This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Resident Doctor Nguyen Thi Hong Tho - Neonatology Department, Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.
Acute otitis media often accompanies an upper respiratory tract infection. Pneumococcal otitis media is a common disease in children under 5 years of age, often recurs many times if not treated promptly, causing serious consequences for children.
1. Causes of acute bacterial otitis media in children
The main causative agent of bacterial otitis media is Streptococcus pneumoniae (40-50%), Haemophilus influenzae (30-40%). Currently, 5-in-1 or 6-in-1 vaccines are available. Widespread immunization for children has been integrated with the prevention of Haemophilus influenza type B. Therefore, otitis media caused by pneumococcal disease is receiving great attention nationwide as well as worldwide
Pneumococcal bacteria often available in the pharynx of children and adults. When health is weakened, the body's immunity is reduced, pneumococcus has an excess of opportunities to attack the respiratory tract and cause otitis media, pneumonia, and meningitis. The ability to develop pneumococcal otitis media depends on the body's resistance, so children with immature immune systems should be susceptible to the disease.
According to a study by Dr. Nguyen Dang Quyet and his colleagues in 2018 on antibiotic resistance of pneumococcal bacteria in the treatment of pneumococcal pneumonia in children at the National Children's Hospital, it was found that: Pneumococcal has a high rate of antibiotic resistance. very high:
Over 95% with antibiotics of the macrolide group 90% with cotrimoxazol 95% with clindamycin 73% with penicillin V. In addition, pneumococcus is less sensitive to penicillin, 56.1% is not sensitive to penicillin G. Only 58.4% of pneumococcus were sensitive to cefotaxime and 62% sensitive to ceftriaxone. However, pneumococcus is still sensitive 95% to amoxicillin, 100% to rifampycin, linezolid, vancomycin and ofloxacin. The pneumococcus was resistant to levofloxacin. The rate of multi-resistant pneumococci was 64%.
2. Symptoms of children with acute otitis media caused by pneumococcal
Symptoms of otitis media are the eardrum bulging, or not moving when pumping air into the ear, fluid draining from the ear. In addition, otitis media in young children often has a number of symptoms such as:
High fever from 30-40 degrees Celsius, fussiness, refusal to breastfeed, picky eating, vomiting and possible convulsions; Ear hurt; Repeated diarrhea, loose stools, appearing almost simultaneously with fever.
3. Complications caused by children with pneumococcal otitis media
Children with pneumococcal otitis media can be completely cured with complete treatment. If treated late, the disease can progress to severe and cause dangerous complications, such as:
Hearing loss: Due to the accumulation of mucus behind the eardrum, it may gradually disappear, or accumulate in the middle ear for many days, damaging eardrum, the chain of bones that conducts sound, causing permanent hearing loss. Perforated eardrum: during acute pneumococcal otitis media, mucus and pus can accumulate in the middle ear, pressing and putting pressure on the eardrum, causing the eardrum to tear and pus to drain out. If the eardrum is torn many times and does not heal, it will puncture the eardrum, the child needs surgery to patch it up. Mastoiditis: This is a common complication of pneumococcal otitis media. If not treated early, the disease will spread to the bone, causing mastoiditis, thereby penetrating the skull, causing meningitis, brain abscess, increasing the risk of death in children. Speech delay, developmental delay: Children with otitis media cause hearing loss or reduction, affecting the ability to learn language in children, causing speech delay, mental retardation.
4. How to prevent children from acute otitis media caused by pneumococcal?
Pneumococcal vaccination is the most effective solution for children worldwide: There are 2 types of vaccines available on the market in Vietnam
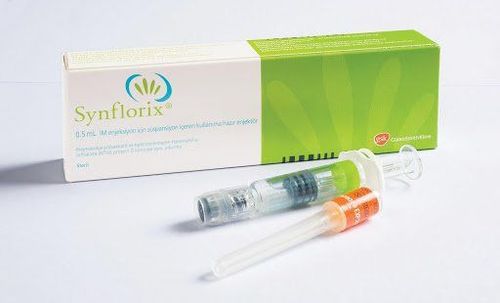
Synflorix vaccine: A vaccine to prevent pneumococcal diseases caused by demand. Synflorix vaccine contains the 10 most common types of pneumococcal antigens: 1, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F and 23F Prevenar 13 vaccine : Contains 13 antigens The most common strains of pneumococci include 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F, and 23F. These two vaccines stimulate the body's immune system to make antibodies against these pneumococcal types, helping to prevent the diseases they can cause
Synflorix (Belgium) vaccination schedule for children from 6 years of age weeks to 5 years Children from 6 weeks to 6 months old:
Schedule of 3 basic doses:
1st dose: 1st injection.
Nose 2: At least 1 month apart from 1st nose.
Nose 3: At least 1 month apart from the 2nd nose.
Repeat dose: after 6 months from the 3rd dose.
Children aged 7-11 months (have never been vaccinated before).
1st injection: First injection.
Nose 2: 1 month away from 1st nose.
Repeater: At the 2nd year of age and at least 2 months after the 2nd dose.
Children 12 months to 5 years old (who have never been vaccinated before)
1st dose: 1st injection.
Nose 2: 2 months apart from 1st shot.
Prevenar 13 vaccination schedule for children Children 2 - 6 months old:
1st dose: The first dose, which can be started when the child is 6 weeks old;
Nose 2: At least 1 month apart from the first dose;
3: At least 1 month after the 2nd dose;
Repeat dose: Inject when the child is 11 - 15 months old and need at least 2 months after the 3rd dose.
Children 7 - 11 months old:
Nose 1: The first injection of the child between 7 - 11 months old;
Nose 2: At least 1 month apart from the first dose;
Repeat dose: Inject when the child is over 1 year old and at least 2 months after the 2nd dose.
Children 12 - 23 months old:
Nose 1: The first injection of the child between 12 - 23 months old;
Repeat injection: At least 2 months apart from the first dose.
Children over 24 months old and adults: Single injection.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a reliable vaccination address chosen by many families. Vaccination service at Vinmec has many outstanding advantages:
Fully meets the demand for vaccines for all ages. The source of high-quality vaccines is preserved in a strict cold chain according to regulations from the stage of importation, preservation to use; A team of professional, friendly, dedicated and experienced vaccination medical staff, able to advise and handle complex vaccination situations; Modern facilities: Post-vaccination monitoring room is fully equipped with emergency facilities, cool, helping children feel comfortable and have a good mentality before and after vaccination. You will receive scheduled reminder messages before the injection date and the vaccination information is synchronized with the national immunization information system. The hospital strictly follows the vaccination process according to the Guidelines of the Ministry of Health to ensure the safety and effectiveness of vaccines:
Before vaccination, customers are thoroughly screened to ensure normal health , eligible for vaccination. Parents are also answered by doctors, providing a lot of useful vaccination and disease prevention knowledge for children. During vaccination: The hospital adheres to the injection procedure in accordance with the Immunization Guidelines of the Ministry of Health to ensure maximum safety for customers. After vaccination: The vaccinated person will be monitored for at least 30 minutes on site after vaccination and instructed to continue monitoring for a minimum of 24 hours after vaccination. For direct consultation, please dial 1900 232 389 (key 0 to call Vinmec) or register for an appointment at the hospital HERE. If you need a remote health consultation with Dr. Vinmec, you can book a consultation HERE. Download the exclusive application MyVinmec for faster scheduling, more convenient calendar tracking