This is an automatically translated article.
Bartholin's gland inflammation is a disease that is common in women of reproductive age, but not all women are at risk of this disease. Bartholin's gland inflammation is dangerous, does it go away on its own?
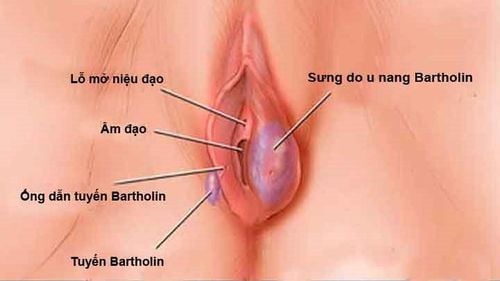
1. What is Bartholin's gland disease?
Bartholin's gland is a small, spherical gland about 1cm in diameter and it is located under the skin on either side of the vagina. Bartholin's glands are made up of mucus-secreting columnar cells, which secrete mucus to help keep the vagina moist and lubricate the vagina during sexual intercourse.
When the Bartholin gland is inflamed, it will appear as a cyst. So, the severity of the disease will depend on the size of the large or small cyst. Based on that, the doctor will evaluate the possibility that the Bartholin's cyst is infected, making the disease worse or not to give appropriate treatment.
The cause of Bartholin's gland inflammation is because the ducts are blocked while the gland is still secreting mucus, causing a blockage of vaginal secretions in the gland. The source of duct obstruction is infection with sexually transmitted bacteria such as Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and intestinal bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E.coli) or trauma to the area. genitalia caused.
Women are at risk for Bartholin's gland inflammation at any age, but women between the ages of 20 and 29 have a higher incidence. Factors that increase the risk of Bartholin's gland disease include:
Women who are pregnant Women with diabetes Having unprotected sex, creating favorable conditions for bacteria to enter and susceptible to sexually transmitted diseases.
2. Is Bartholin's gland disease dangerous?
In the early stages, when Bartholin's cysts are small, they usually won't cause any symptoms. Bartholin's cysts are usually only discovered when a patient notices a small painless mass just outside the vaginal opening, or a doctor detects it during a pelvic exam.
However, if Bartholin's gland inflammation develops with cysts larger than 1cm in diameter, they will cause pain and discomfort when you sit and during sex. If an infected Bartholin's cyst becomes swollen, hard, and filled with pus, you will have symptoms of fever, extreme pain, and difficulty sitting or walking. Infected Bartholin's gland cyst will often form an abscess, which will usually grow very quickly within 2-4 days.
Bartholin gland inflammation will make the bartholin gland no longer secrete mucus into the vagina and cause burning sensation during sex, and it will stimulate the bladder so the patient is very prone to urinary disorders. Bartholin gland cysts or abscesses will typically occur only on one side of the vaginal opening.
To know how dangerous Bartholin's gland inflammation is, you will need to monitor in many different aspects such as the area of inflammation, the possibility of infection, the pain in the body.
3. Bartholin's gland inflammation is self-healing?
Through the process of examination and testing, depending on the condition of each patient, the doctor will offer an appropriate treatment plan for Bartholin's gland inflammation.
For Bartholin's cysts that are small in size and do not have symptoms such as pain, discharge, it can go away on its own without treatment. However, you will still need to visit your doctor at regular intervals so that you can monitor the growth of your cysts. For cases of Bartholin gland swelling, mild inflammation, you can use the method of washing with hot water several times a day to make the cysts burst quickly. Using hot compresses can also help relieve symptoms. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics in combination with anti-inflammatory pain relievers to relieve pain and dissolve cysts. For cases where the Bartholin's cyst has grown and the cyst has become an abscess, causing swelling, pain, infection, and pus discharge, there are two common treatments available today: the Bartholin's cyst incision method. : With this method, the doctor will inject local anesthetic, use a scalpel to make a small incision in the cyst for the fluid to drain out, then the doctor will sew around the edge of the cyst with soluble thread to help regenerate the cyst. Bartholin gland cyst removal method: This method will completely remove the Bartholin gland cyst. After the procedure, your doctor will often prescribe you medications such as antibiotics, pain relievers, and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and prevent infection. At the same time, you also need to use antiseptic cleaning solutions to clean the perineum.
4. Prevention of Bartholin's gland inflammation
It is very difficult to completely prevent the possibility of Bartholin gland inflammation in the body. However, if you have the following good habits that will help you prevent infection from occurring and minimize the risk of abscess formation:
Always maintain and clean the intimate area properly, keep Keep the external genitals dry and clean and use a suitable cleaning solution. When cleaning the private area, proceed from front to back so that bacteria from the anus do not spread to the vagina. Note that you only clean the outer area, do not douche deep inside the vagina. Have healthy, safe sex to avoid the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases. When you detect a small tumor at the entrance to the vagina or later, there are symptoms of pain or swelling in the vaginal area, you need to go to a medical facility to be examined and treated by a specialist. timely. Although Bartholin's gland inflammation is a rare disease, it is treatable, and it can even go away on its own if detected early by a doctor. So, when you notice any abnormal signs in the private area, go to the doctor immediately for proper diagnosis and timely treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.