This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Minh Son - Interventional Cardiologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International HospitalArterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia are dangerous conditions that affect multiple organs and are potentially life-threatening.
1. What is arterial hypoxia and organizational hypoxia?
When the body does not have enough oxygen, it will lead to arterial hypoxia or tissue hypoxia (hypoxia), which are dangerous conditions. Without oxygen, many organs such as the brain, liver,... can be damaged within minutes of the onset of symptoms.
Hypoxia in arterial blood, if not timely intervention, will lead to organizational hypoxia because there is not enough oxygen in the blood to meet the needs of tissues.
2. Symptoms of arterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia
Khó thở là triệu chứng thường gắp của giảm oxy máu động mạch và thiếu oxy tổ chức
Although symptoms can vary from case to case, the most common symptoms of arterial hypoxemia and tissue hypoxia include:
Change in skin color, from pale blue to purple red . Loss of consciousness, confusion. Cough. Tachycardia, or low heart rate. Increase breathing rate. Shortness of breath, shortness of breath. Sweating. Wheezing. If symptoms of arterial hypoxemia and tissue hypoxia appear, seek medical help immediately.
Trắc nghiệm: Huyết áp của bạn có đang thực sự tốt?
Huyết áp cao hay thấp đều ảnh hưởng đến tình trạng sức khỏe con người. Để biết tình trạng huyết áp của bạn có thực sự tốt không, hãy làm bài trắc nghiệm sau đây để đánh giá.3. How to treat arterial hypoxia and organizational hypoxia?
When there are signs of arterial hypoxemia and organizational hypoxia, the patient needs emergency treatment and is taken to the hospital immediately for treatment intervention and oxygen status monitoring.
The most important thing for the treatment of arterial hypoxemia and organizational hypoxia is to provide oxygen to the body, which can be by breathing oxygen through the Canula, breathing oxygen through a mask,... And in many cases, Just like that was able to solve the situation.
Sprays or oral medications for asthma can make breathing easier. If not effective, using intravenous drugs can be prescribed by a doctor. In addition, steroids to fight inflammation or antibiotics to treat underlying infections may also be used.
If the condition is too severe, life-threatening and the above methods are not effective, the doctor may prescribe artificial ventilation (machine ventilation) intervention for the patient.
4. What are the causes of arterial hypoxia and organizational hypoxia?
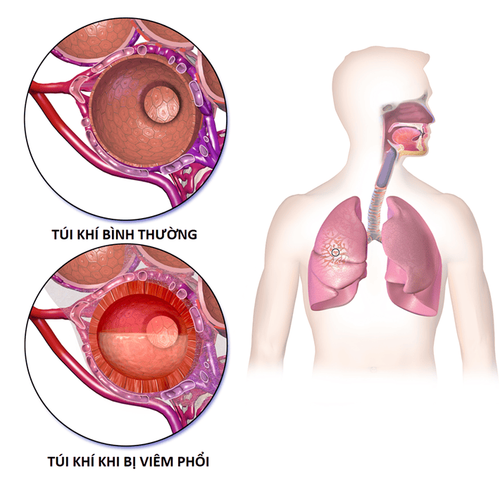
Viêm phổi là một trong các nguyên nhân gây giảm oxy máu động mạch và thiếu oxy tổ chức
An acute attack of bronchial asthma is the most common cause of arterial hypoxemia and hypoxia in both children and adults. During an asthma attack, the airways narrow, making it difficult for air to get into the lungs, and coughs cause even more oxygen loss from the body and worsen the condition.
Arterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia can also result from traumatic lung injury.
Other possible causes of arterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia are:
Lung diseases, such as: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, inflammation bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and pulmonary edema. Medications that cause respiratory depression. Cardiovascular disease. Anemia . Cyanide poisoning.
5. How to prevent arterial hypoxia and organizational hypoxia
Because acute bronchial asthma is the most common cause of arterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia, the most effective way to prevent it is to control asthma well every day.
Adhere to treatment, use medicine exactly as ordered by a specialist to prevent acute asthma attacks. Eat a healthy, balanced diet and stay active. Identify and prevent asthma triggers. Understand how to handle situations when an acute asthma attack occurs.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com