This is an automatically translated article.
Brain aneurysm is one of those health problems that happen silently but is a “slow bomb” for anyone. On average, this pathology occurs in about 2% - 8% of the population worldwide. Knowing the common locations of cerebral aneurysms will support more effective treatment.
1. What is a brain aneurysm?
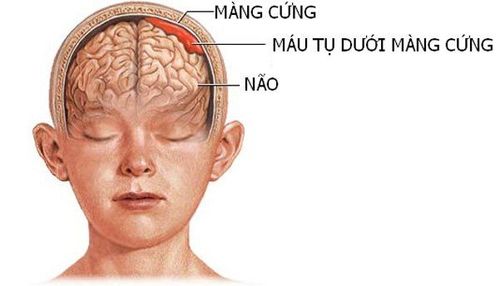
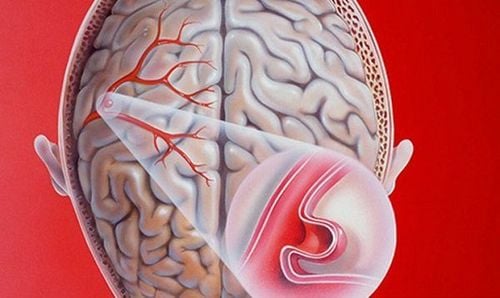
Brain aneurysm is a neurological condition in which the blood vessels of the brain swell to resemble a “berry”. This condition increases the risk of bleeding in the brain or a blood vessel bursting, causing a brain haemorrhage.
Cerebral aneurysms often occur simultaneously in many cerebral vessels and rarely appear in a single vessel. These aneurysms are potentially life-threatening, especially when they are located in a brain artery.
According to the Cerebral Aneurysm Support Foundation, not every aneurysm will cause a ruptured blood vessel. However, when a cerebral artery ruptures, the patient will easily have a stroke and have a high chance of leaving serious brain damage, even death.
2. Some common locations of cerebral aneurysms
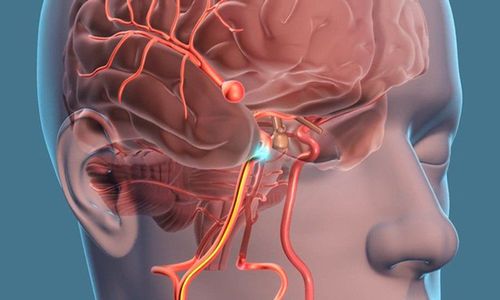
The most common type of brain aneurysm is a cerebral aneurysm, which occurs in 90% of brain aneurysms. This type of aneurysm is also called an aortic aneurysm, aneurysm, or berry... Cerebral aneurysms are often shaped like a "berry" with a narrow stem. Often, a patient may have more than one brain aneurysm.
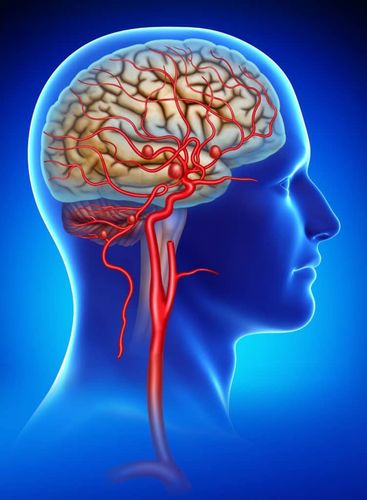
Brain aneurysms occur frequently in arteries located in the anterior part of the brain, especially in the branching area of blood vessels. This is also the group of arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to brain tissue. In reality, however, any arterial region in the brain can develop a brain aneurysm.
The cause of formation of these aneurysms is related to blood dynamics that has exerted pressure on the branches of the cerebral vessels in the bifurcation region, so this area is almost not resistant. In addition, some other causes such as vessel wall structure, infection, trauma, radiation, tumor... also cause brain aneurysms.
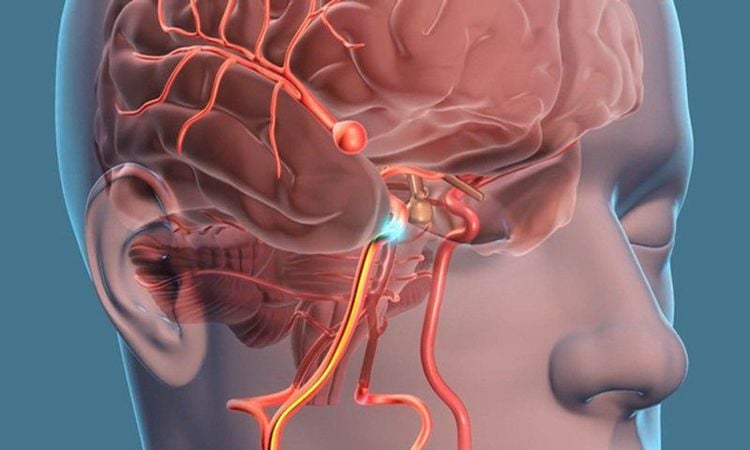
Áp lực máu lên các mạch nhánh não tạo thành các túi phình mạch
In addition to brain aneurysms, the two other types of brain aneurysms are rhabdoid aneurysms and dissection aneurysms.
Dissecting aneurysm is a term used to refer to a hematoma in the wall of a vessel, often associated with trauma or hypertension. And rhombus aneurysms are dilated segments of blood vessels. These circuits are usually very long and have a high degree of kink. A rhabdoid aneurysm is considered a consequence of severe atherosclerotic lesions, and is commonly located in the basilar artery.
3. Causes and risk factors for brain aneurysms
Regarding the cause, cerebral aneurysms can form due to thin arteries or weaker branching sites compared to other sites. Some of the following factors increase the risk of developing an aneurysm in the brain:
Family history or personal medical history; Gender: women are more likely to get the disease than men; High Blood Pressure; Cigarette; Due to trauma or genetics... Along with that, the danger of brain aneurysms lies in the fact that when a blood vessel ruptures, it will lead to serious complications. Some of the following factors are likely to promote aneurysm rupture:
Excessive exercise; Ischemic bowel syndrome; Excessive emotions such as grief, anger, surprise...; sexual relations;
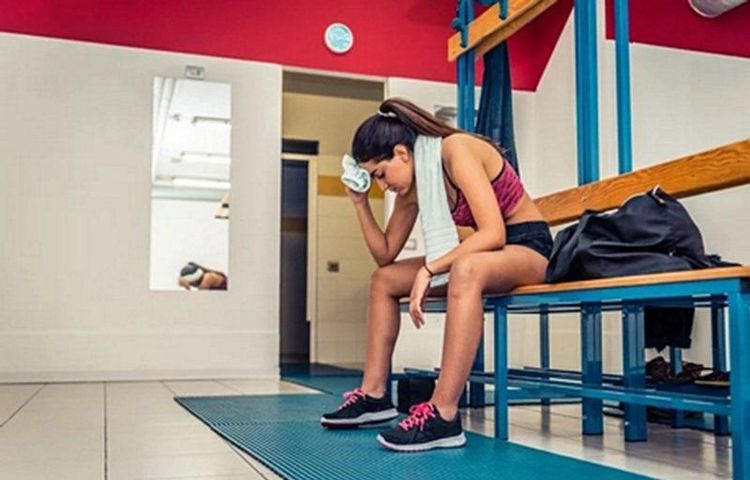

Vận động quá sức có thể làm tăng khả năng vỡ túi phình
4. Common symptoms of brain aneurysm
After studying the common locations of cerebral aneurysms, it can be seen that the aneurysms in the cerebral arteries have a large proportion and are also the most dangerous. Depending on the stage of the disease and based on the state of the brain aneurysms, the symptoms of brain aneurysms can vary.
4.1 In case of ruptured brain aneurysm The patient will feel a sudden, intense and severe headache. In addition, a ruptured cerebral aneurysm can cause more pronounced symptoms including:
Stiff neck, inability to rotate; Nausea and vomiting; Visual disturbances, blurred or double vision, special sensitivity to light; Loss of consciousness, convulsions.
4.2 Cases where the brain aneurysm just leaks In some cases, blood in the artery at the site of the aneurysm can leak out a small amount. At that time, the patient may experience sudden episodes of severe headache. However, there are not as many symptoms as in the case of a ruptured aneurysm.
4.3 Unruptured Cerebral Aneurysms In the absence of rupture, these aneurysms are unlikely to cause obvious symptoms. However, for some large aneurysms, it will put pressure on brain tissue and nerves, thereby causing:
Dilated pupils; Soreness above and behind the eyes; Visual disturbances, easy double vision; One side of the face is weak or even paralyzed. Thus, knowing well about cerebral aneurysms and common locations of cerebral aneurysms will create more favorable conditions for treatment. In addition, you need to visit regularly to monitor the condition of the aneurysm to get the appropriate instructions from the doctor.
You should build a healthy lifestyle, regularly exercise, strengthen the body's resistance and avoid stress. Don't forget to check your health regularly for appropriate adjustments.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages for many different subjects. You can choose a package that suits your needs such as:
Children's General Health Checkup Standard General Health Checkup Comprehensive General Health Checkup Special General Health Checkup VIP General Health Checkup General health Diamond To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.
Reference source: columbianeurology.org