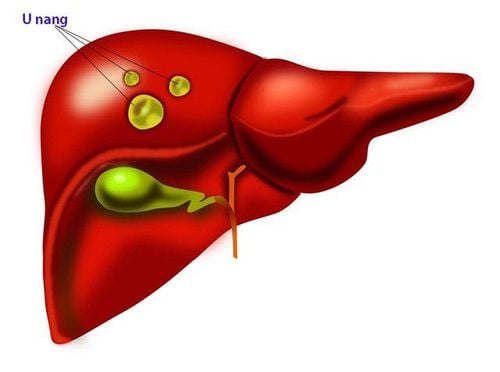
Liver cysts are often asymptomatic and most are simple, benign cysts that do not affect the body. Therefore, treatment of liver cysts is usually only necessary for ones larger than 5cm.
1. What is a liver cyst?
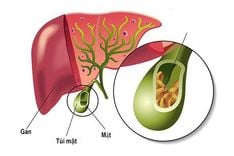
A liver cyst is an empty sac that can contain fluid, blood, or nothing at all, located within the liver tissue. Liver cysts can originate from liver cells, blood vessels supplying the liver, or bile ducts within the liver. Liver cysts are often asymptomatic and are mostly discovered incidentally during a general health check-up or examination for another disease.
Liver cysts are more common in women. There are many different causes of liver cysts: congenital genetic factors; parasites, viruses, echinococcus cysts, and tuberculosis bacteria; and liver structure... can lead to the formation of different types of cysts in various locations.
2. Are liver cysts dangerous?
There are different types of liver cysts, including:
- Simple cysts
- Polycystic liver disease
- Cystadenoma
- Echinococcal cysts
- Liver abscesses
However, most liver cysts are simple and harmless. They rarely become cancerous and usually don't cause any problems.
3. Liver cyst treatment
Liver cyst treatment primarily depends on the type and size of the cyst.
3.1. Based on size
Most cases coexist peacefully with cysts.
If the cyst is smaller than 5cm, no treatment is usually required. Regular check-ups are recommended to monitor the growth rate of the cyst and prevent potential malignant transformation.
If the cyst is larger than 5cm, it often causes clinical symptoms such as pain, blood loss, internal bleeding, digestive disorders, jaundice, etc. In this case, specific treatment indicated by a doctor is necessary to reduce these symptoms.
3.2. Treatment by cyst type
3.2.1. Simple cyst
Simple cysts are often considered congenital. The cyst is lined with epithelium similar to that of the bile duct, but the fluid inside does not contain bile. Due to the continuous secretion of cyst fluid, the cyst often recurs after aspiration or drainage.
Simple cysts are usually asymptomatic. It can cause pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen and abdominal distension if the cyst is large. If the cyst is too large, it can be palpated on abdominal examination. Rupture, torsion of the cyst, and jaundice are complications caused by bile duct obstruction but are 1 very rare.
The disease can heal spontaneously. In case of symptoms, aspiration or cyst sclerosis can be performed. Laparoscopic or open surgery to open the cyst (fenestration) may be more effective but carries a surgical risk. However, symptomatic cysts usually respond well to treatment.
3.2.2. Polycystic liver disease
Adult polycystic liver disease is a congenital disease often associated with polycystic kidney disease and is usually related to a genetic disorder.
Kidney cysts usually appear before liver cysts, and chronic kidney disease is also common. However, polycystic liver disease rarely leads to liver cirrhosis and liver failure. Hepatomegaly and abdominal pain may occur. Cysts are usually detected during puberty. Rupture, hemorrhage, and cyst infection are rare.
Treatment is only necessary when the cyst causes symptoms. Similar to simple cysts, it can be treated by aspiration or sclerosis. Liver transplantation can also be performed. The recurrence rate after aspiration and sclerosis is estimated to be about 19%.
3.2.3. Cystadenoma (Neoplastic cyst)
Cystadenoma and cystadenocarcinoma are rare. Cystadenoma is a precancerous lesion.
This type of cyst is often asymptomatic or has nonspecific symptoms including abdominal distension, nausea, and a feeling of fullness. If the cyst is large, the patient may experience abdominal pain and bile duct obstruction.
Treatment for this type of cyst is mainly surgical removal. However, cystadenocarcinoma can still recur after complete resection.
3.2.4. Echinococcal cyst (caused by Echinococcus)
This type of cyst is formed by infection with a type of tapeworm called Echinococcus granulosus.
Carnivores such as dogs and wolves are considered the primary hosts. They release tapeworm eggs through feces, and then the eggs can infect cattle or humans. Therefore, infection is often found in people who raise sheep or cattle or who come into contact with dogs.
Patients may be asymptomatic for many years or may present with pain in the right upper quadrant. Large cysts can rupture into the bile duct causing jaundice or cholangitis, rupture through the diaphragm into the chest, or rupture into the abdominal cavity causing anaphylactic shock. Secondary infection and liver abscess can occur due to cyst rupture.
It is necessary to prevent complications caused by large cysts and cyst rupture. Treatment includes the use of drugs such as albendazole or mebendazole, percutaneous aspiration, and surgery
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.