This is an automatically translated article.
Gallstone disease (gallbladder or bile duct) is a common disease in Vietnam, with the risk of disease increasing gradually with age. The symptoms of gallstones are not obvious and are only discovered through periodic health examinations or when the stones have caused dangerous complications for the sufferer.
1. What are gallstones?
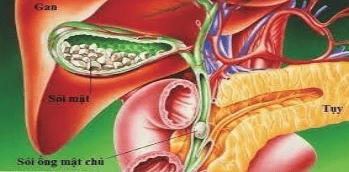
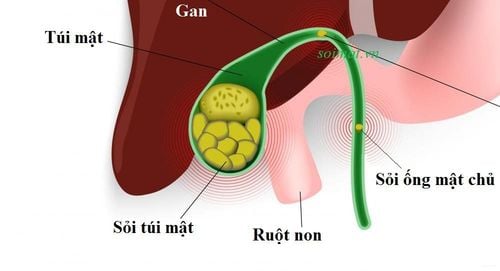
Gallstones are the formation of stones in the gallbladder, the bile duct system inside and outside the liver. Gallstones are the crystallization of components in bile to form solid, hard masses of different sizes, including 2 main types:Cholesterol stones (the majority). Bile pigment stones (bilirubin stones).
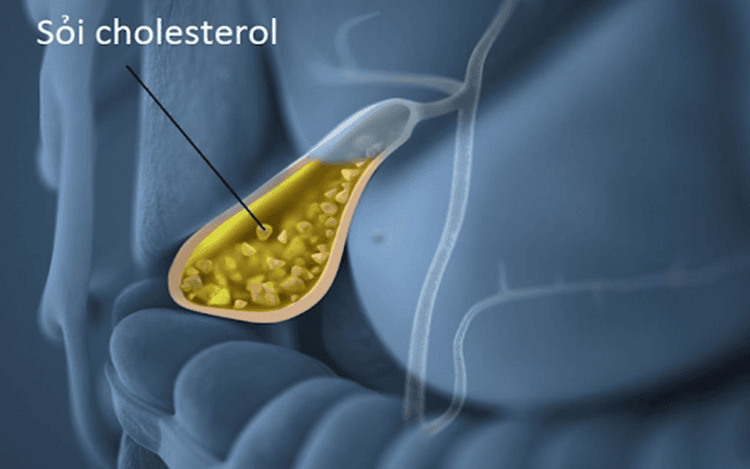
Sỏi cholesterol
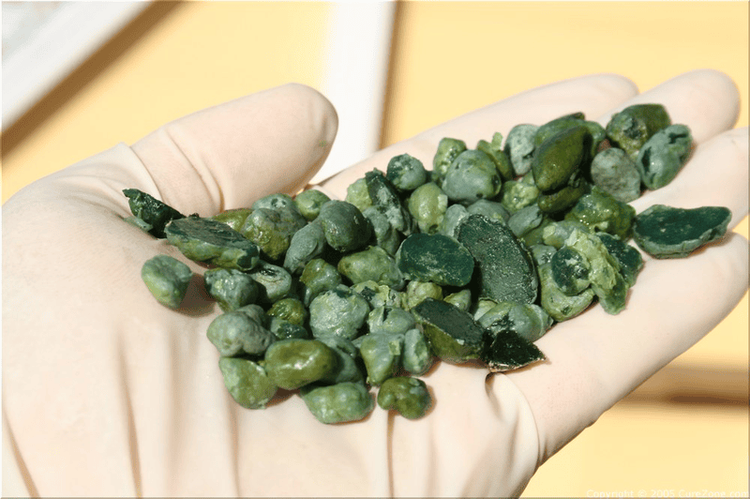

Sỏi bilirubin
2. Causes of gallstones
Causes that promote the formation of gallstones in general can include:
Diet: Patients who fast for a long time will affect the digestive process, bile is easily stagnate in the gallbladder. bile and increases the risk of stone formation. Lifestyle: Lazy exercise, reduced motility of the biliary tract, easy to deposit stones. Patients with rapid weight loss cause the liver to create more cholesterol, increasing the risk of cholesterol stones. Prolonged high blood cholesterol levels. Obesity: Considered one of the biggest risk factors for gallstones. Obesity increases cholesterol levels in the body and makes it difficult to empty the gallbladder. Drug-induced: Abuse of oral contraceptives can increase blood cholesterol levels and increase the risk of cholestasis in the gallbladder. Chronic background disease: Patients with chronic underlying diseases increase the risk of stone formation such as diabetes, cirrhosis, ulcerative colitis, ... Hemolytic anemia increases bilirubin production in the body, easily Formation of bilirubin stones, ... Due to genetics (in the family there are people with liver disease, abnormal biliary tract, ...).
3. Recognize gallstone pain and other gallstone symptoms
Biliary colic is the most typical symptom to help indicate the existence of gallstones in the patient's body. Manifestations of biliary colic usually appear in the right hypochondrium or epigastrium (located between the navel and sternum), with the nature of intermittent pain.
Pain often occurs right after a meal, especially a meal containing a lot of fat will easily trigger the onset of pain. Sometimes the pain suddenly appears at night, causing the patient to lose sleep. This condition, which lasts for a long time, can cause severe weakness in the body.
3.1. Locating stones from biliary colic Pain in the right upper quadrant that lasts 30 minutes or even hours with increasing pain may be a sign of a stone in the gallbladder site. Cramping pain in the right upper quadrant, which may then radiate to the right shoulder or back, and to the epigastrium, may be a sign of liver or common bile duct stones.
Vị trí sỏi từ cơn đau quặn mật
3.2. Other symptoms that may be seen in patients with gallstones The presence of stones in the gallbladder or bile ducts interferes with the flow of bile down to the digestive tract, leading to indigestion, loss of appetite, and bloating. Patients are afraid of greasy foods. Symptoms of this digestive disorder usually appear after meals. In addition, the patient may experience other symptoms as follows:
Severe pain in the abdomen, especially the right lower quadrant, lasting for many hours, the pain level increases gradually and does not subside despite taking pain relievers. Fever over 38 degrees Celsius, fear of wind, fear of cold, sweating. Feeling of bloating, nausea and vomiting. Itchy skin, jaundice, yellow eyes. These symptoms may be indicative of an infection of the gallbladder or bile ducts causing obstruction of the bile ducts. Patients with these symptoms should immediately seek medical advice for appropriate treatment.
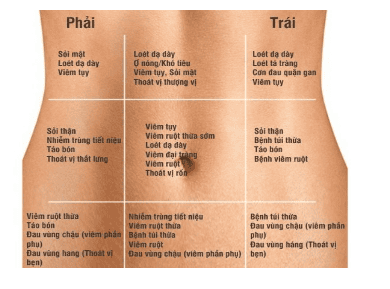
4. Distinguishing symptoms of gallstones and other gastrointestinal diseases
Symptoms of abdominal pain and fullness of gallstones are sometimes easily confused with other gastrointestinal diseases (gastric pain, acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis,...). The best way to diagnose gallstones and distinguish them from other conditions is to use ultrasound to detect stones. However, gallstones can still be diagnosed based on symptom differences when patients have typical symptoms, such as based on different pain locations (gallstone pain in the right upper quadrant, stomach pain, etc.) pancreatitis, epigastric pain), gallstones often appear with other typical symptoms such as:
Fever, sweating, fear of wind and cold: Patients may have fever with sweating, fear of wind and fear of cold. signs of biliary tract infection, cholecystitis caused by gallstones). High fever can be up to 38-39 degrees Celsius, the patient has severe abdominal pain, sweating, but there are also cases where the patient only has a slight fever but the fever lasts a long time. Jaundice and yellow eyes: This is a manifestation of cholestasis, the degree of jaundice in each person will be different depending on the degree of biliary obstruction. Accompanying this sign are other symptoms related to the stagnation of bile, increased bilirubin in the blood, white and discolored stools, itchy skin.
5. Gallstone treatment methods
Currently there are quite a few methods of treating gallstones, according to modern medicine, gallstones are treated if they have caused cholecystitis, acute biliary obstruction.
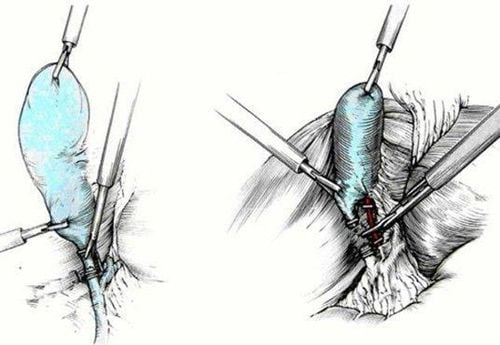
Cholecystectomy: Can be done by open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. However, after cholecystectomy, gallstones can still recur for up to a year, to prevent this situation, people with gallstones need to be supplemented with ursodeoxycholic acid to limit stone formation. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): This procedure is performed by a specialist by giving the patient a local anesthetic and then using a flexible fiber-optic camera, or endoscope, inserted through the mouth. Through the digestive system and into the common bile duct to remove stones, ERCP can help remove stones stuck at the end of the common bile duct. Lithotripsy: This is a method of using ultrasound shock waves to break the gallstone. When gallstones become small enough, they can safely pass through the bile ducts and into the small intestine. This is an uncommon treatment and only applies to patients with few gallstones. However, the common limitation of these methods is that there is still a high rate of stone recurrence and many side effects during and after surgery. For patients who have not yet shown signs of acute biliary obstruction, causing inflammation and biliary tract infection, the use of traditional medicine in combination with treatment of gallstones has also been proven to have many advantages. .
Hope the above information will help readers understand the symptoms of gallstones and how to distinguish pain caused by bile or other organs of the digestive tract to avoid confusion, especially is often mistaken for stomach pain. If the patient has any unusual symptoms, it is necessary to visit reputable facilities to be examined by a specialist and consulted on appropriate treatment methods.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.