This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Phan Van Phong - Emergency Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalMetabolic acidosis is a decrease in [HCO3-], reflecting either the retention of fixed acids or the loss of alkalinity. The compensatory response is hyperventilation leading to a decrease in PaCO2.
1. Causes and management of metabolic acidosis
1.1. Acidosis without anion gap (hyperchloremic hyperchloremia) Classified by serum potassium
Type with high or normal blood potassium: + Decreased secretion of Aldosterone .
+ Intravenous type renal tubular acidosis.
+ Moderate renal failure (glomerular filtration rate > 20 ml/min).
+ Add HCl and then reduce CO2.
Low serum potassium: + Loss through the stomach, intestines due to bicarbonate loss (diarrhea, branching ureter, biliary or pancreatic fistula).
+ Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.
+ Acidosis due to distal and proximal tubular disease.
+ Decreased acid secretion in the renal tubules.
1.2. Anion gap acidosis (anion gap) Ketosis due to hyperglycemia. Lactic acidosis: consequences of shock, acute pancreatitis, poisoning, acute liver failure ... Poisoning with drugs (Methanol Salicylate, Ethylene glycol, Paraaldehyde). Renal tubular acidosis.
Tăng đường huyết có thể gây nhiễm toan có tăng khoảng trống anion
2. Management of metabolic acidosis
2.1. Principles of management Treating the cause, treating acidosis must pay attention to the time of occurrence of acid-base balance disorders.
For example, if ketoacidosis is usually of short duration, maximal respiratory compensation is safest. In contrast, for cases of chronic acidosis (such as kidney failure...) the treatment aims to restore the strong ion difference (Strong ion diffirence - SID).
2.2. Treatment Measures Sodium Bicarbonate Using sodium bicarbonate is the simplest and most effective.
If mild, just give 1g of sodium bicarbonate with 12 mmol of sodium bicarbonate. pH < 7.20 need to compensate for intravenous bicarbonate is calculated by the formula:
[HCO3] deficiency = PKg x (0.4) x ([ HCO3 ]need to achieve - [ HCO3 ] measured)
Half of the deficit can be compensated in 3 to 4 hours in the absence of severe heart failure. Sodium bicarbonate solutions were used 1.4%, 4.2% and 8.4%.
Particularly in diabetic ketoacidosis should not be compensated with Bicarbonate, just enough fluid infusion to eliminate Betahydroxybutyric Acid and correct and timely insulin is enough.
THAM is an H+ ion acceptor indicated when hypernatremic metabolic acidosis is contraindicated with sodium bicarbonate. However, it can cause depression of the respiratory center, hypoglycemia, and severe liver necrosis.
Treatment of metabolic acidosis without increasing anion gap (hyperchloremia).
Extra-renal dialysis In case of renal failure but with strong catabolism causing blood urea, creatinine or potassium to increase rapidly and not eliminate acid radicals, dialysis is indicated.
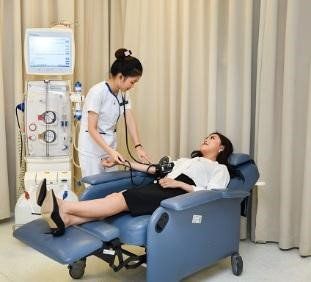
Lọc máu ngoài thận là một trong các biện pháp xử trí toan chuyển hóa
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.