This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Bui Thi Ha - Pediatrician - Neonatologist - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Uncle has over 11 years of working in the field of Pediatrics - Neonatology and has strengths in the field of pediatric cardiopulmonary resuscitation, neonatology, access to diagnosis and treatment, neonatal pathologies such as premature birth, endocardial disease, respiratory failure, neonatal infection.
Choking is a fairly common accident that usually occurs in children between the ages of one and three. The most common choking conditions are infant choking, choking on food, choking on water, and sometimes aspiration of gastric juice or regurgitation.
This is a very dangerous condition, which can cause rapid obstruction of the airways, which, if not treated promptly, can be life-threatening.
1. Causes of choking on milk and food in children
1.1. The common cause of milk choking in babies Babies using a bottle with a teat hole that is too big to make milk flow a lot or because the mother has a lot of milk, the milk comes down quickly, making it difficult for the baby to swallow, causing choking. The mother feeds the baby in the wrong position, the baby sleeps while sucking on the breast but does not swallow, when the baby breathes heavily, it will cause choking of milk into the nose or the baby will choke milk into the lungs. When the baby suckles while talking, laughing and joking will cause milk to overflow into the trachea, causing choking.
1.2. Causes of food choking in children Because parents give children foods that are not suitable for the child's ability to chew and swallow. Parents feed children in the wrong position, children do not sit in one place while eating but constantly move, run, jump, laugh. Parents feed their children when they are crying, force them to eat quickly, swallowing quickly leads to choking.
2. Choking milk in babies, choking on food in children is dangerous like?
When a child chokes, milk or food will enter the airways, spilling into the trachea, bronchi, and alveoli, obstructing oxygen exchange, causing airway obstruction. Children will quickly become deprived of oxygen, have respiratory failure and may stop breathing.Typical symptoms when a child is choking are: a child who is eating or drinking suddenly coughs, cyanosis, choking on milk, wheezing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, eyes rolling back. The child's skin is pale, the body is panicky, the body is soft or stiff.
Choking is a very urgent emergency in children, if not treated promptly, it can cause rapid death due to respiratory failure or the child will have severe neurological sequelae due to lack of oxygen in the brain during a short period of time. long time.
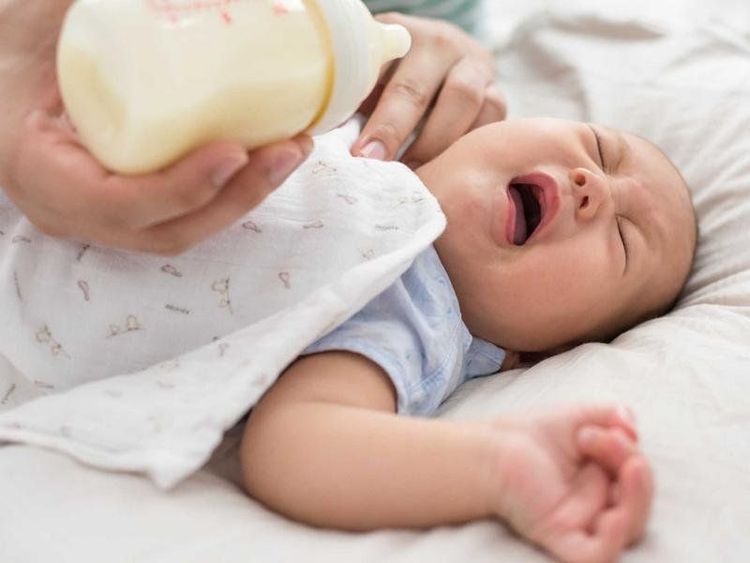

Trẻ sơ sinh bị sặc sữa
3. How to handle when children choke on milk, choke on food
3.1 Handling milk choking in infants Clearing the baby's airway: Use a suction device to suck milk in the baby's mouth and nose as quickly as possible, if left for a long time, the milk will enter deep into the lungs, causing airway obstruction. danger to young life. If you don't have a suction device, you can use your mouth to suck, so suck your mouth first, then your nose. Strong stimulation for babies to cry and breathe on their own: Back patting: put the baby on his stomach, head lower than his chest, use your hands to pat the back between the shoulders of the child in a downward and forward direction about 5 times. . Then, gently flip back to the supine position to see if the baby can breathe on his own. Chest compressions: if after patting the back, the child still cannot breathe, keep the child in the supine position, keeping the head lower than the chest. Apply perpendicular pressure about 5 times in a row, at a rate of 1 press/second, on the lower third of the breastbone (about 1 knuckle below the line connecting the 2 nipples). If the child still has not recovered, continue to alternately perform 5 back pats and 5 chest compressions until the child can breathe.
Take the child to the nearest medical facility for immediate emergency.
3.2. Handling when a child chokes on food Parents should calmly assess the child's situation:
If the child coughs or cries and can still breathe, the child's condition is not serious. Parents should encourage and encourage the child to continue coughing and vomiting to expel food and foreign objects. Check your baby's mouth and pull out visible foods. If you can't see a piece of food, don't dig inside your baby's mouth with your fingers, as it may accidentally push the food deeper into the airways. Monitor your baby's condition, see if he's breathing easier after coughing, take him to the nearest medical facility for emergency care when he has trouble breathing. If the baby is alert and having difficulty breathing: check the baby's mouth, remove all visible food samples, then perform chest patting and back thrusts as in infant choking. If the child is unconscious and has stopped breathing: administer CPR and perform chest compressions, call an ambulance immediately.
4. Prevent choking on milk in babies, choking on food in children
To prevent milk choking in babies, for breastfed babies, if mothers have a lot of milk, they should clamp their nipples to limit the milk rate when the baby sucks. If the mother is bottle-feeding, she should choose the nipple of the right size, there are bottles on the market with anti-colic valves, milk only flows when the baby sucks to help limit the milk flow too quickly, reducing the risk of choke for the baby.
Do not breastfeed while lying down, nursing while sleeping, mother should not breastfeed while laughing with the baby. When breastfeeding, the mother should hold the baby properly, ensuring that the baby's head - back and bottom are in a straight line, the baby's head is facing the mother's chest, the baby's belly is touching the mother's belly. Correct feeding position will reduce the risk of choking in infants.

Tư thế bú đúng cách sẽ giảm nguy cơ sặc sữa ở trẻ sơ sinh
Parents absolutely do not force the child to eat, do not feed too quickly, do not feed the child while crying or playing. Do not feed a large amount of food at the same time but should divide it into small spoons, when the child has abnormal symptoms, quickly check whether the child is choking.
The proper first aid treatment of infant choking will help the child quickly get out of a dangerous situation. And if the child has been handled in the above ways, but the child still shows signs of coughing, cyanosis, apnea, ... the parents need to immediately take the child to the nearest hospital for timely emergency.
In Vietnam today, 7 out of 10 children under 5 years old have zinc deficiency and 8 pregnant women have zinc deficiency. The prevalence of zinc deficiency in pregnant women is 80.3%, women of childbearing age 63.6% and children under 5 years old is 69.4%. The most common manifestations of zinc deficiency in children are growth retardation, mild and moderate malnutrition, delayed growth in height, and some observable symptoms such as anorexia or decreased appetite, decreased suckling, and no meat. fish, slow digestion, mild constipation, persistent nausea and vomiting in children. In addition to reasonable zinc supplementation, parents also need to provide their children with other important vitamins and minerals such as lysine, chromium, B vitamins,... resistance to minor illnesses and less digestive problems.
Please visit the website vimec.com regularly and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.