This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Dr. Phan Nguyen Thanh Binh, Head of Nutrition - Dietetics Department, Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Obesity is increasingly common and younger. Many people look to quick weight loss measures without really paying attention to the long-term effectiveness and safety. In fact, weight loss treatment requires a persistent combination of many measures such as reducing energy intake, increasing physical activity, using weight loss drugs or surgery (when indicated) and combined treatment with other drugs. associated risk factors. In particular, the solution that plays a prerequisite role is the long-term application of an energy-reduced diet, so that the energy input is lower than the energy consumed while still ensuring the needs of essential nutrients.
1. What is a low energy diet?
Very Low Energy Diet (VLED): Provides < 800kcal/day, aims to provide very little energy but still ensures enough essential nutrients. This requirement is difficult to fulfill for the traditional diet when the food is mainly of natural origin, leading to an increased demand for commercial production of VLED products. This type of food is fortified with all the nutrients according to nutritional recommendations. For decades, 250 - 400kcal/day was the most commonly used energy level, but today, the 800kcal/day calorie level is the only recognized option for effectiveness and safety. VLED can cause very rapid weight loss (1.5 - 2 kg/week) but does not facilitate weight maintenance. Besides, it can cause many side effects and complications such as dry skin, fatigue, dizziness, muscle cramps, headache, stomach pain, hair loss, gallstones, and cardiovascular risk. The application of VLED is not recommended in the absence of medical supervision.
Low Energy Diet (LED): Usually provides 800 - 1500 kcal/day. Contrary to VLED, LED can be implemented by traditional diet, with balanced nutritional composition, less side effects and better maintenance of weight loss effect. LEDs have a slower rate of weight loss than VLEDs, but multiple randomized clinical trials have demonstrated that the long-term effects (after 1 year) are no different from those of VLEDs. LED has the benefit of promoting healthy eating habits and changing eating behavior - key factors in maintaining the achieved weight of a weight loss program.

2. What are low energy foods?
To be able to follow the energy-reducing diet, we naturally need to choose to use low-calorie foods. Ready-to-eat or processed foods are considered low in calories when 1g of food provides less than 1.5kcal. If 1g provides 1.5 - 4kcal, it is considered an average energy food, and 1g provides over 4kcal, it is a high-energy food.
Benefits of low-calorie foods:
Because they contain little energy while occupying a large volume or volume, low-energy foods help users "quickly full, long hunger" without being overcharged. more energy - one of the causes leading to overweight and obesity.
The satiety capacity of food:
To assess the satiety level of a food, people use the "fullness index" - the satiety capacity that food brings. Foods with a high satiety index need only a small amount to provide a feeling of satisfaction to the user. As a result, you will limit your energy intake as well as snacking and help control weight.
Foods that combine the two characteristics of low energy and high satiety index are prioritized for selection when restricting food intake.
Low energy foods:
Watery foods Water does not produce energy but occupies a certain volume and weight in our stomach. To reduce energy intake and still feel full, you should drink more water before meals or eat more soup during meals, use foods containing a lot of water such as soup, porridge, vermicelli, pho,... By "diluting" the food as above, you can increase the mass and volume of the food many times over without changing the energy. Obviously, when we eat rice with soup, we are fuller faster than rice without soup. Or porridge has a much lower energy level than rice, 100g of porridge contains about 50kcal while 100g of rice contains up to 140kcal.
Foods rich in fiber Vegetables and fruits have both properties: low energy and high satiety index.
Vegetables and fruits are not only rich in fiber but also rich in water (contains 60-95% water). Therefore, the energy provided by vegetables and fruits is usually not high. The same weight is 100g, but vegetables only provide about 20-30kcal, while protein or starch provides up to 400kcal (20 times higher than vegetables). Fat even provides up to 900kcal (30 times higher than vegetables).
The average satiety index of the fruit group is 170, while the satiety index of the standard food, white bread, is only 100.
All kinds of seeds, dew, latex, seaweed, chia seeds, .. . contains many types of soluble fiber, this type of fiber when absorbed water swells to increase in volume and weight. As a result, they are kept longer in the stomach and make us feel full for longer.
In fact, brown rice makes us fuller longer than rice cooked with white rice because of the indigestible bran component. Soybeans, whole green beans, and whole grains are also high-fiber foods. In legumes, in addition to fiber, there are also anti-absorption substances such as antitrypsin that prevent digestion and absorption, so they give a feeling of hunger.
Fiber does not directly provide energy, so foods containing a lot of fiber help "full" without causing weight gain.

Low-fat, high-protein foods Among the three energy-producing food groups, fat produces the most energy (9kcal/1g). Therefore, to have low-calorie dishes, it is necessary to limit fat and fat. It is recommended to use fats from fish or plants such as sesame, soybeans, and peanuts because they contain more healthy unsaturated fatty acids than animal fats.
Protein-rich foods such as fish, beef,... often have a higher satiety index than starchy foods, even though 1g of protein or 1g of powdered sugar provide 4kcal. Based on this property, some weight loss diets promote protein-rich foods to replace starchy foods.
Processed Low Energy Foods These products on the market have a low level of energy per serving, while being high in protein and fiber to help with satiety, providing adequate content. vitamins and minerals according to recommended needs. In addition, these products are often supplemented with substances that increase fat metabolism or reduce appetite such as carnitine, Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), ... in products Calorie Burner, Slim Fast , Lose Weight.
Foods with a high satiety index:
To determine the satiety capacity of foods, foods are assessed for satiety after eating and every 15 minutes for 2 hours (usually compared to cakes). white noodles). Of the foods tested, potatoes had the highest satiety index.
Saturation index of common foods (compared to white bread):
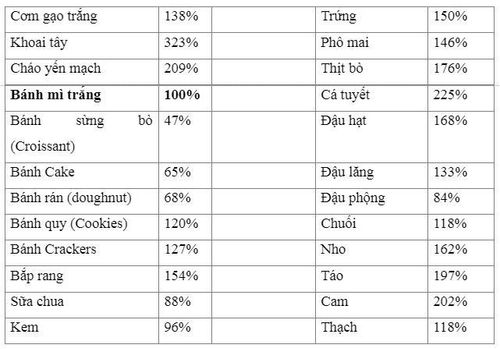
Knowing how to make good use of low-energy foods is considered a safe and effective solution in the treatment and prevention of overweight and obesity.
Please follow the website: Vinmec.com regularly to update many other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.