This is an automatically translated article.
MS is considered an autoimmune disease. When the disease is active, components of the immune system, mainly cells called T cells, attack the myelin sheaths that surround nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord. This leads to inflammation.
1. What is multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis is a disease that causes vision problems, numbness, itching, muscle weakness, and other symptoms. It is an autoimmune inflammatory disease that affects the central nervous system's Myelin.
2. What causes multiple sclerosis?
MS is considered an autoimmune disease. When the disease is active, components of the immune system, mainly cells called T cells, attack the myelin sheaths that surround nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord. This leads to inflammation. It is still not clear what triggers the immune system response in this case. One theory is that a virus, or an environmental factor, triggers the immune system in some people with a certain genetic makeup.
Inflammation around the myelin sheath stops the affected nerve fibers from working properly and causes symptoms. Once the inflammation goes away, the myelin sheath can heal and be repaired, and then the nerve fibers begin to function again. However, inflammation, or repeated episodes of inflammation, can leave small "scars" (scleroderma) that cause permanent nerve fiber damage. In people with typical multiple sclerosis, multiple sclerosis plaques form and grow in the brain and spinal cord.
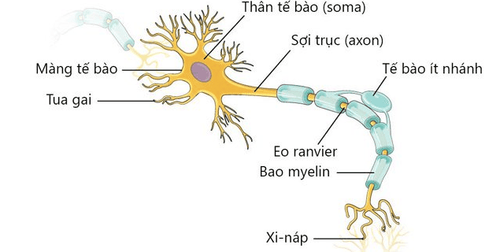
Vị trí bao myelin
3. How does multiple sclerosis progress?
Once the disease is triggered, it tends to take one of the following four forms:
Benign form (Benign form) In less than 1 in 10 people with MS, only a few relapses in a lifetime and long periods of being symptom-free. This is the least severe form of the disease and is called benign multiple sclerosis.
Relapsing-remitting form (Relapsing-remitting form) Nearly 9 in 10 people with MS share the same relapsing form of the disease. Relapse is the stage in which symptoms occur. During relapse, symptoms develop (described below) and can last for days, but usually last 2-6 weeks. Symptoms sometimes last for months. Symptoms may then lessen or go away. You are said to be in remission when your symptoms have subsided or gone. Subsequent relapses continue to occur over time.
The type and amount of symptoms that occur during relapses vary from person to person, depending on where the myelin is damaged. The frequency of recurrence also varies. One or two relapses every two years is quite typical. However, relapses may occur more or less frequently. When a relapse occurs, previous symptoms may return, or new symptoms may appear.
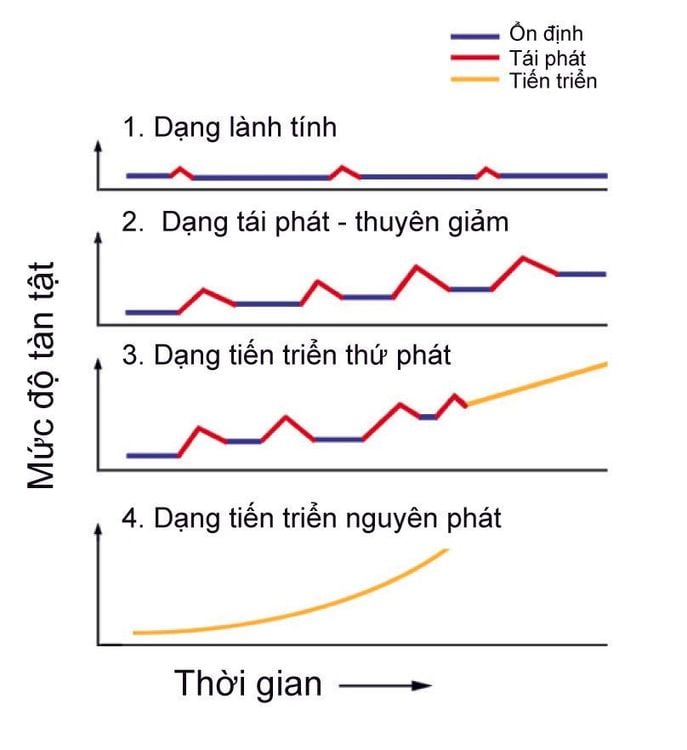
Các giai đoạn tiến triển của bệnh xơ cứng rải rác
This period of relapse-remission tends to last for many years. At first, complete recovery from symptoms, or near complete recovery, is typical after each relapse. Over time, damage to myelin can also damage the nerve fibers themselves.
Finally, usually after 5-15 years, some symptoms often become permanent. Symptoms are usually caused by a buildup of scar tissue in the brain and damage to nerve fibers. The condition usually then slowly gets worse over time. This stage is called secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Typically, about two-thirds of people with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis develop secondary progressive MS after 15 years.
Secondary progressive form Symptoms worsen (with or without recurrence) in this form of multiple sclerosis. Many people with the relapsing-remitting form of MS then develop this secondary progressive form of MS.
Primary progressive form In about 1 in 10 people with MS, there is no relapsing-initial form of remission. Symptoms gradually get worse at the beginning, and do not recover. This is called primary progressive multiple sclerosis.

Điều trị bệnh xơ cứng rải rác bằng phương pháp truyền tế bào gốc tạo máu tự thân tại Bệnh viện Vinmec
Autologous hematopoietic stem cell infusion can alleviate autoimmune reactions and long-term relapses of the disease. At Vinmec International General Hospital, patients with multiple sclerosis have been treated with autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transfusion of autologous hematopoietic stem cells is an attempt to "reboot" the immune system, whose job it is to destroy damage to the brain and spinal cord in multiple sclerosis. For autologous stem cell infusion for multiple sclerosis, hematopoietic stem cells are taken from your body (autologous infusion) from your bone marrow or blood, selected and stored before being depleted. the immune system to the full extent of the chemical. The stored hematopoietic stem cells are then passed back to the body. The new stem cells travel down to the bone marrow and over time restore the immune system.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline HERE for support.
MORE
Multiple Sclerosis: What to Know What is Multiple Sclerosis (or Multiple Sclerosis)? Treatment of systemic scleroderma