This is an automatically translated article.
One of the major advances in obstetrics is the development of assisted reproductive technologies (ART). One of the most commonly used methods today is in vitro fertilization (IVF). This article will provide you with some information related to assisted reproduction and IVF
1. What is assisted reproduction?
In the 1970s, British doctors began removing eggs from women who had difficulty conceiving and fertilizing them in a laboratory. Researchers call this the experimental procedure for in vitro fertilization (IVF), and after many tries, the first in vitro baby was born in 1978.
Today, assisted reproductive technology (ART) refers to all treatments that involve handling eggs or embryos outside of the body, and this includes IVF and some variants of it. These procedures are often combined with fertility drugs to increase success rates, and about 22 percent of ART procedures (or cycles) can be successful and end with the delivery of a baby.
ART procedures are invasive, expensive, and can have side effects. When more than one embryo is placed in the uterus, there is a possibility of a multiple pregnancy if two or more embryos are successfully implanted. But so far, there are no long-term health effects associated with babies born with ART, and for many people with fertility problems, ART is the best chance to have a baby. child.
2. Popular assisted reproductive technology techniques
Below is a summary of the main ART techniques that are common today:
In vitro fertilization (IVF): Approximately 99 percent of ART procedures performed in the United States are IVF treatments. Eggs are combined with sperm in a laboratory. After fertilization, the resulting embryos develop for three to five days before being transferred to the woman's uterus. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI): About two-thirds of all IVF cycles performed in the United States use ICSI as the insemination method. In this procedure, a single sperm is injected directly into your egg, instead of placing multiple sperm next to the egg, as in IVF. After fertilization, the resulting embryos develop for three to five days before being transferred into your uterus. Donor eggs or embryos: If you can't conceive with your own eggs, you can have IVF treatment using eggs donated by another woman. The donor egg is combined with your partner's sperm, and the resulting embryo is transferred into your uterus. This method can also be done with donated embryos or donated sperm. Surrogacy (surrogacy): Another woman carries your embryo until full term and gives birth.
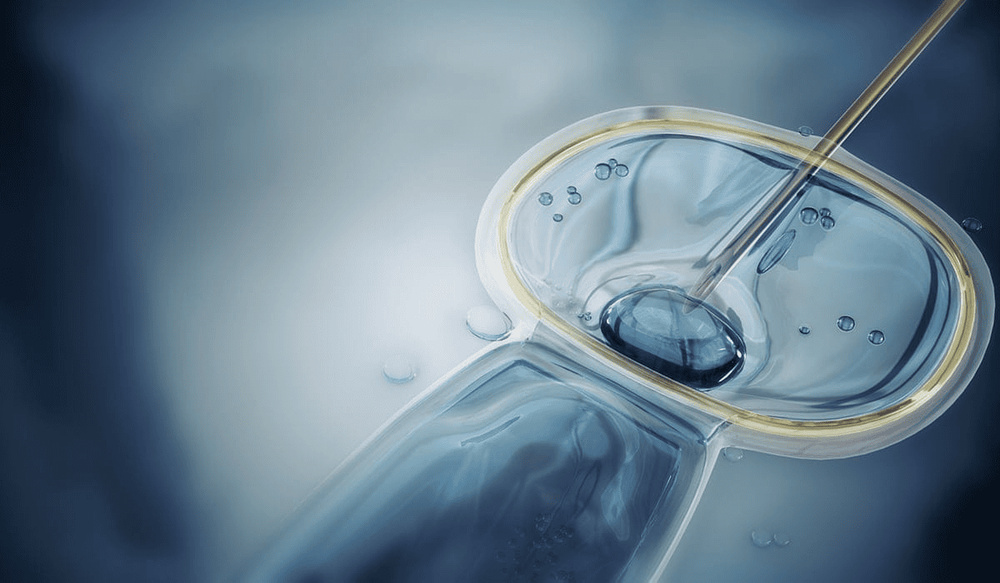
Kĩ thuật tiêm tinh trùng vào bào tương (ICSI)
3. Other fertility treatments, like GIFT or ZIFT?
Unless there are no other alternatives, your doctor probably won't recommend other ART procedures because they require surgery - although each has a similar success rate as IVF.
Intrafallopian Gamete Transfer (GIFT): In this procedure, an egg is combined with your partner's sperm in a lab, and then inserted right into your fallopian tube through a small incision in your abdomen. . Fertilization happens inside your body and the embryo will implant naturally. Intraductal zygote transfer (ZIFT): In ZIFT, your eggs are mixed with your partner's sperm in a lab (as with GIFT). But in this procedure, your doctor will wait until fertilization has occurred before transferring the embryos into your fallopian tubes through a small incision in your abdomen.
4. What is in vitro fertilization (IVF)?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is an assisted reproductive treatment in which sperm and eggs are combined in a laboratory. The embryos after in vitro fertilization will be evaluated for quality, and one or more embryos are inserted into the uterus through the cervix.
IVF is by far the most commonly used high-tech fertility treatment, accounting for more than 99% of assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedures. About 1.5% of babies born in the United States are conceived using ART.
IVF may also be an option if your doctor can't pinpoint the problem (this is called "explained infertility") or if other treatments have failed.
5. How does IVF work?
IVF treatment usually goes like this:
Ovarian stimulation. For the 8 to 14 days near the beginning of your menstrual cycle, you take gonadotropin, a fertility drug that stimulates the ovaries to develop multiple mature eggs for fertilization (instead of just one). You also need to take a synthetic hormone such as leuprolide or cetrorelix to prevent your body from releasing an egg too soon. Follicular development. While taking these drugs, you visit your doctor's office or clinic every two to three days to have your blood hormone levels checked and an ultrasound to measure your ovaries. This allows your healthcare provider to monitor the growth of the follicles - the fluid-filled sacs where eggs mature. Activated. When the follicles are ready, you'll be given an "activator" injection, an injection that makes the eggs fully mature and capable of being fertilized. About 36 hours after you fire the trigger, your eggs are ready to be retrieved. Suck eggs. The doctor will numb the area and insert an ultrasound probe through the vagina to look at the ovaries and identify the cysts. Then, a thin needle is inserted through the vaginal wall to remove the egg from the follicle. Eight to 15 eggs are usually removed. You may experience cramping and a rash for a few days afterward, but most women feel better after a day or two. Fertilization. An embryologist will test your eggs before combining them with your partner's sperm and incubating them overnight. Fertilization usually occurs during this time, but an abnormal egg may not be fertilized. (If sperm quality is poor or if fertilization has not been successful in previous IVF cycles, your doctor may recommend a technique called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). , a single sperm is injected directly into each mature egg.)

Tiến trình điều trị IVF thường diễn ra dưới sự giám sát nghiêm ngặt và cẩn thận
Embryo development. Three days after egg retrieval, some of the successfully fertilized eggs became embryos of 6 to 10 cells. By day five, some of these embryos will become blastocysts with a fluid-filled cavity and tissues that begin to separate into the placenta and baby. Selection of embryos. The embryologist will select the best or live embryos to put in your uterus 3 to 5 days after egg retrieval. Additional embryos, if available, can be frozen and used for future IVF cycles. Embryo transfer. Depending on your age and diagnosis, your doctor will place one to five embryos into your uterus by passing a thin tube (catheter) through your cervix. You may feel some mild cramping, but you don't need anesthesia. Successful embryo implantation. If the treatment works, the embryo will implant in the wall of your uterus and continue to develop into a baby. Remember that if more than one embryo is transferred, your chances of getting pregnant are higher, but so are the odds of having a multiple pregnancy - about 20% of babies born through IVF are twins, triplets, or more.
6. What are the advantages of IVF?
IVF is the oldest assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedure on the block - it's been around since 1978. IVF has been around long enough for researchers to do extensive health studies of what's going on. The child is conceived by this method. To date, there have been no medical problems directly related to the procedure.
Not related to cancer . Recent studies show no link between ovulation-stimulating drugs and cancer. Early studies suggest that exposure to fertility drugs may lead to an increased risk of ovarian cancer or other cancers of the female reproductive system. Technical improvement. Researchers continue to refine and improve IVF procedures. For example, advances in embryo cryopreservation (freezing) have resulted in comparable IVF pregnancy rates for frozen and fresh embryos.
7. What are the disadvantages of IVF?
Expensive cost and time. Insemination of an egg outside your body requires lab work and expensive medication. Monitoring your response to fertility drugs also takes time, with frequent visits to your doctor's office for blood tests and ultrasounds.
Risk of ectopic pregnancy. Women who have difficulty getting pregnant are at a higher risk of having an ectopic pregnancy, regardless of how they conceived. And all assisted reproductive technology treatments, including IVF, also make the chances of an ectopic pregnancy higher. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when an embryo implants in a fallopian tube or abdominal cavity rather than in the uterus. It is treated with the drug methotrexate or by surgically removing the embryo to prevent the embryo from being severely injured from continuing to develop.
Risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). OHSS can happen when a woman responds too well to fertility drugs and produces too many eggs. About 10 to 20 percent of women using gonadotropins develop a mild form of OHSS, a condition characterized by weight gain and a feeling of gas and bloating. Some also experience shortness of breath, dizziness, pelvic pain, nausea and vomiting. If you have OHSS, your ovaries swell to several times their normal size and cause fluid to build up in your abdominal cavity. Usually, this will resolve on its own with careful monitoring by your doctor and bed rest. But in rare cases, it's life-threatening and you may need to be hospitalized for monitoring or more intensive treatment.
Possible complications for the baby. Babies conceived with high-tech infertility treatments such as IVF may be born prematurely or with lower birth weight. They may also have a slightly higher risk of birth defects. But experts aren't sure if it's due to infertility factors (such as age) or treatments.
It may not work . Up to 20% of IVF cycles can be aborted prior to egg retrieval, often due to insufficient follicle development. Reducing OHSS risk is another reason to cancel.

Các cặp vợ chồng nên lựa chọn cơ sở y tế uy tín để thực hiện các phương pháp hỗ trợ sinh sản
Vinmec IVF Reproductive Center is the address of infertility - infertility treatment chosen by many couples. So far, the Center has performed fertility support for over 1000 infertile couples with a success rate of over 40%. This rate is equivalent to developed countries such as the UK, USA, Australia,...
The center gathers a team of leading experts in the field of obstetrics and gynecology nationally and internationally, trained in centers leading in the world such as in the US, Singapore, Japan, Australia and famous fertility centers in the world.
With a high level of expertise and extensive experience, Vinmec IVF Center's experts are capable of synchronously and comprehensively deploying the most advanced assisted reproductive techniques today, helping realize the dream of becoming a parent of hundreds of families across Vietnam.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: babycenter.com