This article has been consulted with Dr. Phan Diem Doan Ngoc, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Bartholin's gland cyst is a common gynecological disease in women of reproductive age. Whether a Bartholin's cyst is dangerous depends on its size, the degree of pain, and whether the cyst is infected. Additionally, attention must be paid to relapse potential and differential diagnosis to determine the appropriate treatment.
1. What is a Bartholin's cyst?
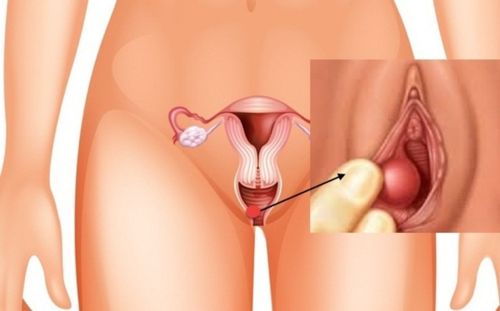
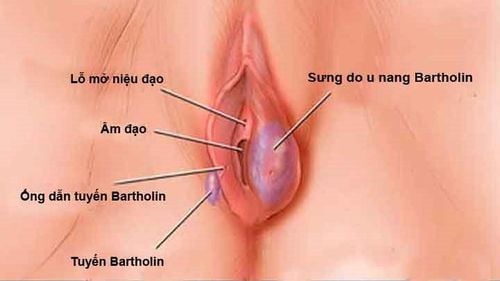
A Bartholin cyst, also known as Bartholin's gland inflammation, is a cystic lesion in Bartholin's glands. These glands are located on each side of the vulva (the external part of the vagina). The function of these glands is to secrete fluid on the surface of the labia minora to moisturize and lubricate during sexual intercourse.
Sometimes, the ducts of the Bartholin glands can become blocked, causing the fluid to flow back into the gland, which results in the formation of a thin-walled, painless cyst, known as a Bartholin cyst. If the fluid in the cyst becomes infected, it can lead to an abscess, which is an accumulation of pus surrounded by inflamed tissue.
Bartholin cysts and abscesses are common pathologies. The severity of a Bartholin cyst depends on the size of the cyst, the level of pain, and whether the cyst has become infected. These factors also guide doctors in selecting the appropriate treatment after a correct diagnosis.
In some cases, patients may only need home treatment under the guidance of a doctor. However, for more severe cases, the doctor may recommend surgery to drain the cyst. If an infection occurs, treatment may include antibiotics.
2. Is Bartholin’s Cyst Dangerous?
If a small, non-infected Bartholin cyst is present, the patient may not experience any symptoms. If the cyst grows, the patient may begin to notice a lump near the vaginal opening. Most cases of Bartholin cysts are painless. Whether a Bartholin's cyst is dangerous depends on its size, the degree of pain, and whether the cyst is infected. Additionally, attention must be paid to relapse potential and differential diagnosis to determine the appropriate treatment.
In severe cases of infection, the Bartholin cyst can evolve into an abscess within a few days. Symptoms of an infected Bartholin cyst may include:
- A lump causing pain near the vaginal opening
- Discomfort when walking or sitting
- Pain during sexual intercourse
Fever
Symptoms of a Bartholin cyst or abscess usually occur on one side of the vulva.
Patients should seek medical attention if the painful lump near the vaginal does not improve after 2 to 3 days of self-care, such as warm water baths. If a lump near the vaginal is detected in women over 40, a doctor should be consulted for an evaluation. Although rare, such a lump could be a sign of a more serious condition, such as cancer. If the pain worsens, the patient should see a doctor as soon as possible.
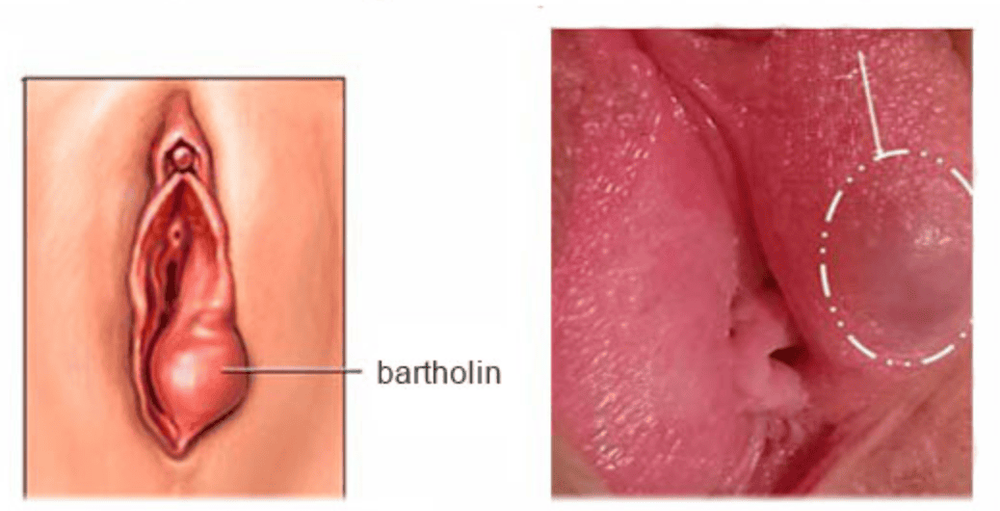
3. Causes of Bartholin Cysts
The cause of a Bartholin cyst is the blockage of vaginal secretions. Fluid can accumulate when the duct becomes obstructed, which may result from infection or injury.
Bartholin cysts can lead to infection and abscess formation. Some bacteria, including Escherichia coli, and sexually transmitted bacteria such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis, are common causes of infection.
4. Diagnosis of Bartholin Cyst
To diagnose a Bartholin cyst, a doctor may:
- Take the patient's medical history
- Do a pelvic examination
- Collect a sample of vaginal or cervical discharge to check for sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Recommend a biopsy to screen for cancerous cells, especially if the patient is postmenopausal or over 40 years old.
5. Treatment of Bartholin Cyst
In most cases, Bartholin cysts do not require treatment, especially if the gland is not symptomatic. When treatment is needed, it depends on the cyst's size, the degree of discomfort, and whether there is an infection (which could lead to an abscess).
Treatment options for Bartholin gland inflammation include:
- Warm Sitz Baths: Soaking in a warm bath multiple times a day for three or four days may help small infected cysts rupture and resolve on their own.
- Surgical Drainage: If the cyst is infected or very large, surgery may be required to drain the cyst. This procedure is supported with anesthesia or pain relief. The doctor will make a small incision in the cyst to allow the fluid to drain, then insert a small rubber tube (drain) to keep the incision open for up to 6 weeks to ensure proper drainage.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed if the cyst becomes infected or if test results indicate a sexually transmitted infection. However, if the abscess is drained properly, antibiotics may not be necessary.
- Marsupialization: If the cyst recurs or significantly affects quality of life, marsupialization may be recommended. The doctor will create a permanent opening about 6mm wide to allow the fluid to drain. A drain is placed temporarily to promote drainage and prevent relapse

In rare cases, for persistent Bartholin cysts that do not improve with the above methods, the doctor may recommend surgery to remove the Bartholin gland. This procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia in a hospital operating room. This method may carry a higher risk of bleeding or complications compared to other methods.
6. Home Remedies
PatPatients can manage Bartholin cysts by taking daily warm sitz baths to help prevent infection or abscess formation.
After surgery to treat an infected cyst or abscess, warm baths are especially important to keep the area clean, alleviate discomfort, and promote effective fluid drainage from the cyst. Pain relievers may be needed if the pain is not manageable.
Currently, there is no way to prevent Bartholin cysts, but women can reduce their risk by practicing safe sex, using protection (e.g., condoms), and maintaining good hygiene. These measures help prevent infections and abscess formation.
For early detection and treatment of gynecological conditions, Vinmec International General Hospital offers a basic gynecological screening package to help detect infections and facilitate early treatment. The screening includes cancer detection (e.g., cervical cancer) even before symptoms appear.
Basic Gynecological Screening Package for women, regardless of age, with symptoms such as:
- Unusual vaginal bleeding
- Period issues (irregular cycles, abnormal duration)
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (foul smell, unusual color)
- Itching or pain in the genital area
- Women with risk factors such as poor hygiene, unsafe sexual practices, or a history of abortion
- Women with symptoms such as abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, pain in the genital area, and abnormal vaginal bleeding
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
References: mayoclinic.org