This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by a doctor of Biochemistry - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Ha Long International HospitalHCG is a test used routinely to confirm pregnancy or not, to monitor fetal development. HCG is also used in the diagnosis and monitoring of the effectiveness of germ cell cancer treatment.
1. What is HCG?
HCG is an abbreviation of the phrase Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, known as Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) belongs to the glycoprotein family and consists of 2 subunits (α and β chains) that combine to form an intact hormone. .2. Origin of hCG
In pregnant women, HCG is produced in the placenta during pregnancy and the biological activity of hCG helps maintain the corpus luteum during the first weeks of pregnancy. The serum of pregnant women mainly contains intact hCG. However, a small fraction of the α and β subunits circulate as unbound (Free beta HCG). The percentage of F.B hCG averages ~1% compared with intact hCG.In non-pregnant humans, hCG can also be produced from trophoblastic tumors, germ cell tumors with a trophoblast component, and some non-trophoblastic tumors.
3. When is the hCG test used?
In current medical examination and treatment, there are two types of HCG tests: quantitative beta HCG (B.hCG) and quantitative Free beta hCG (F.B hCG).3.1. Free beta hCG quantitative test (F.B hCG) The quantitative test of F.B hCG in pregnant mother's blood is used as a screening test for the risk of fetal chromosomal abnormalities (chromosome 13, 18 and 21) during pregnancy. week 11-13 of pregnancy (Double test, including F.BhCG and PAPP-A).
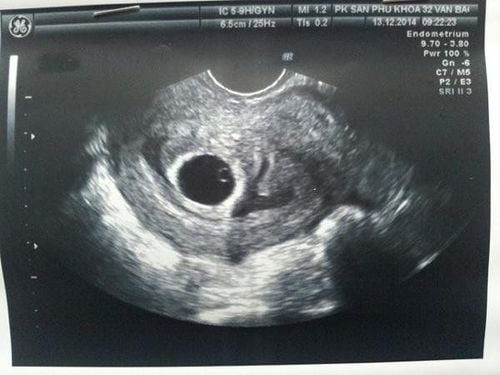
3.2.Quantitative beta hCG (B hCG) test 3.2.1. Diagnosis and monitoring of pregnancy In case it is necessary to confirm pregnancy or not. When to monitor fetal development: Usually (up to 85% of pregnant women) hCG levels will double every 48 to 72 hours in the early weeks, reaching a peak between 11-12 weeks of pregnancy. pregnancy, then taper and level off for the rest of the pregnancy. When there are abnormalities in the fetal development process (eg, fetal growth retardation, stillbirth, miscarriage) the change in BhCG concentration will be especially significant for the assessment and prognosis of fetal development. The quantitative test for B.hCG in pregnant women's blood is used in the screening test for fetal chromosomal abnormalities (chromosome 13, chromosome 18, and chromosome 21) during the 16-18 week of pregnancy (Testing) Triple test ).

Xét nghiệm định lượng beta HCG được sử dụng để chẩn đoán, theo dõi thai nhi
In men and non-pregnant women, hCG and AFP levels are very low:
Example: Cobas test, the reference range is as follows:
+ Beta hCG: Male: < 2.6 mIU/mL
Healthy female not pregnant: Premenopausal: ≤ 5.3 mIU/mL; Postmenopausal: ≤ 8.3 mIU/mL
+ AFP ≤ 7 ng/mL in men and non-pregnant women.
When levels of AFP and BhCG are simultaneously elevated, it is an indicator of germ cell cancer. In the treatment of germ cell cancer, AFP and hCG levels support monitoring and evaluation of treatment effectiveness: With effective treatment, AFP and BhCG levels decrease and may return to normal; if AFP and BhCG levels do not decrease or continue to increase, then the treatment is not effective; If the levels of AFP and BhCG have decreased and increased again, it indicates a recurrence of cancer or the appearance of new cancer.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.