This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Dang Huy Toan - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Urticaria is a common skin disease, caused by many causes. Early diagnosis and treatment of urticaria will help reduce uncomfortable symptoms for patients and reduce the risk of unpredictable complications.
1. What is urticaria?
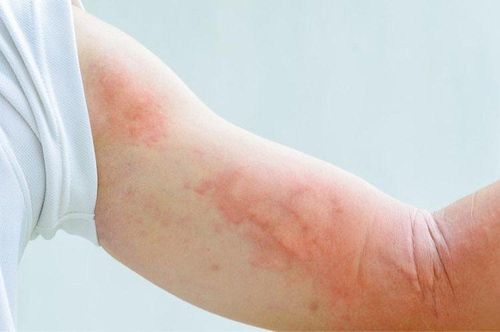
Urticaria is a skin rash, which is a reaction of the skin capillaries due to various factors, causing acute or chronic edema in the dermis.About 20% of the population has experienced urticaria at least once in their life. The disease is the result of a complex chain reaction that releases histamine and other inflammatory mediators. The presentation of urticaria is papules, erythematous or white patches, edematous, clearly delimited. The size and shape of urticaria varies, may be round or oval, clustering into a polyarche. Urticaria may also have blisters, hemorrhages, or scabs on the skin. The patient may have more or less itching. Common sites of urticaria are the skin, mucous membranes, larynx, and gastrointestinal tract.
Bệnh mày đay thường xuất hiện trên da
2. Classification of urticaria
2.1. General Urticaria (acute and chronic) Acute urticaria: Lasts less than 6 weeks and is caused by a variety of causes, such as food allergies, medication that causes hives, infections, or hormonal changes. ..; Chronic urticaria: Lasts more than 6 weeks, often no cause can be found, only the cause is found in 5-20% of cases.
Bệnh máy đay mạn tính thường không rõ nguyên nhân gây bệnh
Urticaria due to mechanical stimulation: Includes urticaria, delayed pressure urticaria and vibration urticaria; Urticaria due to temperature changes: Includes cholinergic urticaria, local heat exposure urticaria and cold urticaria; Hives caused by the sun. 2.3 Angioedema (Quincke's edema) Lesions are similar to urticaria but deeper and more diffuse; The cause of the disease is unknown; Urticaria pain, burning sensation; Location: Eyelids, lips, palms, feet, external genitals, organs of the respiratory system, digestive system,...; May be accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever, digestive disorders, joint pain, headache, and most seriously, heart failure (anaphylaxis), requiring prompt emergency care. 2.4 Other forms of urticaria Contact urticaria; Urticaria vasculitis.
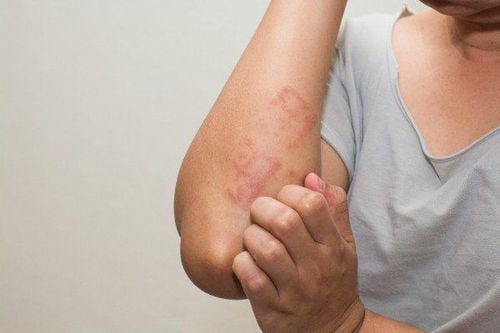
Mày đay tiếp xúc chỉ xuất hiện khi cơ thể tiếp xúc với hóa chất, các loại thuốc trừ sâu, mỹ phẩm
3. Diagnosis of urticaria
3.1. Clinical diagnosis Basic lesions: These are edematous papules of different sizes, appearing in any skin area on the body. High raised papule on the skin, paler or redder than the surrounding skin. The size and shape of the papules change rapidly, appear quickly and also disappear quickly; Distribution of urticaria may be localized or widespread; In areas of loose organization such as lips, eyelids, external genitalia, ... the sudden appearance of erythema and papules will cause swelling of the whole area, called angioedema or Quincke's edema. If angioedema occurs in the larynx or gastrointestinal tract, it will cause severe symptoms such as severe shortness of breath, abdominal cramps, loose stools, low blood pressure, cardiovascular disorders or anaphylaxis; Functional symptoms: Most cases of urticaria cause itching, the more you scratch, the more itchy and more papules appear. However, there are cases where the patient only feels a stinging or burning sensation; Progression: Urticaria or recurrent episodes, according to the progression is divided into 2 types: acute urticaria and chronic urticaria.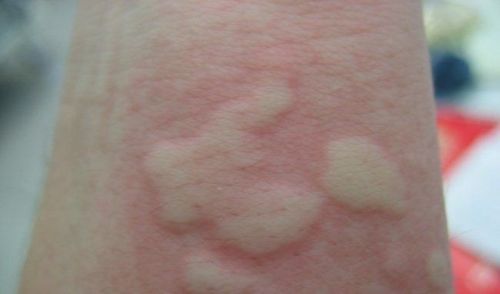
Kích thước các nốt sần to nhỏ khác nhau trên da là dấu hiệu đầu tiên của bệnh
Complete blood count: Determine the polymorphonuclear leukocyte count, if this white blood cell count is elevated suggest a parasitic allergy, a decreased white blood cell count suggests systemic lupus erythematosus ; Prick test: with suspected allergens such as pollen, house dust mites, ...
4. Treatment of urticaria
What to do if you have a rash? There are 2 commonly applied treatment options for patients with urticaria:4.1 Non-pharmacological treatment Explain clearly to the patient when performing the treatment; Find and eliminate the cause of the disease; Get plenty of rest, avoid stress, too hot or too cold; Avoid using drugs that can cause urticaria such as Aspirin, NSAIDs, codeine, morphine, ACE inhibitors, ... if there is a local allergy; Avoid foods that can cause allergies such as eggs, strawberries, tomatoes, chocolate, ...; Avoid stimulants such as spices, tea, alcohol, coffee,...; Limit scratching, strong rubbing on the skin; Can apply cold or cold water bath, avoid hot water bath; Avoid direct exposure to the sun; Anti-constipation, deworming; Wear light and well-fitting cotton clothing; Avoid strenuous activities or other causes of sweating;
Hạn chế gãi mạnh trên da khiến da càng tổn thương thêm

Nên sử dụng thuốc theo chỉ dẫn của bác sĩ
There is no absolutely safe drug for pregnant women; Hydroxyzine is contraindicated for use in pregnant women; Cetirizine and loratadine (group B) can be used to treat urticaria because these drugs do not increase the risk of fetal malformations; Treatment of urticaria in lactating women:
Do not take most antihistamines; Can use cetirizine, loratadine, chlorphenamine. Treatment of urticaria in children:
Avoid possible causes of the onset of the disease; Antihistamines are the treatment of choice; Use Cetirizine, Desloratadine for children 1 year of age and older; Use Loratadine, levocetirizine for children 2 years of age and older; Use Acrivastine, Bilastine, Mizolastine, Fexofenadine and Rupatadine for children 12 years of age and older; Use Loratadine, Desloratadine, Cetirizine and Levocetirizine syrups; The metabolism of cetirizine in children is different from that of adults, so it can be used twice a day; 1st generation antihistamines can be used in children, but they cause drowsiness. Drugs including diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine, promethazine, chlorphenamine; Short-term corticosteroids (3-5 days) can be used for children with pressure urticaria. Do not use corticosteroids for a long time because it can cause serious side effects; Tranexamic acid is used to treat angioedema alone with a dose of 15-25mg/kg (maximum 1500mg), 2-3 times/day; Anti-IgE antibody (Omalizumab) can be used to treat chronic urticaria in children over 7 years old, who do not respond to antihistamine therapy; dose is 3 - 6 injections, 150-300mg/month; Children need to be monitored in a special treatment center; Cyclosporine can be used to treat urticaria in difficult-to-treat cases. Cases of chronic urticaria are often related to other internal diseases, so the patient needs to be examined by a specialist, perform the necessary tests to find the right cause and have an appropriate treatment plan.
Urticaria is a common disease that can seriously affect the patient's health and easily cause many unpredictable complications. Therefore, when there are symptoms of urticaria, the patient should see a specialist in Dermatology - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. With a team of highly qualified and experienced medical doctors and modern machinery, Vinmec Times City will accurately diagnose and propose active and effective treatment plans for patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.