentage developing in the milk sacs or lobules.
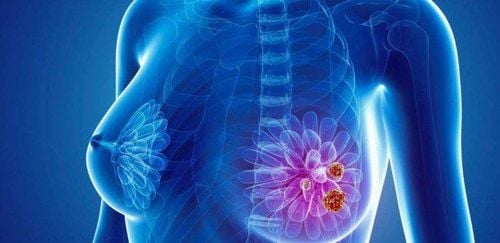
3. Diseases related to the mammary gland
3.1 Fibroids of the mammary gland Fibroids are a common benign tumor of the mammary gland. Round, smooth, easily mobile lump in the breast tissue, usually located near the nipple but can also appear in many other places on the breast.Women with fibrocystic breasts often experience pain, burning, swelling, and sensitivity in the breast area. These symptoms increase during menstruation and gradually decrease as the date of menstruation is further away. The patient only accidentally discovered when touching the chest, a painless tumor, which did not affect daily activities. The disease occurs more often in young women, under the age of 50.
3.2 Mammary gland papilloma A mammary gland papilloma is a breast tumor located in the epithelial tissue of the mammary gland. The tumor is formed from squamous epithelial cells in the lumen of the main duct. Patients present with discharge from one breast to the touch, colorless, bloody or brownish-green discharge. Patients must have regular tests to differentiate with breast cancer.
Tests for the diagnosis and prognosis of mammary gland papillomatosis include nipple discharge and mammography. After the diagnosis of the disease, the indicated treatment is resection of the tumor.
3.3 Fibrocystic breast disease Cystic fibrosis of the breast is a disease occurring in the ductal system of the lobes and lobules of the mammary gland. The disease occurs mainly in the age group 35-45, with prominent clinical symptoms such as pain, discomfort in the mammary glands, increased sensation during menstruation. In some cases, the patient feels so much pain that he cannot wear a bra and dare not touch it. Lesions appear on both breasts. Cysts are formed from lobular and lobular ducts of milk ducts, within each cyst containing exudate and extruded epithelial cells.
Cystic fibrosis of the breast may increase the risk of breast cancer, especially for those with a family history of breast cancer and a biopsy showing atypical hyperplasia.
3.4 Dilatation of the ducts. The disease occurs mainly in women who have had many children and have had a long parenting period. Accordingly, after many years of breastfeeding, the main ducts of the milk ducts will be dilated, filled with milky fluid, these fluids will thicken, and an inflammatory reaction will appear around the dilated ducts.
Patients often have symptoms of white or yellow nipple discharge. Touching the breast, there is a hard band forming strings just below the areola, radiating a few centimeters outside.
Diagnostic criteria are ultrasound of the mammary gland showing dilated milk ducts and aspiration biopsy of the mammary gland showing milky fluid. At mild level, the patient is assigned infrared radiation, hot compress, combined with expressing milk 1-2 times a day. If there are recurrent infections, surgical removal of the dilated main duct system may be indicated.
The disease appears with symptoms of breast palpation with a raised, movable, painless mass of different sizes. When squeezing, there is milky fluid coming out of the nipple. Easy to cause breast abscess
The disease is diagnosed by ultrasound with mammary gland cysts and aspiration biopsy shows milky fluid. First, the patient is treated with aspiration to treat cystic milk cysts. If after aspiration, there is a recurrence of the cyst within 2 months, surgical removal of the cyst should be indicated.
4. Classification of BIRADS in breast ultrasound
4.1 Classification of BIRADS in breast ultrasound BIRADS 1: No lesion found, need more imaging to evaluateBIRADS 2: Normal mammary gland organization to benign lesion (typical cyst, thick echogenic nodules)
BIRADS 3: Benign nodule (fibroadenoma), only 0.8% chance of malignancy
BIRADS 4: Suspected malignancy (signs suggestive of malignancy), need further work biopsy, there is a 31.1% chance of malignancy
BIRADS 5: Very high suspicion of malignancy (with 2 or more suggestive signs of malignancies), need to do biopsy, has 96.9% chance Malignancy
BIRADS 6: The malignancy was confirmed by pathological examination, the patient continued treatment.
4.2 Some signs suggest a benign tumor Shape: The tumor is oval in shape (main sign)
Direction: Parallel (main sign)
Borderline: Well separated border (sign) major sign)
Lesions limit: Clear and thin septum from adjacent benign tissue (secondary sign)
Echogenic structure:
cystic drum echo (main sign) Thick echo (minor sign) Posterior hyperechoic (sub-sign) Gross calcification (sub-sign)
Direction: Non-parallel (main sign)
Borderline: thorny margin (main sign) or unclear, folded Angle, small polyarthral (additional sign)
Lesions limit: Thick echogenic margin (additional sign)
Echogenic structure: Very poor or mixed echogenicity (additional sign)
Calcification: Microscopic presence Calcification (main sign)
Doppler ultrasound: There is perfusion in the tumor, RI > 0.83, PI > 1.6
Metastatic lymph nodes:
Diameter > 1cm Lymph node thickness > 3mm No hilum no more Yes extra-umbilical lymph node perfusion With multi-arc border The Imaging Department at Vinmec International General Hospital is equipped with ultrasound machines with specialized transducers, high frequency for breast examination. Especially, Vinmec has applied the world's advanced automatic 3D ultrasound technology to Vietnam. This system is manufactured by GE Heathcare (USA) with the name Invenia TM ABUS.
This is a device capable of screening, diagnosing, monitoring before and after treatment of breast diseases and together with a mammography system to help increase the ability to detect breast cancer from a very early stage when it is not yet diagnosed. have clinical manifestations.
Outstanding advantages of 3D Invenia ABUS breast ultrasound machine:
Helps accurately detect abnormalities or lesions in the breast. In women with thick breast tissue like Vietnamese, the accuracy is up to 90%. No harmful chemicals are used, no X-rays are emitted - Short ultrasound time: only about 15 minutes
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.