This is an automatically translated article.
Phaeohyphomycosis is a pathology of lesions in the subcutaneous tissue caused by fungi deep under the skin. The disease is not only seriously affected in terms of aesthetics but also can be fatal if not diagnosed and treated in time.
1. Learn about Phaeohyphomycosis
Phaeohyphomycosis is an infection of the deep dermis, subcutaneous layer or sometimes the epidermis caused by a dematiaceous fungus (brown pigment mold).
Phaeohyphomycosis is characterized by the formation of inflammatory cysts in the subcutaneous tissue. These cysts are termed phaeomycotic cysts characterized by central necrosis, fibrin, and neutrophil infiltration, surrounded by epithelial cells and fibrosis. However, early lesions that may include an abscess rather than a cyst may also present as non-necrotic.
There were no systemic signs or symptoms, regional lymph nodes were not involved, nor did any patient have systemic spread.
Favorable conditions for fungal growth:
Infections are rare but tend to be more common in warm tropical and subtropical climates Patients are immunocompromised, on long-term corticosteroid use, or ill weakness is at increased risk.
Suy giảm hệ miễn dịch làm tăng nguy cơ mắc nấm sâu Phaeohyphomycosis
Live in rural areas gardeners, vegetable growers, barefoot people Contaminated environment The correct diagnostic method for all agents of phaeohyphomycosis is fungal culture and histopathological examination through microscopy . Lesions show brown-walled mycelium in the dermis, the subcutaneous layer.
2. Causes of deep fungal disease Phaeohyphomycosis
Deep fungal disease is caused by a heterogeneous group of fungi known as molds. These molds are ubiquitous but are found mostly in soil. Characteristic of this fungus is the dark pigment cell wall that is melanin.
Studies have shown that more than 130 species of fungi belonging to 70 different genera have been reported to be the causative agents of human and animal phaeohyphomycosis. Among them, Exophiala jeanselmei and Wangiella dermatitidis are the most commonly isolated fungi causing subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis.
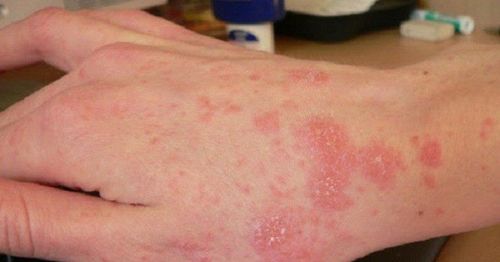
Pathogenicity: These fungi grow on soil, decaying wood and other plant materials. They then enter the skin and subcutaneous tissue through skin abrasions, skin trauma, inflammation of the skin ulcers causing deep fungal disease. In addition, they can enter by inhaling fungi that cause fungus in the lungs or sinuses, ingesting contaminated food or water, then entering through the digestive tract and contaminating the digestive tract, entering the bloodstream.
Nấm sâu xâm nhập vào cơ thể qua vết thương hở trên da gây viêm loét nhiễm trùng
3. Clinical and subclinical symptoms of deep fungal disease
Clinical symptoms
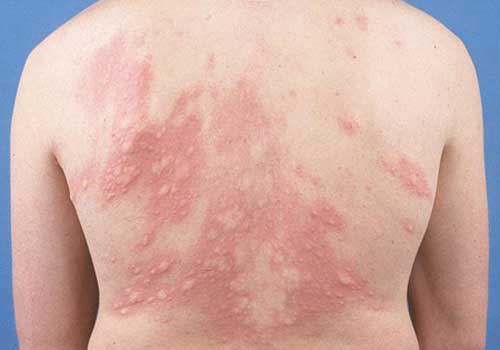
Disease manifests as subcutaneous cysts with subcutaneous tumor characteristics, separate, solid, easy to identify, less painful. This lesion can spread to become chromomycosis-like warts. May invade the ethmoid bone, leading to destruction of the ethmoid bone. Invasion into deep tissues: severe, forming leaky visceral abscesses (bone, bone marrow, especially in the brain). Subclinical symptoms
Fresh examination: mycelium has a brown septum, 5-10μm in diameter, is in a twisted state and produces numerous thick-walled spores. Culture: on Sabouraud or Mycosel medium at 35°C, after 1-4 weeks grow solid and curly colonies, 1cm in diameter, dark brown to black.
4. Treatment
Treatment includes antifungal therapy and surgical removal of the fungal lesions.

Bệnh nhân được điều trị bằng thuốc hoặc phẫu thuật cắt bỏ tổn thương do nấm
Antifungal agents including Amphotericin B are active against many fungal organisms responsible for phaeohyphomycosis. Other antifungal agents that are active against some organisms that cause phaeohyphomycosis include voriconazole, itraconazole, and posaconazole. Regardless of the antifungal regimen, the mortality rate of invasive phaeohyphomycosis was more than 70%.
In addition, itraconazole should be used with Itraconazole for several weeks to several months to prevent disease.
Surgical excision can invade the ethmoid bone using surgical curettage of the entire diseased area.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.