This is an automatically translated article.
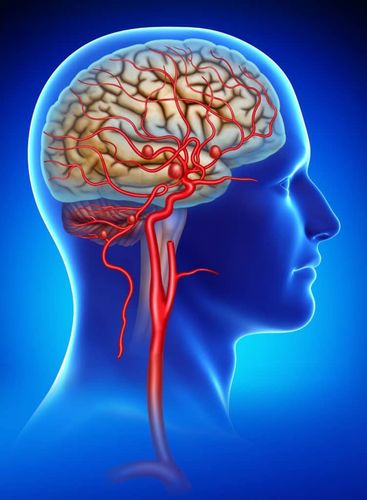
Cerebral aneurysm is a disease of blood vessels located in the brain that are at risk of rupture, causing intracranial haemorrhage and possibly death if the aneurysm ruptures suddenly. Brain aneurysm surgery is the procedure used to treat this condition. Brain aneurysm surgery can cause a number of dangerous complications.
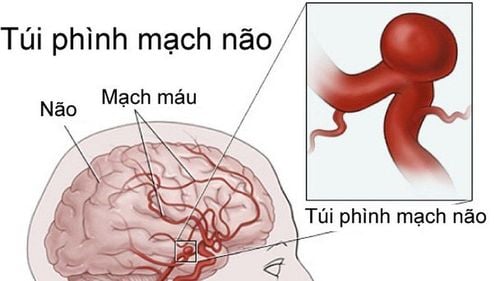
1. What is a brain aneurysm?
Cerebral aneurysm is an enlarged blood vessel inside the brain. The disease causes a brain vessel to leak or burst, causing a brain hemorrhage. Cerebral aneurysms can be life-threatening when a brain artery ruptures, which can lead to stroke, brain damage, and even death if not treated right away. However, not all aneurysms will rupture.
The cause of cerebral aneurysms is because the artery walls are thin and it usually occurs at the junction or division of the artery because these parts of the blood vessel are weaker.
When the patient has a cerebral aneurysm, if exercising too hard; use stimulants; Being angry or surprised can cause the aneurysm to burst. Common symptoms of cerebral aneurysm disease include:
When the aneurysm bursts: The patient suddenly has a severe headache; nausea and vomiting; stiff neck; dizziness; convulsions; loss of consciousness; drooping eyelid,... Leaky aneurysm: Sudden severe headache. The rupture of an aneurysm is worse after a leak. Unruptured aneurysms: In some cases, there may be no symptoms. Other conditions can cause pain above and behind the eye; pupil dilation; blurred vision; numbness, weakness, or paralysis on one side of the face ; eyelid collapse.

Túi phình rò có thể dẫn đến tình trạng đau đầu dữ dội
2. Brain aneurysm surgery
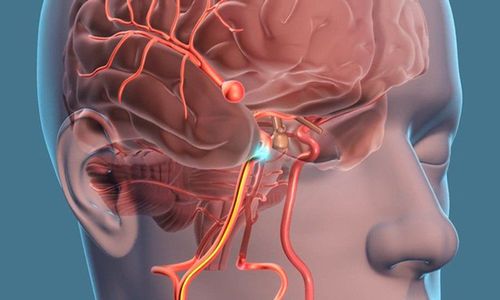
2.1. When is brain aneurysm surgery necessary? A brain aneurysm can lead to a stroke or brain damage if it's left untreated. Brain aneurysm surgery is a procedure used to treat a bulging blood vessel in the brain that is at risk of bursting or tearing. However, not all brain aneurysms require immediate surgery. The likelihood of a brain aneurysm depends on your age, medical history, and the size and location of the aneurysm.
Small aneurysms and aneurysms in the arteries located in the front of the brain are less likely to rupture. Aneurysms smaller than 7mm that are less likely to rupture can be monitored to make sure the aneurysm is not getting larger.
2.2. Steps of brain aneurysm surgery Step 1: Prepare specialized tools for brain aneurysm surgery. Step 2: General examination of the patient. Step 3: Clamp: The surgeon makes an incision in the scalp to make a small hole in the skull; Place a small metal clip at the base of the aneurysm to prevent it from bursting, then close the skull and suture the scalp. In the case of intravascular surgery, the surgeon inserts a small wire into an artery in the groin, directing the small wire through the incision to follow the artery to the brain aneurysm. A catheter will follow the wire and thread thin metal wires into the aneurysm to prevent the aneurysm from bursting.
3. Complications after brain aneurysm surgery and how to manage
All surgeries can have mild to severe complications. For brain aneurysm surgery, the most common complications include: Aneurysm rupture, brain contusion, bleeding, vascular clamping, recurrent bleeding, infection or postoperative cerebral edema.
Tai biến thường gặp nhất sau phẫu thuật là vỡ túi phình
Management:
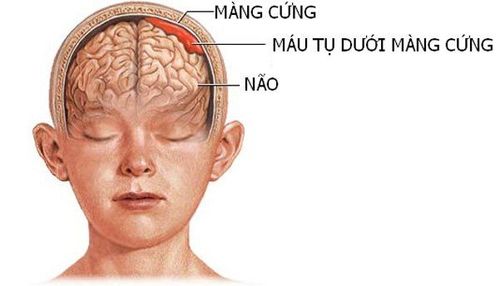
Aneurysm rupture: Prepare carefully for hemostatic methods such as temporary clamping, compression of the internal carotid artery, clamping of the internal carotid artery or around the aneurysm Brain contusion: Avoid direct pressure on the cerebral cortex. Use cotton, rubber pieces to protect the brain from damage. Intracranial hematoma: Intracranial hematoma includes subdural, epidural, and intracerebral hematoma. Diagnosis is based on clinical evidence, computed tomography. Surgery to remove the hematoma, stop bleeding if the hematoma is large, compressing causes increased pressure in the skull and worsening consciousness. Cerebrospinal fluid leak: Cerebrospinal fluid leak is a scary complication because cerebrospinal fluid leaks pose a high risk of infection and meningitis. Treatment of cerebrospinal fluid leak by conservative method of continuous lumbar puncture, Diamox drug. If not, the leak must be operated on. Meningitis: Meningitis usually occurs after a cerebrospinal fluid leak. Isolation of bacteria to determine the antibiogram to treat meningitis is the most effective method. Wound infection, osteomyelitis: surgical removal of inflammatory tissue, inflammatory bone, antibiotic treatment (isolation of bacteria from the infection site, antibiogram). Some neurological problems that affect memory, coordination, or other functions may occur after surgery. They can vary in severity, and can be temporary or permanent. In most cases, the risks of not having surgery will outweigh the risks associated with surgery.
4. Living habits help limit disease progression
You will be able to control this disease if you take the following measures:
Quit smoking and drugs. Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and low-fat dairy products; Exercise regularly but do not overdo it; Monitor high blood pressure or high cholesterol. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Why is brain aneurysm dangerous? Extremely dangerous brain aneurysms Subjects prone to brain aneurysms