This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Van Duong - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.When unstable angina occurs, the patient should be diagnosed early on whether it is caused by acute coronary syndrome or not. Currently, myocardial biomarkers are important tests for early diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes.
1. Overview of acute coronary syndromes
Acute coronary syndrome is one of the leading causes of death related to cardiovascular disease. Over a short period of time, acute coronary syndromes can occur as either acute myocardial infarction or unstable angina.Unstable angina: The cause of unstable angina is mainly due to the sloughing off of atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries, incompletely clogging the coronary arteries and leading to blood flow. The heart is reduced, depriving the heart of oxygen and nutrients, causing the heart muscle to work ineffectively. While unstable angina occurs when the body is asleep or at rest, stable angina occurs only during physical exertion. Acute myocardial infarction: Acute myocardial infarction occurs when the myocardium is necrotic. There are two types of acute myocardial infarction with ST wave elevation and without ST wave elevation on electrocardiogram. Based on clinical symptoms, ECG measurement and cardiac markers can diagnose acute myocardial infarction early. However, acute non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction on the electrocardiogram (also known as silent myocardial infarction) is more difficult to diagnose. Currently, myocardial biomarkers play an important role in the early detection of acute myocardial infarction because this test has high sensitivity and specificity.
2. Cardiac markers in early diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes
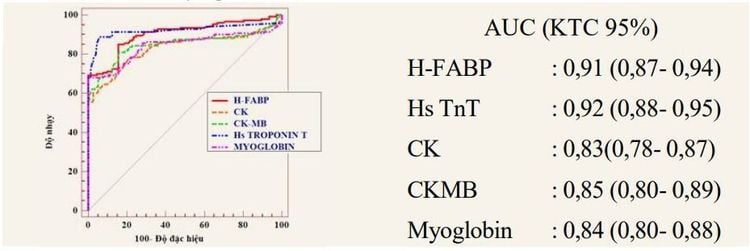
2.1 Cardiac markers Clinically, myocardial biomarkers used for early diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes include:Troponins: Troponins include troponin C, troponin I and troponin T, which are complex proteins found in cardiac and skeletal muscle. In which, in the myocardium, there are many troponin T and troponin I (TnT and TnI). When myocardial cells are injured, they release TnT and TnI into the blood, so they are important myocardial biomarkers in the diagnosis and detection of damaged myocardium. However, now hs-TnT and hs-TnI are used more because of their higher sensitivity. The mean value of hsTnT was 17pg/mL (range 14-19 pg/mL), in which it was 18.6 pg/mL for men (range 17-25pg/mL) and 12 pg/mL for women; The mean value of hsTnI in men is 2.5 pg/mL (range 1.9-3.4 pg/mL), female is 1.7 pg/mL (range 1.4-3.4 pg/mL). . CK-MB: CK (short for creatine kinase) is an enzyme found in many muscles that plays a role in muscle contraction. CK-MB is one of three iso-enzymes found in the heart when combining 2 subunits M and B together (there are also CK-MM and CK-BB). When there are signs of necrosis, the myocardium will release CK-MB into the blood, so CK-MB is also considered as one of the myocardial biomarkers to help detect damaged myocardium. CK-MB values in normal people range from 0.6-6.3 ng/mL. Myoglobin: Myoglobin is a protein in skeletal muscle and heart, not present in muscle tissue. When the myocardium is damaged, myoglobin is rapidly released, so myoglobin is considered one of the important cardiac markers in the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Myoglobin can be combined or replaced with/with troponin T or troponin I because myoglobin is also present in skeletal muscle. Normal values for myoglobin are between 0-85 ng/mL. H-FABP: H-FABP (Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein) is a cardiac fatty acid-binding protein that is abundant in cardiac muscle but less abundant in skeletal muscle. When myocardial damage occurs, the myocardium releases H-FABP into the blood and thus H-FABP is also a cardiac marker used to diagnose acute myocardial infarction. H-FABP is especially important when other cardiac markers such as TnT, TnI are not elevated. The normal value of H-FABP is <5.6 ng/mL. See also: Diagnosis and treatment of acute coronary syndrome
Chest pain: Chest pain usually comes on suddenly with varying intensity depending on the individual patient. People. After appearing in the chest, the pain can slowly spread to the shoulders, arms, neck and jaw area. However, not most cases of angina are acute myocardial infarction. Other symptoms: In addition to angina, the patient also feels short of breath, nausea or vomiting, dizziness, headache, profuse sweating, bloating, a feeling of wanting to defecate, ...
3. The role of cardiac markers in early diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome
Currently, cardiac markers play an important role in early diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes, because:Patients have almost no typical symptoms of acute coronary syndromes, except for chest pain due to the syndrome. cause. The electrocardiogram method has no value in early diagnosis due to its low sensitivity, especially, in some cases the patient could not be diagnosed even though the electrocardiogram was performed. In addition, ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction can be detected by electrocardiogram. However, for acute non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, or unstable angina, cardiac markers must be performed to determine, because these values increase markedly with sensitivity and specificity. high. In elderly patients, chest pain accompanied by dyspnea makes diagnosis difficult. Therefore, cardiac markers are an important test for early diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes.
The Cardiology Department of Vinmec International General Hospital has always received much praise and satisfaction from domestic and international customers, being pioneers in successfully applying the world's most advanced techniques in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. treat cardiovascular diseases.
A team of highly qualified and experienced specialists: qualified doctors from Master's to Professor's and Doctor's degrees, reputable in medical treatment, surgery, interventional cardiac catheterization. Intensive training at home & abroad. In particular, Prof. TS.BS Vo Thanh Nhan - Cardiology Director of Vinmec Central Park was recognized as the first and only expert in Vietnam to be awarded the "Proctor" certificate on TAVI. State-of-the-art equipment, comparable to major hospitals in the world: The most modern operating room in the world; The most modern silent magnetic resonance imaging machine in Southeast Asia; The CT machine has a super-fast scanning speed of only 0.275s/round without the use of drugs to lower the heart rate; 16-sequence PET/CT and SPECT/CT systems help to detect early damage to cardiovascular organs even when there are no symptoms of the disease. Applying the most advanced advanced cardiovascular techniques in the world in treatment: Painless open heart surgery; Percutaneous aortic intervention without general anesthesia; Treatment of mitral regurgitation through the catheter has a success rate of 95%; Ventricular-assisted artificial heart transplantation for patients with end-stage heart failure prolongs quality of life beyond 7 years. Cooperating with leading cardiovascular centers in Vietnam and the world such as: National Heart Institute, Cardiology Department of Hanoi Medical University, University of Paris Descartes - Georges Pompidou Hospital (France), University of Pennsylvania (France), University of Pennsylvania United States)... with the aim of updating the most modern cardiovascular treatments in the world. To register for examination and treatment with the leading doctors of the Cardiology Department at Vinmec International General Hospital, please click the "Contact Us" button on the website, or register for an online examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.