This is an automatically translated article.
Answered by Doctor Vu Dung Kien - Doctor of Neurology - Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common mononeuropathy, local damage to the median nerve due to compression at the passage through the carpal tunnel (carpal tunnel). The disease has a great impact on labor and quality of life, is one of the major causes of absenteeism, even loss of hand function. Early and accurate diagnosis is an important factor in the treatment and preservation of hand function.
1. What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), also known as carpal tunnel syndrome, is a single nerve injury most commonly caused by compression of the median nerve at the passageway. wrist tube. Clinical symptoms include paresthesia and numbness of the thumb, index finger, middle finger and the outer half of the ring finger, which may be sharp or prickly, symptoms often occur at night, hand grip Weak and limited grip, which can cause muscle atrophy. The disease has a great impact on work, quality of life and is one of the biggest causes of absenteeism, even loss of hand function.A study in the US showed that 10% of the population had carpal tunnel syndrome in their lifetime, female/male ratio = 4/1 and over 50% of patients had bilateral CTS. Accordingly, there are many causes of the disease, which can be mentioned as: work (many hand movements, vibrations caused by vibration, especially recently common in people who often use computer mice), diseases Treatment of wrist arthritis, herniation of the synovial synovial tissue of the wrist joint, inflammation - fibrosis of the wrist ligaments, wrist injury. This syndrome is also common in some diabetic polyarthritis, chronic alcohol intoxication....
The carpal tunnel is the space between the carpal bones and the ligaments that surround the flexor tendons of the hand. The carpal tunnel is covered above by the carpal ligament (the fascia that holds the flexor tendon) and the surrounding walls. is the border of the carpal bones. The carpal tunnel, the median nerve goes together with the flexor tendons of the fingers in the carpal tunnel, because it is located in an inelastic structure, so when there is an increase in volume (the flexor tendons are inflamed or excessive and frequent wrist flexion and stretching postures, etc.), the median nerve is easily compressed, the small blood vessels that go close to the nerve are also compressed, causing hypotrophy. After passing through the carpal tunnel, the median nerve splits into branches that supply the motor worms 1 & 2, the short fascia of the thumb, the short flexor of the thumb (shallow bundle) and the thumb contralateral muscle, the innervating branches. This movement can detach in the carpal tunnel and pass through the carpal ligament (the membrane that holds the flexor tendon). In the palmar segment, the median nerve splits into branches supplying sensation to the 1, 2, 3 and 1⁄2 fingers of the 4th, dorsal 2, 3, and 3 fingers, and the lateral half of the 2 & 3 fingers of 4
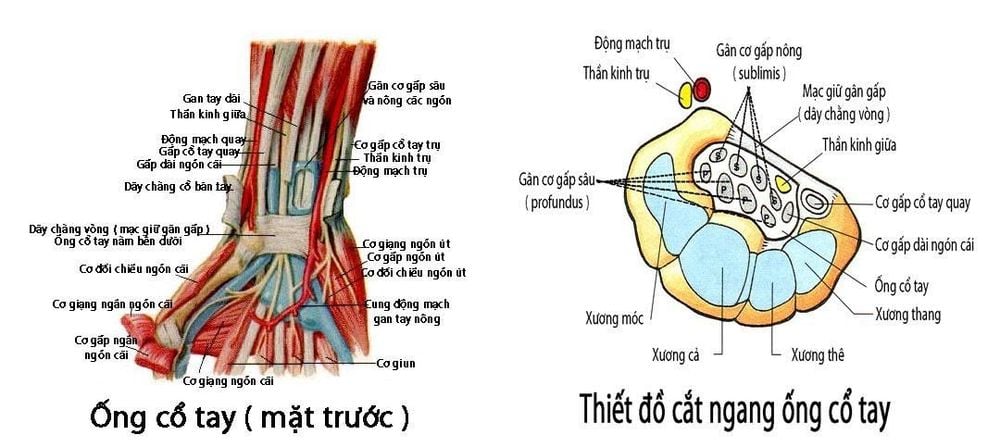
2. Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome should be based on clinical features (epidemiological, occupational, underlying disease, clinical symptoms...). However, carpal tunnel syndrome is a localized median nerve injury, so it's easy to confuse it and it's necessary to differentiate it from other medial neuropathy. Some peripheral nerve diseases and many CNS diseases have clinical symptoms similar to carpal tunnel syndrome. Clinically, the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome and the differential diagnosis is quite difficult when the symptoms are atypical, the patient has mixed lesions or is at a mild stage. Peripheral nerve lesions that need to be differentially diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome include: median nerve disease in the elbow area, brachial plexus disease, and cervical radiculopathy.
Sensory disturbances that can be confused with carpal tunnel syndrome are most commonly cervical radiculopathy, especially C6-C7 root lesions which can cause pain in both hands and sensory disturbances like as characteristic of carpal tunnel syndrome. Clinical signs suggestive of cervical radiculopathy are pain in the neck, radiating to the shoulder and arm, and worsening with neck movement. At that time, clinical examination suggestive of radiculopathy are abnormalities at C6-C7 level: abnormal tendon reflexes (biceps, rotator cuff, triceps), decreased proximal muscle strength (especially flexors, extensors, and pronations of the forearm) and palmar or forearm sensory disturbances exceed the sensory distribution of sensory disturbances in carpal tunnel syndrome.
Elbow median nerve disease and brachial plexus disease are less common than carpal tunnel syndrome, but are often clinically confusing. The most important suggestion is that the physical examination reveals signs of damage to the base of the median nerve: sensory disturbances in the hand and paralysis of the muscles that are innervated by the median nerve proximal to the wrist, especially flexor of thumb, pronation forearm, flexor wrist. In brachial plexus lesions, neurologic examination may reveal abnormalities similar to those in cervical radiculopathy, and paralysis and loss of sensation may extend beyond the distribution of a segment of the spinal cord.
There are many paraclinical methods to support the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome such as ultrasound of the median nerve at the wrist, MRI of the wrist. However, imaging methods only help diagnose when there is physical damage to the median nerve and surrounding tissues.
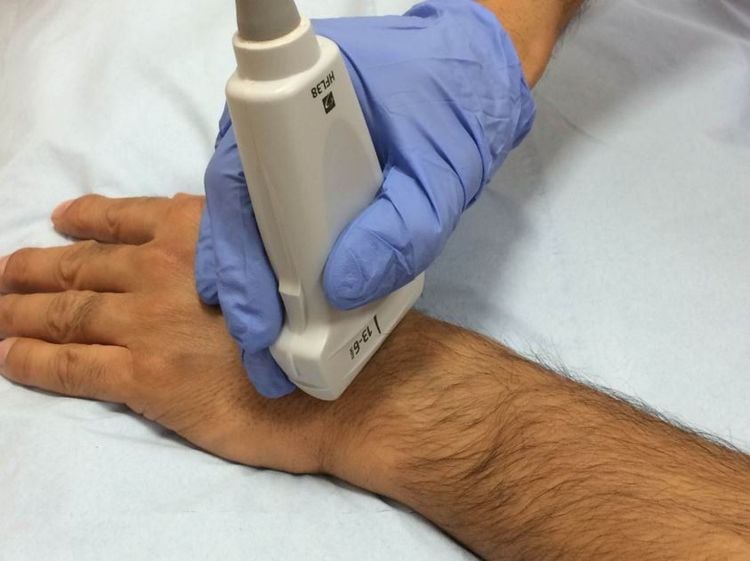
3. Electrodiagnostic method of carpal tunnel syndrome
Electrodiagnostic method (electromyography) helps to detect abnormalities of the median nerve conduction through the carpal tunnel even when there is no physical damage, even detect abnormalities even when the patient has not yet appeared. show symptoms. Many studies have demonstrated that electrodiagnostic results are the gold standard in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.
The electrodiagnostic investigation of a patient with suspected carpal tunnel syndrome is directed towards the following purposes:
To demonstrate slow or blocked conduction of the median nerve fibers through the carpal tunnel. Exclude median nerve disease at the elbow. Exclude brachial plexus disease that mostly affects the fibers of the median nerve. Exclude cervical radiculopathy, especially C6 – C7. If the patient has comorbid polyneuropathy, it should be demonstrated that there is a median median nerve conduction delay at the wrist that exceeds the delay expected from polyneuropathy alone. To do that, the electrical diagnostic survey needs to be done in a complete and methodical manner. The pathophysiology of carpal tunnel syndrome is typically a demyelinating lesion, which, depending on severity, may be accompanied by secondary axonal damage.
Electrodiagnostic method (electromyography) helps to detect abnormalities of the median nerve conduction through the carpal tunnel even when there is no physical damage, even detect abnormalities even when the patient has not yet appeared. show symptoms. Many studies have demonstrated that electrodiagnostic results are the gold standard in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.
The electrodiagnostic investigation of a patient with suspected carpal tunnel syndrome is directed towards the following purposes:
To demonstrate slow or blocked conduction of the median nerve fibers through the carpal tunnel. Exclude median nerve disease at the elbow. Exclude brachial plexus disease that mostly affects the fibers of the median nerve. Exclude cervical radiculopathy, especially C6 – C7. If the patient has comorbid polyneuropathy, it should be demonstrated that there is a median median nerve conduction delay at the wrist that exceeds the delay expected from polyneuropathy alone.
Therefore, any conduction delay of the median nerve compared with the ulnar nerve could be due to a delay in conduction through the carpal tunnel. Diagnostic capacity increases from about 75% using routine motor and sensory investigations to about 95% using these sensitive techniques.
Electromyography is important in detecting secondary axonal lesions. The detection of secondary axonal injury helps clinicians to predict and decide on more aggressive interventions than medical therapy and conservative approaches.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a disease of localized damage to the nerve holding the carpal tunnel, is a common disease and is easily misdiagnosed with other medial nerve damage such as: cervical radiculopathy, brachial plexus, median nerve damage at the elbow. Some polyneuropathy and CNS disorders also have symptoms that are easily confused with carpal tunnel syndrome. Electrodiagnostic is a method to probe the function of median nerve conduction, the results are valuable as a gold standard in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. However, this technique needs to be performed in a complete and methodical manner, in order to detect median nerve conduction delay even when symptoms are atypical.
When there are symptoms suggestive of carpal tunnel syndrome, such as: pain radiating from the wrist and arm with sensory disturbances in the hand, diffuse aching sensation, rarely localized to include the entire arm, sensory disturbances (pins and needles, burning pain, numbness...) often appear in the distribution area of the median nerve (thumb, index finger, middle finger, outer ring finger), Symptoms increase with wrist movement. You need to have an electrodiagnostic survey with a neurologist, to get an early and accurate diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome, and to predict and decide on the optimal treatment method for each level.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has performed surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome with a small incision. In particular, with the pioneering of electrical diagnostic techniques. Vinmec is one of the few addresses that deploys specialized techniques, with modern equipment of NATUS (USA), the specialist doctor after performing the examination, recording and reading the results will provide a method to diagnose the disease. accurately, giving the patient a chance to recover, safely treating carpal tunnel syndrome and leaving no complications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.