This is an automatically translated article.
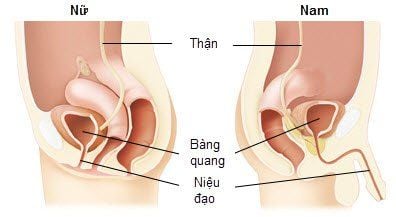
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a Gram (-) bacterium. Bacterial infections can occur in the urethra, anus, cervix, throat, and eyes. In more dangerous cases, gonorrhea bacteria can enter the bloodstream, at this time the patient has symptoms of fever, skin lesions, joint pain.1. How is gonorrhea transmitted?
Gonorrhea is usually transmitted directly through unprotected sex, such as vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected partner.In the absence of timely detection and treatment, gonorrhea can turn into chronic gonorrhea, leading to complications that adversely affect the patient's health, especially in reproductive problems.
2. Neisseria gonorrhoeae – The causative agent of gonorrhea
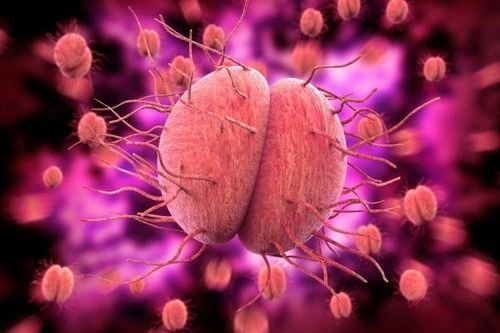
Vi khuẩn lậu Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Gonorrhea has the shape of coffee beans, growing in pairs. Gonorrhea is about 1.6mm long; width about 0.8mm; The distance between two bacteria in the same pair is 0.1mm. Gonorrhea is non-motile, non-sporeforming, and usually exists in the cytoplasm of neutrophils. Gonorrhea bacteria can hardly survive in the outside environment, easily destroyed by ambient temperature, the dryness of the environment or when using disinfectants. Gonorrhea bacteria can only survive for a few hours after leaving the body. In the case of acute gonorrhea, a clear image can be seen through the test. However, for chronic gonorrhea, it is necessary to conduct a culture to have a suitable treatment plan.
Due to the characteristics of gonorrhea bacteria do not tolerate drying, so after taking the specimen, it should be immediately put into a suitable culture medium. The most commonly used culture medium is Thayer - Martin with CO2 pressure of 5%, ambient temperature ranging from 35-37oC, pH from 7.2-7.6. In the culture medium, the size of gonorrhea bacteria can vary widely and atypically, depending on the conditions of each environment.
Gonorrhea, compared with other Gram-negative cocci, is particularly sensitive to antibiotics. However, according to many studies, within the past few decades, gonorrhea bacteria have shown signs of resistance to some components such as penicillins, tetracyclines, sulfonamides, quinolones....
Besides, gonorrhea bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae can be combined with other bacteria causing urethritis, the most typical of which is with bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma, Mycoplasma or some other agents such as fungi, flagellates.
3. Test method to find gonorrhea bacteria
3.1 Bacterial cultureBacterial culture can be considered the standard method in the diagnosis and treatment of gonorrhea. After taking the patient samples, they will be placed in a suitable environment for culture. The culture medium used by doctors today is Thayer-Martin containing Vancomycin. After culture of gonorrhea, the result is positive if there are signs of bacterial growth and negative if no growth is present.
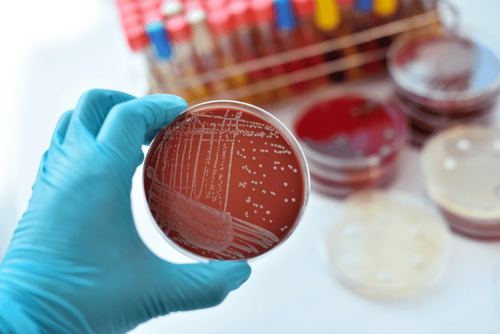
Nuôi cấy vi khuẩn là phương pháp phổ biến trong việc xác định vi khuẩn lậu
This method is the method that gives the most accurate results about the possibility of gonorrhea. However, because the characteristics of gonorrhea bacteria are quite sensitive to the environment, the culture process is quite difficult, which can lead to erroneous results if errors occur in the process.
3.2 Gonococcal Gram staining Gonococcal Gram staining is a method of staining bacterial samples with specialized dyes, through which they can be clearly observed under the microscope. Samples for testing are usually taken from the urethra or a urine sample upstream.

Phương pháp nhuộm Gram lậu cầu
Gram staining method only gives accurate results for men, for women because gonorrhea bacteria are often distributed in many locations and can be mixed with beneficial bacteria, so the results after Gram staining not enough to determine disease status.
3.3 PCR test PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction, polymerase chain reaction) test is a type of molecular biology test, conducted by generating a target amount of DNA copy in vitro based on the operating principle. of the thermal cycle.
Xét nghiệm PCR lậu cho kết quả chính xác cao
PCR test is a new method with high specificity and sensitivity. However, it should be noted that storage temperature and transit time can affect the results of the test. In addition, test results may be erroneous if the specimen is contaminated from the outside.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers a Package of Examination and Screening for social diseases to help customers detect diseases early and have effective treatment and prevent dangerous complications. The screening package for social diseases at Vinmec is for all ages, both men and women.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
MORE:
How long does gonorrhea incubate? Can gonorrhea be cured? Symptoms of gonorrhea in men