This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Viet Thu - Doctor of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Dr. Nguyen Viet Thu has more than 20 years of experience working in the field of diagnostic imaging, former Secretary of the Hanoi Department of Radiology, directing the lower level in the field of Diagnostic Imaging.Abdominal X-ray without preparation is one of the most common laboratory methods used to orient the diagnosis as well as find the cause of the disease when the patient has symptoms of abdominal pain. For each specific patient case for different diseases, the requirements for the basic imaging position of the unprepared abdominal X-ray are also different.
1. What is an abdominal X-ray?
X-ray is a method of using the energy of X-rays which is a type of radiant energy capable of focusing into a beam of light that penetrates the organs of the human body and produces images on a projection screen. For organs and solid tissues in the body such as bones, the ability to absorb X-rays is very high, so the resulting image is usually white. In contrast, with hollow organs such as the stomach and intestines, the ability to absorb X-rays is lower, so the X-ray beams reaching these organs can reach the projection screen more, so the image is often gray. With the feature of being able to pass through mainly air, the images recorded when taking a chest x-ray are usually black.X-ray of the abdomen is a common imaging method today, giving imaging results of some organs in the abdomen such as stomach, liver, spleen, large intestine, small intestine, diaphragm and some other muscles at the junction of the chest and abdomen. This is one of the first laboratory indications that the treating doctor gives to a patient with symptoms of abdominal pain, bloating, nausea and vomiting, helping to find the cause of these symptoms quickly. best. In addition, a number of other subclinical indications are also performed to confirm the diagnosis such as abdominal ultrasound, abdominal computed tomography, urography with intravenous contrast.
Find the cause of the patient's pain, swelling in the abdomen or the feeling of nausea and vomiting several times a day. Find the cause of the pain in the lower back on both sides. Look for gallstones, kidney stones, ureteral stones, or bladder stones. Investigate for gas outside the intestines, such as air under the diaphragm. Look for foreign bodies in the body's abdominal cavity due to being swallowed or not. Abdominal X-ray is also taken in some procedures such as gastric tube placement, renal drainage... to determine the appropriate position and length of these tubes in the internal organs that the naked eye can see. cannot be observed.
2. X-ray abdomen unprepared
Unprepared abdominal radiograph is an upright abdominal radiograph, the primary purpose of which is to assess the water-vapor status in intestinal obstruction and to evaluate the free air in the abdomen in case of perforation of the hollow viscera.X-ray - unprepared abdomen is the first laboratory indication of a doctor before a patient is admitted to the hospital because of abdominal pain, because this imaging technique is common, common, and has a low radiation dose.
Some indications of unprepared abdominal X-ray are:
Patients with suspected bowel obstruction. The patient has a perforated hollow viscera and has free air in the abdomen. Assess for contrast-enhanced foreign bodies. Contrasts of gallstones, pancreatic stones and some cases of urinary stones... For patients with intestinal obstruction, there can be 2 types: mechanical intestinal obstruction and functional intestinal obstruction:
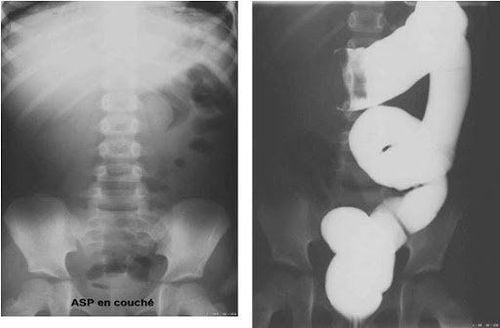
Mechanical intestinal obstruction Study: Unprepared abdominal X-ray may show some radiographic findings such as dilatation of the bowel above the obstruction during the first 3 to 8 hours after the obstruction, visualization of the air-fluid level above the obstruction. In about 12-24 hours after bowel obstruction, in contrast, there are cases where the image of loss of air below the intestinal obstruction appears about 12 to 48 hours after intestinal obstruction, the two air levels are often different from each other for the same loop. intestine. Functional intestinal obstruction: The cause of functional intestinal obstruction is usually not due to obstruction but due to some other causes such as peritonitis, abdominal trauma or patients with electrolyte disturbances... Therefore, X-ray results - Unprepared abdominal radiographs in patients with functional bowel obstruction often show no signs of obstruction, no bowel movements, and patients have total or focal dilatation of the bowel, in addition, the two air-fluid levels are often equal for the patient. with a loop of intestine. Unprepared abdominal X-ray images can also guide the distinction of patients with small bowel obstruction or colonic obstruction. If it is small bowel obstruction, the location of the obstruction is usually located in the center of the abdomen, the mucosa runs across the entire diameter of the diameter and is small, the width of the loop is usually larger than the height, many obstructions in the intestine can be seen and Usually there is no image of stool in the intestine. As for colonic obstruction, it is usually located in the periphery of the abdomen, the mucosa only runs across a part of the aperture, large size and distance from each other, bowel loops are higher than width, the number of bowel obstructions is usually not profuse and present with fecal appearance in bowel loops.
3. Basic position of X-ray – unprepared abdomen
When taking an unprepared abdominal X-ray, there are certain precautions that need to be taken, in which some basic X-ray positions of the unprepared abdomen that the patient may be asked to perform are as follows:Upright position: As one of the most common positions, the patient is asked to stand upright, bring the abdomen to the film and take the image from back to front, the patient may need to lean to the right or to the left for certain cases. Supine position: The film is placed behind the patient and the X-ray is directed from front to back, can be taken in combination with parallel X-rays on the table. In some other cases, the patient will have to lie on the right or left side depending on the condition of the disease. In addition, an unprepared abdominal X-ray film needs to ensure some of the following factors to be a qualified radiograph, helping to best support the diagnosis:
The X-ray film must capture all major anatomical landmarks. of the abdomen such as two diaphragms, the more pelvic sections, the better. The right film shows the image of the lumbar spine, the lumbosacral shadow and 2 bands of paraperitoneal opacity.
4. Conclusion
Unprepared abdominal X-ray is considered an indispensable laboratory technique in most diseases related to the gastrointestinal tract and some urinary tract diseases. of gastrointestinal diseases with the most common symptom being abdominal pain.Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORE
CT scan of the abdomen: What you need to know Indications of X-ray of the small intestine Measures to treat intestinal obstruction