This is an automatically translated article.
Macrolide antibiotics (Azithromycin, Erythromycin...) are antibiotics widely used in the treatment of infectious diseases. So what should be noted when using Azithromycin to treat bacterial infections?
1. Uses of Azithromycin
Azithromycin is used to treat bacterial infections. This is a macrolide antibiotic, which works by stopping the growth of bacteria.Azithromycin oral tablet will not work for viral infections (such as common cold, flu). Overuse or misuse of any antibiotic (including Azithromycin) can lead to antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
2. Instructions for using Azithromycin oral tablet
Read all instructions for use carefully before treating an infection with Azithromycin. Azithromycin oral tablet is used by mouth, once daily, before or after meals as prescribed by the doctor. Patients can take the medicine after meals if they have stomach pain. The dose of Azithromycin depends on the severity of the infection, the patient's health status and response to treatment. Particularly for children, the dose of Azithromycin is calculated by weight.
For Azithromycin suspension, before use, shake the bottle well. Dose carefully with special measuring device, do not use household spoon that can give wrong dose. If the child vomits within 30 minutes of taking the medicine, call the doctor to see if the child needs to repeat the dose.
Use Azithromycin oral tablet according to the correct dose and time, continue taking it even if the symptoms of infection disappear. Stopping the medication too soon can allow bacteria to continue to grow, leading to a return of the infection.
Stomach antacids containing aluminum or magnesium may reduce the absorption of azithromycin if taken at the same time. Therefore, if you are taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, take them at least 2 hours (before or after) your dose of Azithromycin.
MORE: Possible side effects when using the antibiotic Azithromycin

Azithromycin cần được sử dung theo đúng hướng dẫn của nhân viên y tế
3. Azithromycin side effects
Common symptoms of Azithromycin include:
Stomach upset; Diarrhea with loose stools; Nausea, vomiting; Stomachache. If any side effects of Azithromycin persist or worsen, the patient should contact their doctor for instructions.
Some less common side effects of Azithromycin include:
Changes in hearing (such as hearing loss, deafness); Eye problems (such as drooping eyelids, blurred vision); Difficulty speaking, swallowing, muscle weakness; Signs of liver disease (eg, unusual tiredness, nausea, persistent vomiting, severe abdominal pain, yellow eyes, jaundice, dark urine). Some serious side effects of Azithromycin require medical attention:
Fast or irregular heartbeat; Severe dizziness; Faint. Azithromycin can cause diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile bacteria (resistant bacteria). The condition may occur immediately or after several weeks to months of stopping the drug. Do not use antidiarrheal drugs or opioids when the patient suddenly has persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain, gastrointestinal spasms, bloody stools, mucus.
Prolonged or repeated use of Azithromycin may lead to oral thrush, vaginal thrush or other yeast infections. Contact your doctor if you have white patches on your mouth, a change in vaginal discharge, or other symptoms of a fungal infection.
Drug allergy may occur when using Azithromycin oral tablet (the rate is not high). Be on the lookout for signs of a serious drug allergy to Azithromycin, such as persistent fever, swollen lymph nodes, rash, itching of body parts, dizziness, and trouble breathing. Allergic reactions can occur even after stopping the drug.

Azithromycin có thể gây ra một vài tác dụng phụ không mong muốn cho người bệnh
4. Precautions when using Azithromycin
Before taking Azithromycin, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to this active ingredient or to other antibiotics in the same class (such as erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin) or to any other allergies. Also, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: liver disease, kidney disease, certain muscle diseases (myasthenia gravis).
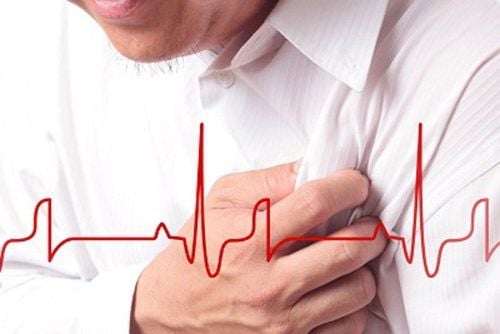
Azithromycin may affect heart rate (QT prolongation). QT prolongation is rare but can cause tachycardia, severe irregularity (rarely fatal), and other symptoms (severe dizziness, fainting). In this case, the patient needs immediate medical attention.
The risk of QT prolongation may be increased if the patient has certain medical conditions or is taking medications that can prolong QT. Therefore, before using Azithromycin, patients need to tell their doctor or pharmacist all the medicines they are taking and any heart problems if any (heart failure, bradycardia, QT prolongation in the ECG), Family history of QT prolongation in electrocardiogram, family history of sudden cardiac death.
Low levels of potassium or magnesium in the blood can also increase the risk of QT prolongation. This risk may be increased if you take certain medications (such as diuretics) or if you sweat a lot, have diarrhea, or are vomiting. Azithromycin may cause live attenuated bacterial vaccines (such as typhoid vaccine) to not work. Therefore, patients should not be vaccinated while using Azithromycin unless directed to do so by their doctor.
In addition, some subjects need to be careful when using Azithromycin as follows:
Elderly people are more sensitive to the side effects of Azithromycin, especially QT prolongation. Newborns (especially less than 6 weeks) may be at increased risk for some serious stomach problems when taking Azithromycin, and parents should contact their doctor immediately if their baby is vomiting or irritable while feeding. During pregnancy and lactation, Azithromycin should be used only when clearly needed and after discussing the risks and benefits with your doctor.
5. Azithromycin drug interactions
Drug interactions can change the way Azithromycin works or increase your risk of serious side effects. Patients need to make a list of all the products they are using (including prescription/nonprescription and herbal medicines) and then share it with their doctor and pharmacist, do not start/stop/change on their own. change the dose of any medicine without your doctor's approval.
Many drugs besides Azithromycin can affect heart rhythm (QT prolongation), including amiodarone, chloroquine, disopyramide, dofetilide, dronedarone, hydroxychloroquine, ibutilide, pimozide, procainamide, quinidine, sotalol...
Azithromycin only If you are prescribed an existing infection, do not use Azithromycin to prevent another infection unless directed to do so by your doctor. Azithromycin overuse or indiscriminate use increases the risk of side effects and the development of antibiotic resistance. Therefore, patients should choose reputable medical facilities with good expertise to treat the disease and guide the most effective use of antibiotics.
Azithromycin có thể tương tác với một số loại thuốc khác trên thị trường
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used the modern facilities and machinery system along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of the doctors. Good doctors, well-trained both at home and abroad.
In case it is necessary to use antibiotics to treat infectious diseases, doctors at Vinmec will provide a treatment regimen, and advise and guide patients to use drugs effectively, avoiding abuse. Indiscriminate use of antibiotics causes undesirable side effects such as antibiotic resistance.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com