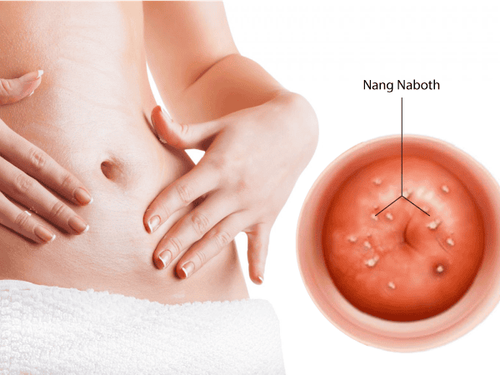
Nabothian cysts of the cervix are small growths that form on the surface of the cervix. These cysts are mostly small and benign, and if they are small, they may resolve on their own. Treatment for nabothian cysts may include medication, aspiration of the fluid, or cauterization of the cysts.
1. What are nabothian cysts?
Nabothian cysts of the cervix are small growths that form on the surface of the cervix and are benign lesions. These cysts arise from the epithelial cells of the cervix, which excessively grow and cover the glandular epithelium at the junction of the cervix.
Depending on the duration and extent of development, the cysts can be either small or large. Nabothian cysts are yellow or white in color and are usually very smooth.
The cause of nabothian cyst formation is due to the glandular epithelium secreting mucus, which cannot escape because the glandular epithelium layer covers it. Over time, this results in the formation of cysts that swell and become as large as a grain of rice, a bean, or even larger.
2. Are nabothian cysts of the cervix dangerous?

Patients usually do not have specific symptoms when they have nabothian cysts. Some cases may experience vaginal bleeding after intercourse or pelvic pain, but these occurrences are very rare. Nabothian cysts are generally not life-threatening, but they can significantly affect a woman’s sexual life and fertility.
However, nabothian cysts can still cause some dangerous complications:
- Cervical damage: When these cysts grow large, they can deform the cervix, altering its shape and size. If these cysts grow large enough, they may rupture, causing severe ulceration and infection of the cervix, leading to cervical inflammation.
- Infection: The cysts may rupture and cause infections in the cervix, which can spread upward into the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes, causing inflammation, and blockages in the fallopian tubes, thereby affecting the process of conception.
- Menstrual pain: Pain may occur before and during the menstrual cycle, severely affecting daily activities, work, and study.
3. Treatment of nabothian cysts
Nabothian cysts of the cervix are benign changes in the cervix, typically small and few in number.
This condition occurs when the squamous epithelium of the cervix covers the opening of a gland, but the gland continues to secrete, causing fluid to be trapped inside and forming a cyst. If the cysts are few and small, they may resolve on their own without the need for treatment.
However, if nabothian cysts become too large, they may rupture, causing inflammation and very dangerous uterine infections.
Treatment of nabothian cysts includes basic methods:
- Medical treatment: This involves using medication for cases with small cysts and a small number of cysts. In these cases, the doctor will prescribe medication to shrink the cysts and completely eliminate them, returning the cervix to its normal state.
- Aspiration: Aspiration is performed to drain the fluid, helping the cysts shrink and preventing them from growing larger. This treatment is usually applied when the cysts have grown large and have formed clusters.
- Cauterization of nabothian cysts: The most common methods used are electrocauterization and cryocauterization.
- Electrocauterization: This method uses an electric current (diathermy) to burn the outer layer of the cervix and is typically performed under local anesthesia. This is the most commonly used treatment for nabothian cysts because it minimizes bleeding during the removal of the cyst.
- Cryocauterization: This method uses liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy the cyst.
Vinmec International General Hospital offers women a screening package for the early detection of gynecological cancers. When registering for this package, patients will receive:
- Consultation with a specialist in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
- Necessary tests to detect cancers such as cervical, uterine, and ovarian cancers, even in the absence of symptoms.
- Screening for cervical cancer with tests like liquid-based cytology (Liqui Prep), HPV genotype PCR using automated systems, and ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries through the vaginal route.
- Specialists will review test results and examine specific cases to provide appropriate advice.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.